Q. Discuss the processes through which the earth-atmosphere system maintains heat balance.
Ans: The Earth-atmosphere system maintains a heat balance through various processes that involve the exchange of energy between the Earth’s surface, the atmosphere, and space. This equilibrium is essential for maintaining a stable climate and supporting life on our planet.
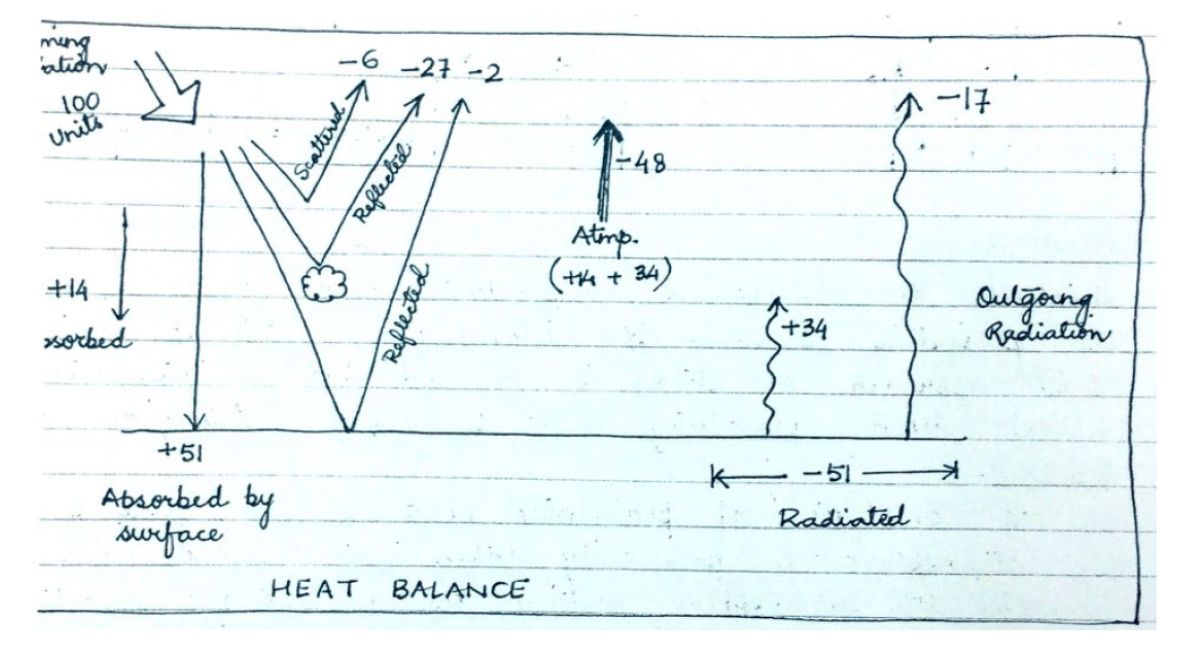
The key processes include:
- Radiation:
- Solar Radiation: The Sun emits electromagnetic radiation, including visible light and other wavelengths. Solar radiation heats the Earth’s surface when it’s absorbed by land, water bodies, and vegetation.
- Terrestrial Radiation: The Earth’s surface re-emits some of this absorbed energy in the form of infrared radiation. This thermal radiation is released back into the atmosphere and space.
- Conduction:
- Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical contact between objects with different temperatures. It occurs primarily in solids and involves the transfer of kinetic energy from hotter to colder regions.
- Convection:
- Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (air and water). Warm air near the Earth’s surface expands, becomes lighter, and rises, creating vertical convection currents. As it rises, it cools and sinks back down, creating a cycle of heat transfer.
- Evaporation and Condensation:
- Evaporation occurs when liquid water absorbs heat energy and transforms into water vapor. This process cools the surface it’s evaporating from.
- Condensation is the opposite process, where water vapor releases heat energy as it changes back into liquid water, forming clouds and releasing latent heat.
- Advection:
- Advection refers to the horizontal movement of air masses that carry heat from one region to another. For example, warm air moving from the tropics to higher latitudes transfers heat along with it.
- Longwave and Shortwave Radiation:
- The Earth’s surface absorbs shortwave solar radiation and re-emits longwave thermal radiation. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, absorb and re-radiate some of this longwave radiation back towards the Earth’s surface, creating a greenhouse effect that helps regulate the temperature.
- Albedo Effect:
- Albedo refers to the reflectivity of a surface. Surfaces with high albedo, like snow and ice, reflect more incoming solar radiation, while surfaces with low albedo, like forests and oceans, absorb more radiation. Changes in surface albedo influence the amount of heat absorbed or reflected.
- Global Heat Redistribution:
- Atmospheric and oceanic circulation patterns, such as jet streams, ocean currents, and trade winds, redistribute heat from warmer to cooler regions across the planet, helping to regulate temperature gradients.
These interconnected processes maintain a delicate balance of energy input and output within the Earth-atmosphere system. Any disruption or alteration to these processes, such as through human activities like deforestation or greenhouse gas emissions, can have significant impacts on the Earth’s heat balance, leading to changes in climate patterns and global temperatures.
Thanks for reading the answer to the question: Discuss the processes through which the earth-atmosphere system maintains heat balance.
Read: