The Earth receives unequal amounts of solar energy at different latitudes due to its spherical shape and axial tilt. This uneven heating results in the formation of distinct temperature zones and pressure belts across the globe. These zones and belts play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, wind systems, and weather patterns.
While temperature belts are based on latitude and solar radiation, pressure belts are formed by the vertical movement of air influenced by temperature differences. Together, they form a dynamic system that drives the global circulation of air.
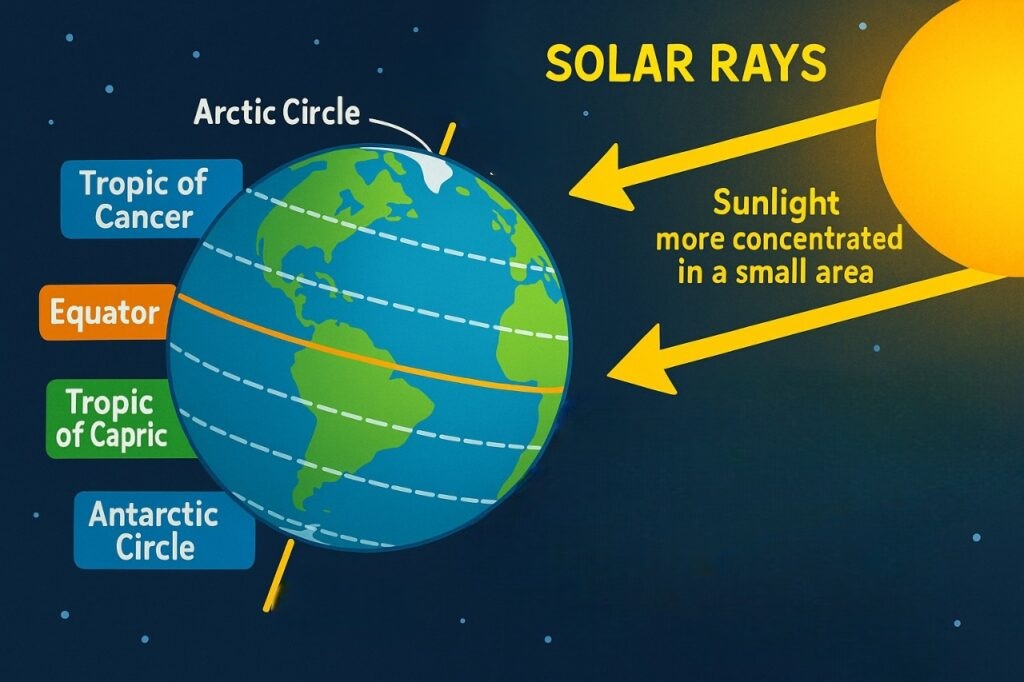
Table of Contents
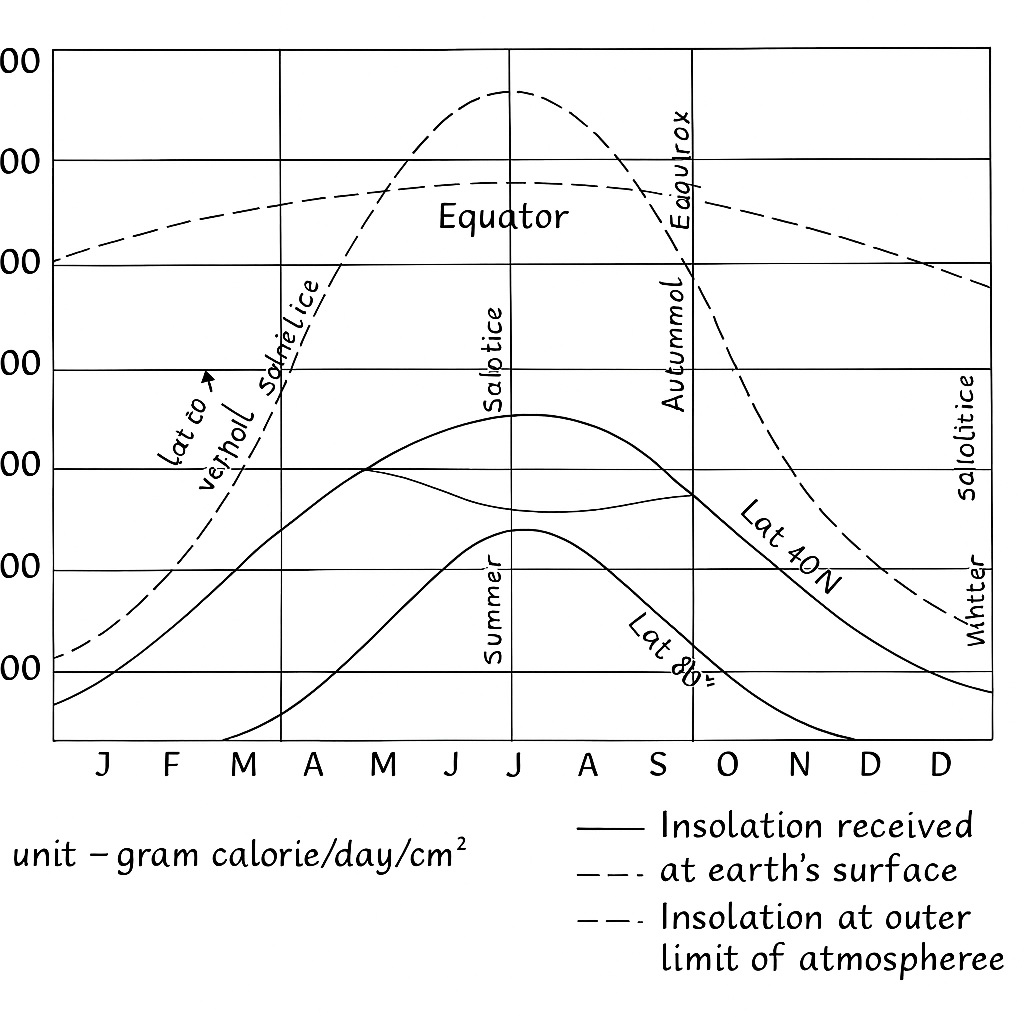
Solar Insolation
Insolation (Incoming Solar Radiation) is the amount of solar energy received by a given area on Earth’s surface. This energy is not received equally at all places — it varies with latitude due to the curvature and tilt of the Earth.
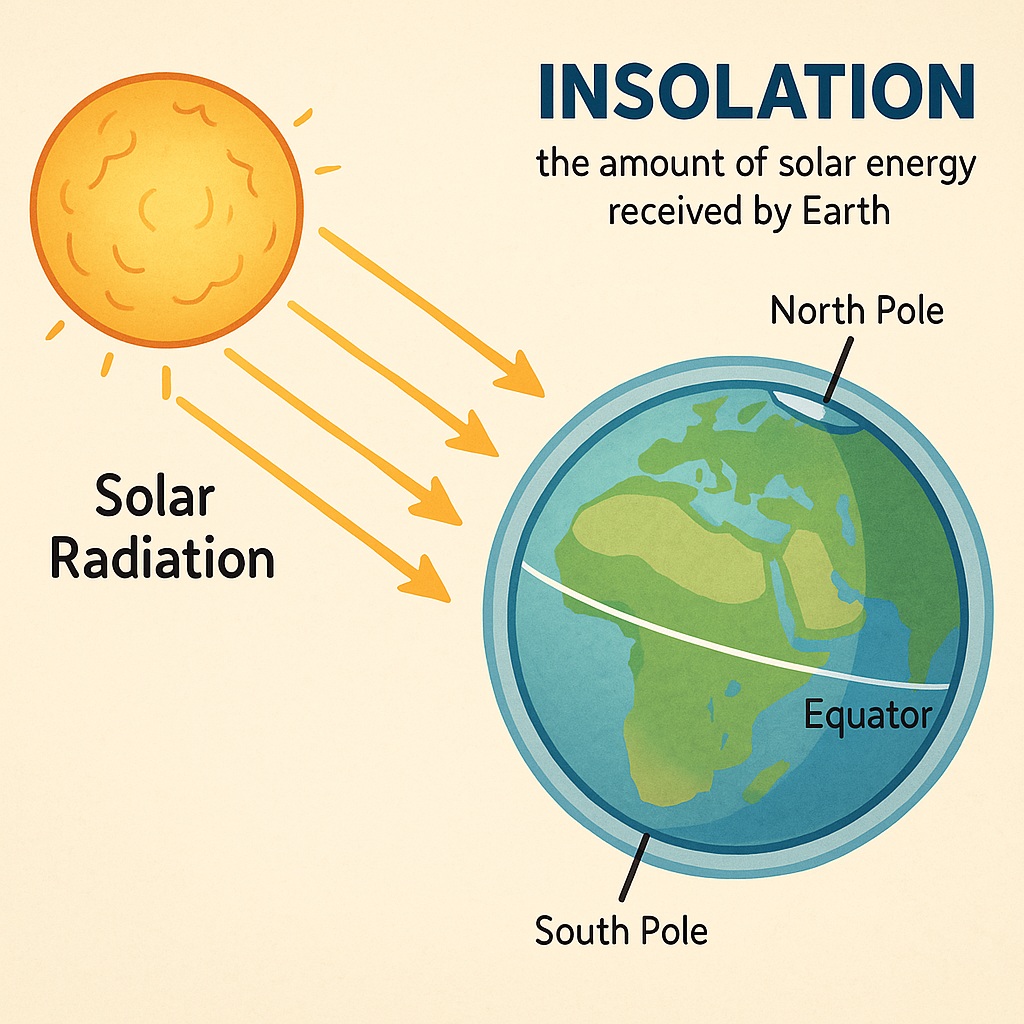
Why Insolation Varies with Latitude
Angle of the Sun’s Rays
-
Equator (0° Latitude):
-
Sun’s rays fall directly overhead.
