The Malthusian Theory is a population theory developed by Thomas Robert Malthus. The theory was first published in the year 1798 in the paper titled “An Essay on the Principle of Population“. The theory suggests that population growth will eventually outstrip food production, leading to widespread poverty and famine. Despite its controversial nature, the Malthusian Theory has been widely studied and discussed by economists, population specialists, and policymakers.
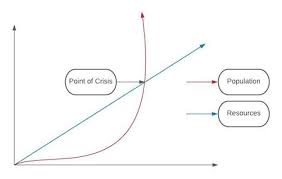
Table of Contents
Who will will the race Population or Resources?
Malthus argued that population growth would eventually outstrip food production, leading to widespread poverty and famine. He believed that population growth would occur in a geometric progression, while food production would increase in an arithmetic progression, leading to an eventual imbalance between population and food supply.
Population growth: Malthus believed that population growth would occur in a geometric progression, meaning that population would increase at a faster rate than food production. He believed that this population growth would be driven by several factors, including increased birth rates and decreased death rates.

Population = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, …….
Food = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9…….
Further, he opined that the Population doubles itself in every 25 years. Therefore, after 200 years, the ratio of food & population reaches a critical point where a world crisis will take place & eventually by natural force, food crisis, or civil war population size will be brought back to the pre-industrial level.

Food production: Malthus believed that food production would increase in an arithmetic progression, meaning that it would increase at a slower rate than population growth. He believed that this was due to limitations in the amount of arable land available for food production and the difficulty of increasing food production beyond a certain point.
Why Population is exploding?
Malthus considered human have 2 propensity or instincts for rapid growth of population.
- To have sex
- To have children
Malthus was in favour of capitalism & the population explosion takes place in the labour because they considered children as wealth. He justified capitalism or supported capitalism because in capitalistic economy the available surplus is reinvested & more employment generation and economic growth takes place.
But, Is there any Control Measure?
Malthus suggested two control measures.
- Positive Checks (Natural Forces): The natural controls have been termed as positive checks e.g. Earthquakes, natural, hazard, Tsunami, civil war, famine, etc.

- Preventive Checks:
It includes manmade actions like delay in marriage, use of contraceptives, etc. Further, vices like prostitution, adultery (such measures are evil for the society but yet, to have control over the population they can be part of society.)

Implications of the Malthusian Theory
The Malthusian Theory has had a significant impact on economic thought and policy. Some of the key implications of the theory include:
-
Population control: The Malthusian Theory has been used to argue for the need for population control measures, such as birth control and family planning programs. This is based on the belief that population growth will eventually outstrip food production, leading to widespread poverty and famine.
-
Agricultural development: The Malthusian Theory has also been used to argue for the need for increased agricultural development and technological innovation in order to increase food production and mitigate the effects of population growth.
-
Social policies: The Malthusian Theory has also been used to inform social policies, such as poverty reduction programs and educational initiatives aimed at reducing population growth.
Criticisms of the Malthusian Theory
Despite its widespread influence, the Malthusian Theory has also been widely criticized. Some of the key criticisms of the theory include:
- Malthusian Theory oversimplifies the complex relationships between population growth and food production, and does not take into account other factors that can impact these relationships, such as technological innovations and changes in social and economic conditions.
- Malthus’s predictions about population growth and food production have not come to fruition, as technological innovations and improved agricultural practices have helped to increase food production and mitigate the effects of population growth.
- The arithmetic rate & geometric rate is incorrect.
- Prediction of food crisis after 200 years has been proven wrong.
- He ignored the technological progression of the man.
- Too deterministic & predictive in nature.
- 25 years for doubling the population is incorrect.
- To have children is not a biological instinct but a social instinct.
- Natural disasters controlling the population are questionable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Malthusian Theory is a population theory developed by Thomas Robert Malthus in the late 18th century. The theory suggests that population growth will eventually outstrip food production, leading to widespread poverty and famine. Despite its criticisms, the Malthusian Theory has had a significant impact on economic thought and policy, and has been used to inform population control measures, agricultural development, and social policies.
Important Links


