The savanna climate, also known as the Sudan-type climate or tropical dry forest, is a type of climate found in regions close to the equator. It is characterized by a distinct dry season and a wet season, with average temperatures ranging from 20-30°C throughout the year. In this article, we’ll explore the characteristics of the savanna climate and its importance.
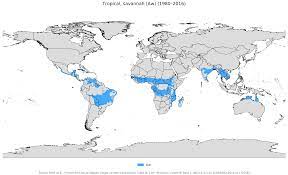
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Savanna Climate
- Rainfall: It receives moderate rainfall, ranging from 500-1,500mm annually. However, it is not evenly distributed throughout the year, with most of the rainfall occurring during the wet season. The dry season can last for several months, resulting in long periods of drought.
- Temperature: The average temperature ranges from 20-30°C, with little seasonal variation. However, the temperature can be much higher during the dry season, resulting in hot and arid conditions.
- Vegetation: It is characterized by a mix of grassland and scattered trees. The grasses are adapted to survive the long dry season, while the trees have deep roots that can access water stored deep underground.
- Wildlife: It is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including large herbivores such as elephants, giraffes, and zebras, as well as predators such as lions, cheetahs, and hyenas. These animals have adapted to the unique conditions of the savanna, including the long dry season and the availability of seasonal water sources.

Importance of Savanna Climate
- Agriculture: It is ideal for agriculture, with fertile soils and a long growing season. Many crops, such as maize, cassava, and groundnuts, are well-suited to the conditions of the savanna and are an important source of food and income for local communities.
- Biodiversity: It is home to a rich diversity of plant and animal species, including many that are found nowhere else on earth. These species are an important part of the local ecosystem and are critical to maintaining the balance of the savanna.
- Tourism: It is a popular destination for tourists, who come to see the diverse range of wildlife and experience the unique landscape. This provides an important source of income for local communities and helps to promote conservation efforts.
Savanna Climate in India
India is a diverse country with varying climatic conditions across different regions. While most parts of India have a tropical monsoon climate, some areas in the southern part of the country have a savanna climate. The Deccan Plateau, which covers most of the southern peninsula of India, has a typical savanna climate.
The vegetation in the savanna climate in India is a mix of grasslands and scattered trees. The region is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, elephants, and antelopes.
The savanna climate in India is important for agriculture, particularly for crops such as cotton, groundnuts, and millet. The long growing season and fertile soils make the region ideal for farming. The savanna climate in India is also important for tourism, as it is home to several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries that attract visitors from across the world.
Natural Vegetation in Savanna Climate
The natural vegetation in the savanna climate is a mix of grassland and scattered trees. The vegetation in this climate type is adapted to tolerate both the wet and dry seasons and has developed specific mechanisms to survive in these conditions. Here are some common examples of natural vegetation found in the savanna climate:
- Grasslands: Grasses are the dominant vegetation in the savanna climate, and can grow up to 2 meters tall. These grasses have deep roots that can reach the water table, enabling them to survive long periods of drought. Some common grasses found in the savanna include buffalo grass, red grass, and star grass.
- Trees: While grasses are the dominant vegetation in the savanna, scattered trees are also present. These trees are usually deciduous, meaning they lose their leaves during the dry season to conserve water. Baobab, acacia, and shea trees are some common trees found in the savanna.
- Shrubs: Shrubs are also present in the savanna, and can survive in the dry season by storing water in their leaves and stems. Some common shrubs found in the savanna include the combretum and the lantana.
The natural vegetation in the savanna climate plays an important role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. It provides food and shelter for a diverse range of wildlife and helps to regulate the water cycle and prevent soil erosion.
Savanna or Sudan Climate UPSC
The Savanna or Sudan Climate is a significant topic in the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) examination. The UPSC examination is conducted annually to recruit candidates for various administrative positions in the Indian civil services. Questions related to the Savanna or Sudan Climate can be asked in the Geography or Environmental Science paper of the UPSC examination.
Here are some key points related to Savanna or Sudan Climate that can be helpful for UPSC preparation:
- Definition: Savanna or Sudan Climate is a tropical climate characterized by a distinct dry season and wet season. The dry season can last up to 8 months, and the wet season can last for 4 months.
- Geographical location: This climate is found in the tropical regions of the world, between the equator and the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. In India, the Savanna or Sudan Climate is found in the southern part of the country, particularly in the Deccan Plateau region.
- Vegetation: The natural vegetation is a mix of grassland and scattered trees. The grasses and trees in this climate type are adapted to tolerate both the wet and dry seasons and have developed specific mechanisms to survive in these conditions.
