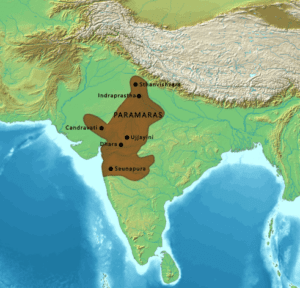
The Parmar Dynasty was founded by Upendra. The dynasty ruled over Malwa region located north of the Narmada river. The rule continued from 9th century to 14th century.
Origins and Rise to Power
The dynasty originated in the Malwa region of present-day Madhya Pradesh, India. Under the rule of Raja Bhoj, the Parmar Dynasty experienced a golden age of cultural renaissance. Raja Bhoj was not only a skilled ruler but also a patron of art, literature, and science. He invited scholars from across the Indian subcontinent, creating an intellectual hub that fostered creativity and innovation.
Architecture of Parmar Dynasty
The Parmar rulers were renowned for their architectural achievements. They constructed magnificent temples and forts, showcasing their engineering skills and aesthetic sensibilities. The Khajuraho Group of Monuments, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is a prime example of the Parmar Dynasty’s architectural legacy. These temples, known for their exquisite carvings and sculptures, provide a glimpse into the religious and artistic traditions of the time.
Military Exploits and Expansion of Parmar Dynasty
The Parmar rulers were skilled warriors who expanded their kingdom through military conquests. They engaged in numerous conflicts with neighboring dynasties, such as the Chandelas and the Chauhans. King Bhoja, in particular, led several successful military campaigns, significantly expanding the Parmar territories and establishing his dominance in Central India.
Legacy and Decline
Despite their achievements, the Parmar Dynasty began to decline in the 13th century due to invasions by the Delhi Sultanate. The Sultanate’s forces gradually weakened the Parmar rulers, leading to the ultimate demise of their kingdom. However, the Parmars left an enduring impact on Indian history through their cultural and architectural contributions, as well as their influence on subsequent dynasties in the region. The dynasty shaped the culture of central India through its rule.
Important Links