Laterite Soil in India
India is a land of diverse soil types, and one such soil type is laterite soil. Laterite soil is widely found in India, especially in the Western Ghats, Konkan region, Eastern Ghats, and parts of northeastern India. They are ideal for brick-making. This type of soil is highly unique and has a distinctive red color. In this article, we will discuss laterite soil in India, its characteristics, formation, and its significance.

Table of Contents
Characteristics of Laterite Soil
It is highly unique and has several distinguishing features. Here are some of its significant characteristics:
- Red Color: The most distinctive feature of laterite soil is its red color, which is due to its high iron and aluminum oxide content.
- Porous: Laterite soil is highly porous, which makes it ideal for storing water.
- Low in fertility: Laterite soil is deficient in nutrients, especially nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which makes it unsuitable for farming.
- Hard and Compact: It is highly compact and hard, making it difficult to till.
- High Acidity: Laterite soil is highly acidic, with a pH ranging from 4 to 6.
Formation of Laterite Soil
Laterite soil is formed by the process of weathering, which involves the breakdown of rocks by physical and chemical processes. The process of weathering is gradual and occurs over millions of years. Laterite soil is formed in areas with high rainfall, warm temperatures, and high humidity.
The process of lateralization involves the leaching of soluble minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, leaving behind insoluble iron and aluminum oxides. These oxides form a hard layer of laterite soil that is highly porous and can store water.
Significance of Laterite Soil
It has several significance and importance in India. Here are some of them:
- Construction Material: It is widely used as a construction material, especially in the coastal regions of India. The hard and compact nature of laterite soil makes it ideal for building houses and roads.
- Iron and Aluminum Production: It is rich in iron and aluminum oxides, making it an important source of these minerals.
- Forests: It is highly porous, which makes it ideal for growing forests. The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats are home to some of the most diverse forests in India, which are supported by laterite soil.
- Tourism: The unique red color of laterite soil and its distinctive landscapes make it a popular tourist destination. The Konkan region of Maharashtra and the Western Ghats in Kerala are some of the most popular tourist destinations in India.
Distribution in India
Laterite soil is widely distributed in India, especially in the following regions:
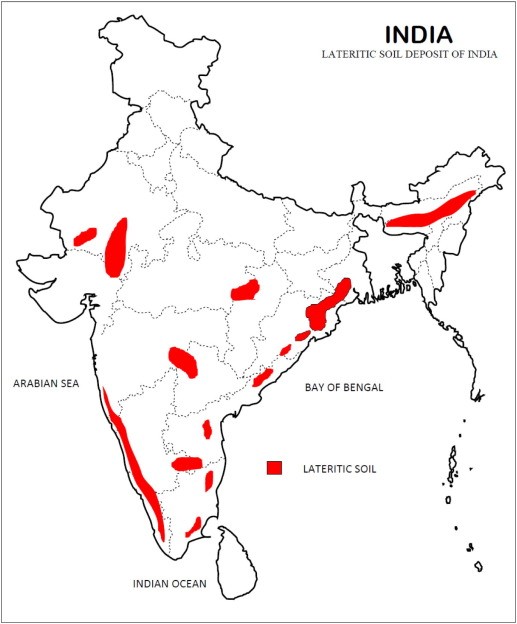
- Western Ghats: The Western Ghats are a mountain range running parallel to the western coast of India, and laterite soil is widespread in this region. The region covers parts of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- Konkan Region: The Konkan region is a narrow coastal strip in western India, stretching from the state of Maharashtra to the state of Karnataka. Laterite soil is abundant in this region.
- Eastern Ghats: The Eastern Ghats are a mountain range that runs parallel to the east coast of India, covering parts of Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu. Laterite soil is widespread in this region.
- Northeastern India: Laterite soil is also found in parts of northeastern India, including the states of Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura.
- Other Regions: Laterite soil is also found in some parts of central India, including parts of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Overall, laterite soil covers a significant portion of India and plays a crucial role in the country’s construction, agriculture, and tourism sectors.
Conclusion
It is a unique type of soil found in India, which has several significant features and importance. Its distinctive red color and hard and compact nature make it ideal for construction, while its high porosity supports forests and tourism. Although laterite soil is deficient in nutrients, it is an essential source of iron and aluminum.
Important Links