Multi level planning in India is a crucial component of India’s planning process, which involves the role of planning institutions at the national, state, and local levels. The planning process in India is characterized by a hierarchical structure, with the NITI Aayog at the national level, State Planning Boards at the state level, and District Planning Committees at the local level.
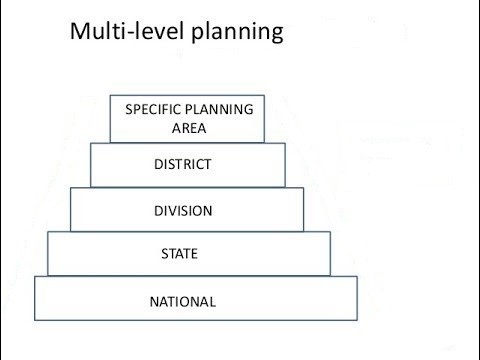
Table of Contents
Objectives of Multi Level Planning in India
Promoting balanced regional development: The planning process aims to promote balanced regional development by allocating resources and development projects based on the needs of each region.
Enhancing economic growth: The planning process aims to enhance economic growth by promoting investments in infrastructure, industry, and agriculture.
Improving social indicators: The planning process aims to improve social indicators such as education, healthcare, and sanitation, to reduce poverty and inequality.
Ensuring environmental sustainability: The planning process aims to ensure environmental sustainability by promoting renewable energy, conservation of natural resources, and pollution control measures.
Challenges of Multi-Level Planning
Multi-level planning in India faces a range of challenges:
Coordinating multiple institutions: The planning process involves coordinating multiple institutions at the national, state, and local levels, which can lead to delays and inefficiencies.
Lack of participation: There is a lack of participation by local communities and civil society in the planning process, which can result in projects that do not address the needs and priorities of the people.
Limited resources: There are limited resources available for planning and development projects, which can result in competing demands and inadequate funding.
Political interference: Political interference can result in decisions that are not based on sound economic or social criteria, leading to inefficient and ineffective projects.
Conclusion
Multi-level planning in India is a complex and challenging process, which involves coordinating institutions at the national, state, and local levels to promote balanced regional development, economic growth, social indicators, and environmental sustainability. The planning process faces several challenges, such as coordinating multiple institutions, lack of participation, limited resources, and political interference. Addressing these challenges and promoting greater participation and transparency in the planning process can lead to more effective and efficient development projects that better serve the needs and priorities of local communities.