India is a vast country with diverse topography and landforms. The Physiographic Regions of India can be divided into various parts.
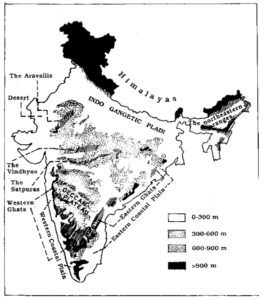
Table of Contents
The Himalayan Region
The Himalayan Region is located in the northern part of India and is characterized by a complex network of mountain ranges and valleys. The region is home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest and Kanchenjunga. The Himalayan Region is also the source of several major rivers in India, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
The Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain is located in northern and eastern India and is one of the most fertile regions in the world. The region is characterized by a flat landscape and is fed by several major rivers, including the Ganges, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra.
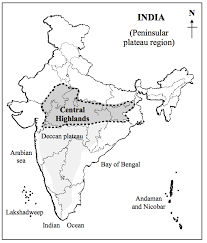
The Peninsular Plateau
The Peninsular Plateau is located in central and southern India and is characterized by a complex network of plateaus, hills, and valleys. The region is rich in mineral resources and is home to several important rivers, including the Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery.
The Western Ghats
The Western Ghats are a mountain range located along the western coast of India. The region is characterized by dense forests, waterfalls, and several important rivers, like Narmada, Godawari, Cauvery, etc.
The Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a mountain range located along the eastern coast of India. The region is characterized by a series of low hills and plateaus and is home to several important rivers, including the Godavari, Mahanadi, and Krishna.
The Thar Desert
The Thar Desert is located in western India and is characterized by a dry and arid landscape. The region is home to several important cities, including Jaipur and Jodhpur.
The Coastal Plains
India is surrounded by several coastal plains, including the Konkan Coast, Malabar Coast, Coromandel Coast, and the Andhra Coast. These regions are characterized by a flat and fertile landscape and are home to several important ports and cities.
In conclusion, India’s physiographic regions are a testament to the country’s rich geological and ecological diversity. By understanding these regions, we can gain a greater appreciation for the natural beauty and ecological significance of this vast and complex country.
Physiographic Regions of India : Summary
- India can be divided into seven physiographic regions, each with distinct topographical features and geological formations.
- The Northern Mountainous Region includes the Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, and is characterized by high peaks, deep valleys, and glacial rivers.
- The Northern Plains Region is a flat, fertile plain that covers most of northern India and is home to the Ganges and its tributaries.
- The Peninsular Plateau Region is a rugged, hilly region that covers most of central and southern India, with the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats forming its boundaries.
- The Indian Desert Region is a vast, arid region that covers parts of western Rajasthan and Gujarat and is home to the Thar Desert.
- The Coastal Plains Region is a narrow strip of land that runs along India’s east and west coasts and is characterized by fertile river deltas, sandy beaches, and lagoons.
- The Islands Region consists of two island groups, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea, which are known for their pristine beaches and coral reefs.
- The physiographic regions of India have a significant impact on its climate, with the Himalayas blocking cold winds from the north and the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats acting as barriers to the monsoon winds.
- India’s diverse physiographic regions support a rich array of flora and fauna, with the Himalayan region being home to rare and endangered species like the snow leopard and the Indian rhinoceros.
- India’s varied landscape has also shaped its cultural and social history, with the Ganges and other rivers playing a significant role in the country’s mythology, religion, and daily
Physiographic Regions of India : Questions
here are 5 multiple-choice questions based on the topic of Physiographic Regions of India, along with explanations for each answer:
Which physiographic region in India is home to the Thar Desert?
A. Northern Mountainous Region
B. Indian Desert Region
C. Northern Plains Region
D. Coastal Plains Region
Answer: B. Indian Desert Region. The Thar Desert is located in the Indian Desert Region, which covers parts of western Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Which physiographic region in India is known for its fertile river deltas and sandy beaches?
A. Northern Plains Region
B. Peninsular Plateau Region
C. Coastal Plains Region
D. Islands Region
Answer: C. Coastal Plains Region. The Coastal Plains Region runs along India’s east and west coasts and is characterized by fertile river deltas, sandy beaches, and lagoons.
Which physiographic region in India is characterized by high peaks, deep valleys, and glacial rivers?
A. Northern Mountainous Region
B. Peninsular Plateau Region
C. Indian Desert Region
D. Islands Region
Answer: A. Northern Mountainous Region. The Northern Mountainous Region includes the Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, and is characterized by high peaks, deep valleys, and glacial rivers.
Which physiographic region in India is a rugged, hilly region that covers most of central and southern India, with the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats forming its boundaries?
A. Northern Plains Region
B. Peninsular Plateau Region
C. Indian Desert Region
D. Coastal Plains Region
Answer: B. Peninsular Plateau Region. The Peninsular Plateau Region is a rugged, hilly region that covers most of central and southern India, with the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats forming its boundaries.
Which physiographic region in India is known for its pristine beaches and coral reefs?
A. Northern Mountainous Region
B. Indian Desert Region
C. Coastal Plains Region
D. Islands Region
Answer: D. Islands Region. The Islands Region consists of two island groups, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea, which are known for their pristine beaches and coral reefs.
Physiographic Regions of India
Important Links