Dravida Style Temple is a unique and traditional style of temple architecture that originated in the southern part of India. The temples are known for their towering gopurams (entrance gateways), intricate carvings, and rich symbolism. In this article, we will explore the history and architecture of the Dravida Style Temple.
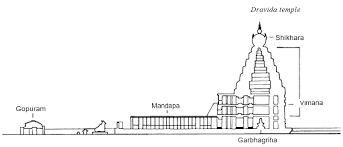
Table of Contents
Origin and History of Dravida Style Temple
Dravida Style Temple originated in the southern part of India during the 6th century CE. The style was developed by the Cholas, Pandyas, and Cheras, who were powerful dynasties of the time. The temples were built to honor various deities, and the style evolved over time to incorporate different features.
Architecture
Compound Wall: Unlike the Nagara temple, the Dravida temple is enclosed within a compound wall. The front wall has an entrance gateway in its center, which is known as a gopuram.
Gopuram: The Gateway – The most significant visual difference between the later northern and southern styles is the gateways. In the north, the shikhara remains the most prominent element of the temple and the gateway is usually modest or even absent. While in the Dravidian style, the Gopuram is very stylized and big in size.

The shape of the main temple tower known as Vimana in Tamil Nadu is like a stepped pyramid that rises up geometrically rather than the curving shikhara of North India.
Vimana: The central figure (like Shikhara in North India) of Dravida temples is usually smaller because a temple was improved upon by many rulers and every one of them enhanced the gopuram by redrawing a new gopuram with a new boundary wall to show his might. This is also the reason that Dravidian temples may even have multiple concentric gopurams and a comparatively smaller central vimana.
Temples have not only been religious centers but were also used for administrative activities, controlling vast areas of land, and were also centers of education.
Symbolism in Dravida Style Temple
The Dravida Style Temple is rich in symbolism, and each element of the temple has a specific meaning. The gopurams, for example, are meant to represent the gateway to the divine. The vimanas are symbolic of the mountain peaks that are believed to be the abode of the gods.
The walls of the temples are adorned with sculptures and carvings of various deities, and each has a specific meaning. For example, the sculpture of Ganesha, the elephant-headed god, is believed to bring good fortune and remove obstacles.
Famous Dravida Style Temples
There are many famous Dravida Style Temples in India, each with its own unique features. Some of the most well-known temples include:
- Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu: This temple is known for its towering vimana and intricate carvings.
- Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai, Tamil Nadu: This temple is dedicated to the goddess Meenakshi and is known for its gopurams and beautiful sculptures.
- Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple in Srirangam, Tamil Nadu: This temple is dedicated to Lord Vishnu and is known for its seven enclosures and intricate carvings.
- The Shore Temple in Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu: This temple is known for its beautiful coastal location and intricate carvings.
Conclusion
The Dravida Style Temple is a unique and traditional style of temple architecture that originated in the southern part of India. The temples are known for their towering gopurams, intricate carvings, and rich symbolism. Each element of the temple has a specific meaning and is designed to honor the divine. There are many famous Dravida Style Temples in India, each with its own unique features, and they continue to be an important part of India’s cultural heritage.
Temple Architecture:
- Nagara: North India
- Dravida: South India
- Visara: Mix of both
- Panchayatan: Famous during the Gupta age
Comparison of Nagara and Dravida style Temples
| Nagara Style Temple | Dravida Style Temple | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Northern India | Southern India |
| Entrance | One main entrance is known as a mandapa or porch | Multiple entrances are known as gopurams |
| Tower | Curvilinear shape | Rectangular shape with a pyramidal top |
| Roof | Curved shape with a multi-curved shikhara | Pyramid-shaped roof made up of stepped stories |
| Decoration | Usually adorned with intricate carvings, sculptures, and friezes depicting Hindu deities and mythological figures | Adorned with intricate sculptures and carvings of various deities, and each has a specific meaning |
| Famous Temples | Kandariya Mahadeva Temple in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh; Sun Temple in Konark, Odisha; Kedarnath Temple in Uttarakhand | Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu; Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai, Tamil Nadu; Sri Ranganathaswamy Temple in Srirangam |
Important Links