Land is one of the most critical resources in India, with agriculture being the primary occupation for a significant portion of the population. However, landholding in India is characterized by several challenges, including fragmentation, tenancy, and lack of access to credit. In this article, we will explore the issues surrounding landholding in India and the opportunities for improving the situation.
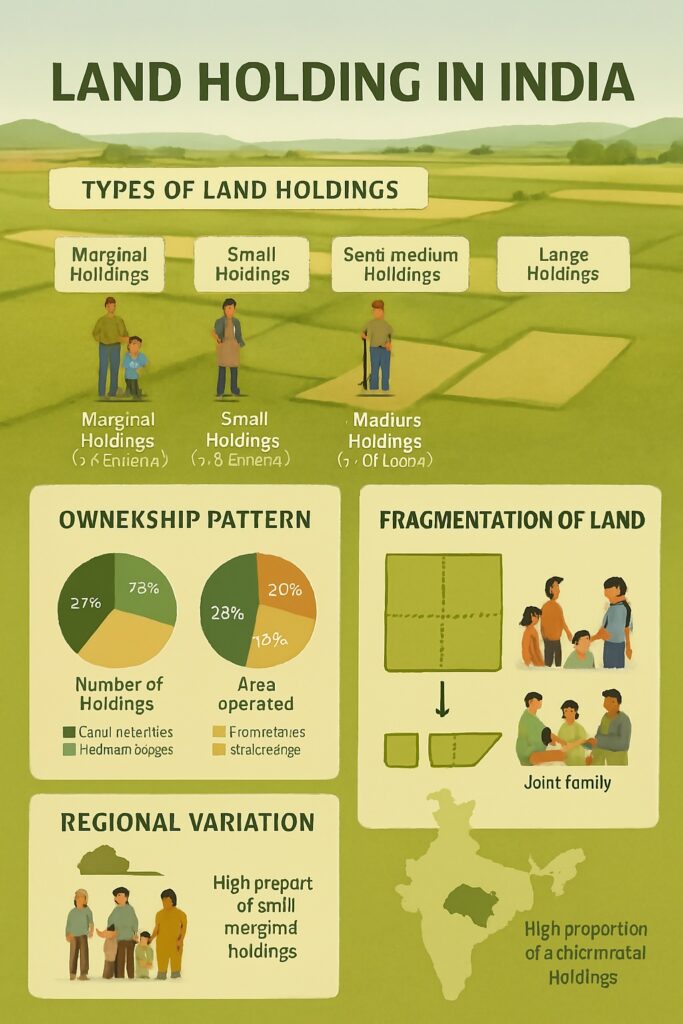
Table of Contents
Fragmentation of Land
One of the most significant challenges in Indian agriculture is the fragmentation of land. The majority of farmers own small plots of land, which can make it difficult to achieve economies of scale and adopt modern farming practices. Fragmentation also makes it challenging to implement irrigation systems and other forms of infrastructure, as it requires the coordination of multiple landowners. The government has implemented several policies to address fragmentation, including land consolidation schemes and the implementation of land leasing laws.
Tenancy
Tenancy is another significant issue in Indian agriculture, with many farmers leasing land from absentee landlords. Tenancy can create a complex set of issues, including disputes over rent, land use, and land ownership. The government has implemented several policies to address tenancy issues, including the implementation of tenancy laws and the promotion of contract farming.
Access to Credit
Access to credit is a critical issue for small and marginal farmers in India, who often struggle to access formal credit channels. Lack of access to credit can make it difficult for farmers to invest in modern farming practices and technologies, leading to low crop yields and income levels. The government has implemented several schemes to address this issue, including the provision of agricultural credit through various agencies and the promotion of self-help groups.
Conclusion
Landholding in India is characterized by several challenges, including fragmentation, tenancy, and lack of access to credit. These challenges can make it difficult for farmers to adopt modern farming practices, leading to low crop yields and income levels. However, the government has implemented several policies to address these challenges, including land consolidation schemes, tenancy laws, and the provision of agricultural credit. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring the long-term sustainability of Indian agriculture and improving the livelihoods of small and marginal farmers.
Read: Geography Notes