The Mahanadi River is one of the most important rivers in India, flowing through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha. It is the sixth-largest river in India and has a total length of 858 km. The river is a vital source of water for irrigation, hydropower, and other purposes, and is also home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. In this article, we will explore the geography, history, and significance of the Mahanadi River.
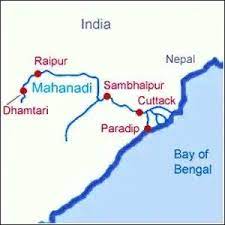
Table of Contents
Geography of Mahanadi River
The Mahanadi River originates in the Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and flows eastwards towards Odisha before emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The river has a catchment area of 141,600 square km and is fed by several tributaries, including the Seonath, Mand, and Ong.
The Mahanadi River basin is divided into two parts – the Upper Mahanadi Basin and the Lower Mahanadi Basin. The Upper Mahanadi Basin covers an area of 54,000 square km and includes the districts of Raipur, Bilaspur, and Durg in Chhattisgarh. The Lower Mahanadi Basin covers an area of 87,000 square km and includes the districts of Sambalpur, Cuttack, and Puri in Odisha.
History
The Mahanadi River has played a significant role in the history of India. The river has been mentioned in several ancient texts, including the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. It was also an important trade route during the Maurya and Gupta empires.
During the British colonial period, the Mahanadi River was used to transport goods such as coal, timber, and grains. Several ports were established along the river, including Cuttack and Sambalpur, which were important centers of trade.
Significance of Mahanadi River
The Mahanadi River is a vital source of water for irrigation, hydropower, and other purposes. The Hirakud Dam, located on the river in Odisha, is one of the largest earthen dams in the world and provides irrigation water to over 2 million hectares of farmland. The dam also generates hydroelectric power, which is used to supply electricity to several cities and towns in Odisha.
The Mahanadi River is also home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. The river supports a variety of fish species, including the critically endangered Ganges river dolphin. The river is also an important habitat for several species of migratory birds, such as the Asian openbill stork, the black-necked stork, and the grey heron.
Challenges
Despite its significance, the Mahanadi River faces several challenges. The river is heavily polluted, with industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and domestic sewage being major sources of contamination. The pollution levels in the river have resulted in the decline of fish populations and the degradation of aquatic habitats.
The construction of dams and barrages on the river has also led to the displacement of several communities. The Hirakud Dam, for instance, displaced over 150,000 people from their homes and land. The construction of dams and barrages has also affected the river’s flow, resulting in reduced water availability and increased flooding in downstream areas.
Conclusion
The River is an important river in India, playing a vital role in the economy and ecology of the region. The river has a rich history and has been mentioned in several ancient texts. Despite its significance, the river faces several challenges, including pollution and displacement of communities due to the construction of dams and barrages. It is essential to take steps to address these challenges and ensure that the river continues to provide water and support life.
Important Links