The Benguela Current is a cold oceanic current that flows northward along the western coast of southern Africa. It is named after the Benguela region, which encompasses parts of Angola, Namibia, and South Africa. The current is part of the larger South Atlantic Gyre circulation system.
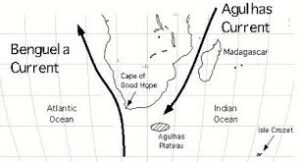
Characterized by its cold waters, the Benguela Current is formed by the convergence of two major oceanic currents—the cool, northward-flowing Antarctic Circumpolar Current and the warm, southward-flowing Agulhas Current. The Benguela Current is a nutrient-rich upwelling system, meaning that it brings deep, cold, and nutrient-rich waters to the surface, promoting high biological productivity.
Several factors contribute to the formation and characteristics of the Benguela Current:
- Prevailing Winds: The dominant winds in the region are the southeast trade winds, which blow parallel to the coastline. These winds, combined with the Earth’s rotation, result in the Ekman transport, causing surface waters to move offshore. This offshore movement allows nutrient-rich, cold water to rise to the surface.
- Upwelling: As the southeast trade winds blow offshore, they create a vacuum effect that draws deep, nutrient-rich waters from the ocean’s depths to replace the displaced surface waters. This upwelling of cold water provides an abundant supply of nutrients, such as nitrates and phosphates, which support the growth of phytoplankton and other marine organisms.
- Coastal Topography: The steep, narrow continental shelf along the western coast of southern Africa enhances the upwelling process by providing a physical barrier that restricts the offshore movement of surface waters, leading to a more pronounced upwelling effect.
The Benguela Current has significant ecological importance, supporting a diverse marine ecosystem and sustaining rich fisheries. The upwelling of nutrient-rich waters fuels the growth of phytoplankton, which forms the base of the marine food web. This, in turn, supports abundant populations of fish, marine mammals, and seabirds.
Additionally, the Benguela Current has socio-economic significance for the countries bordering its path. The fisheries industry in Angola, Namibia, and South Africa relies on the productivity of the current, providing a vital source of livelihood and food security for coastal communities.
The Benguela Current’s unique characteristics and ecological significance make it an area of scientific interest and conservation focus, as understanding its dynamics can help manage and sustain the valuable marine resources it supports.
Important Links