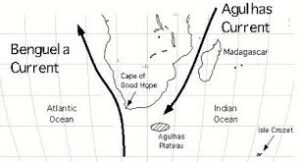
The Agulhas Current is a warm oceanic current that flows southward along the eastern coast of South Africa. It is one of the western boundary currents, which are strong, narrow, and fast-moving currents that flow along the western margins of ocean basins. The Agulhas Current is named after Cape Agulhas, the southernmost point of the African continent, near where the current is most prominent.
Key features and characteristics of the Agulhas Current include:
- Origin and Path: The Agulhas Current originates from the Indian Ocean near Mozambique and flows southward along the east coast of South Africa. As it reaches the Agulhas Bank, it curves eastward, forming large meanders and rings.
- Warm and High Velocity: The Agulhas Current is warm, carrying tropical waters from the Indian Ocean. It is also a fast-flowing current, with velocities that can reach up to 4-6 knots (2-3 meters per second) at its core.
- Agulhas Retroflection: As the Agulhas Current reaches the southern tip of Africa, it undergoes a significant feature known as the Agulhas Retroflection. Here, the current deflects eastward and forms large clockwise loops, or eddies, in the southwestern Indian Ocean.
- Mixing and Ecosystem Impact: The Agulhas Current plays a crucial role in the mixing of water masses and the exchange of heat and salt between the Indian and Atlantic Oceans. This mixing has a significant influence on the region’s climate and marine ecosystems.
- Influence on Climate: The Agulhas Current’s warm waters transport heat from the tropics to higher latitudes, affecting the climate along the southeastern coast of South Africa. It contributes to the warm and subtropical climate of the region, influencing weather patterns, rainfall distribution, and marine biodiversity.
- Maritime Navigation and Hazards: The Agulhas Current is an important maritime route due to its strong currents. However, it poses challenges for navigation, as the swift flow can impact ship routes and cause difficulties for vessels. Additionally, the Agulhas Current interacts with the cold Benguela Current, leading to the formation of powerful oceanic eddies and potentially hazardous conditions for maritime activities.
Understanding the dynamics of the Agulhas Current is important for various scientific disciplines, including oceanography, climate research, and marine conservation. Its influence on regional climate, marine ecosystems, and oceanic circulation patterns makes it a topic of interest for scientists studying global climate change and the functioning of oceanic systems.
Important Links