- Importance: The Savanna or Sudan Climate is important for agriculture, particularly for crops such as cotton, groundnuts, and millets. The long growing season and fertile soils make the region ideal for farming. The Savanna or Sudan Climate is also important for tourism, as it is home to several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries that attract visitors from across the world.
- Challenges: Climate change, deforestation, and desertification are some of the major challenges faced by the Savanna or Sudan Climate. These factors can have a significant impact on the natural vegetation, wildlife, and agricultural productivity in the region.
Overall, understanding the Savanna or Sudan Climate is essential for UPSC preparation, as it is an important topic in the Geography and Environmental papers.
Fire in Savanna Climate
Fire is a natural and integral part of the Savanna climate ecosystem, and plays an important role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. The Savanna climate is characterized by a distinct dry season, during which vegetation becomes dry and prone to fires. Here are some key points about fire in the Savanna climate:
- Natural phenomenon: Fire is a natural phenomenon in this climate, and occurs regularly during the dry season. Lightning strikes and spontaneous combustion of dry grass are some of the natural causes of fire in the Savanna.
- Importance: Fire plays an important role in this ecosystem, and has several benefits. It helps to recycle nutrients by burning dead vegetation, promotes the growth of new vegetation, and controls the spread of invasive species. It also creates habitats for certain species, such as burrowing mammals and insects.
- Challenges: Climate change is expected to have a significant impact on the occurrence and intensity of fires in this climate. Increased temperatures and changes in rainfall patterns could lead to more frequent and severe fires, which could have a significant impact on the ecosystem.
World Wide Distribution
The climate, also known as the tropical wet-dry climate, is a type of climate found in various parts of the world, particularly in the tropics. Here are some of the regions where the this climate is found:
- Africa: The African Savanna is the most well-known and extensive Savanna climate region in the world, covering a large part of sub-Saharan Africa. The African Savanna is characterized by a distinct wet season, from May to October, and a dry season, from November to April.
- South America: It is also found in parts of South America, particularly in Brazil, Venezuela, and Colombia. The South American Savanna is known as the Llanos, and is characterized by grassy plains and scattered trees.
- Australia: It is found in parts of northern Australia, particularly in the Northern Territory and Queensland. The Australian Savanna is characterized by a monsoon season from November to April, and a dry season from May to October.
- India: It is found in parts of India, particularly in the Deccan Plateau and the eastern coast. The Indian Savanna is known as the “dry tropical” climate and is characterized by a distinct wet season, from June to September, and a dry season, from October to May.
- Southeast Asia: It is also found in parts of Southeast Asia, particularly in Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia. The Southeast Asian Savanna is characterized by a wet season from May to October and a dry season from November to April.
In conclusion, It is a unique and important part of the earth’s ecosystem. Its distinct characteristics, including a dry season, moderate rainfall, and diverse wildlife, make it an ideal location for agriculture, biodiversity, and tourism. Understanding its importance is essential for protecting and preserving this valuable resource.
Summary
- The savanna climate is a type of climate found in regions close to the equator.
- It is characterized by a distinct dry season and a wet season, with average temperatures ranging from 20-30°C throughout the year.
- Rainfall is moderate, ranging from 500-1,500mm annually, and is not evenly distributed throughout the year.
- It is characterized by a mix of grassland and scattered trees and is home to a diverse range of wildlife.
- It is important for agriculture, biodiversity, and tourism.
- The fertile soils and long growing seasons in the savanna climate make it ideal for crops such as maize, cassava, and groundnuts.
- It is home to a rich diversity of plant and animal species and is critical to maintaining the balance of the savanna.
- It is a popular destination for tourists, providing an important source of income for local communities and promoting conservation efforts.
MCQ
Q. What is the savanna climate characterized by?
a) A distinct wet season and snowy winters
b) A distinct dry season and a wet season
c) Constant rainfall throughout the year
d) Extreme heat and humidity
Answer: b) A distinct dry season and a wet season.
Q. What is the range of average temperatures in the savanna climate?
a) 0-10°C
b) 10-20°C
c) 20-30°C
d) 30-40°C
Answer: c) 20-30°C.
Q. What is the typical range of rainfall in the savanna climate?
a) 100-500mm annually
b) 500-1,000mm annually
c) 1,000-1,500mm annually
d) 1,500-2,000mm annually
Answer: b) 500-1,000mm annually.
Q. What type of vegetation is found in the savanna climate?
a) Dense forests
b) Tundra
c) Grassland and scattered trees
d) Mangroves
Answer: c) Grassland and scattered trees.
Q. What is the importance of the savanna climate?
a) It is important for fishing
b) It is important for mining
c) It is important for agriculture, biodiversity, and tourism
d) It is important for skiing
Answer: c) It is important for agriculture, biodiversity, and tourism.
Important Links