The impacts of ozone depletion can be significant and far-reaching.
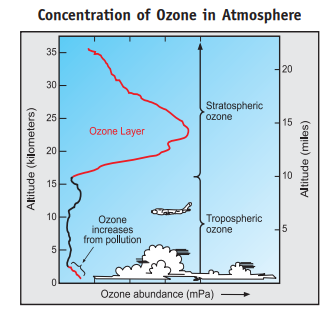
Some of the most important impacts include:
- Increased UV radiation: Ozone depletion allows more harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation to reach the Earth’s surface, which can have serious impacts on human health, wildlife, and the environment.
- Increased rates of skin cancer: Ozone depletion can increase the risk of skin cancer, as well as other types of skin damage such as sunburn, premature aging, and cataracts.
- Harm to wildlife and ecosystems: UV radiation can also harm wildlife and ecosystems, including phytoplankton (the base of the ocean food chain), zooplankton, and other small organisms.
- Impacts on agriculture: UV radiation can damage crops and reduce yields, leading to decreased food security in some regions.
- Impacts on human health: In addition to increasing the risk of skin cancer, ozone depletion can also weaken the immune system and increase the risk of other health problems, such as respiratory diseases.
- Changes in atmospheric circulation: Ozone depletion can also affect atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to changes in climate and weather patterns, particularly in the polar regions.
These impacts demonstrate the far-reaching effects of ozone depletion, and the importance of taking action to protect the ozone layer and reduce the risk of further harm. The international community has taken action to address the problem of ozone depletion, and the signing of the Montreal Protocol has led to a reduction in the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances. However, it will take several decades for the ozone layer to recover, so it is important to continue to monitor the situation and take steps to protect the Earth and its inhabitants from the harmful effects of ozone depletion.