-
Energy is concentrated over a small area → more insolation.
-
-
Higher Latitudes (e.g., 60° or 90°):
-
Sun’s rays are slanted.
-
Energy is spread over a larger area → less insolation.
-
Thickness of Atmosphere
-
Near the Equator: Rays pass through a shorter atmospheric path, so less energy is lost.
-
Near the Poles: Rays travel a longer distance through the atmosphere, losing more energy due to reflection, scattering, and absorption.
Duration of Daylight
-
In tropical regions, day and night are nearly equal throughout the year → steady insolation.
-
In higher latitudes, day length varies:
-
Longer days in summer = more insolation.
-
Shorter days in winter = less insolation.
-
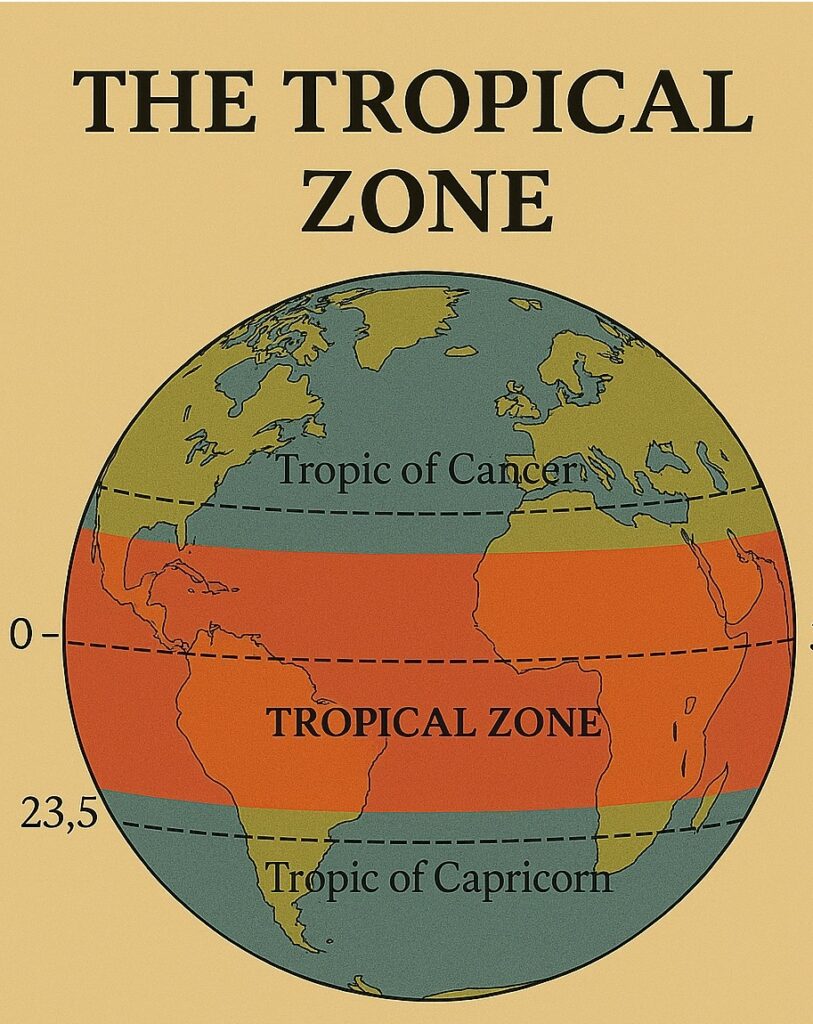
The Tropical Zone
The tropical zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn and extends from 23.5 degrees north to 23.5 degrees south latitude. This region is characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. The tropical zone is also home to some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, coral reefs, and savannas.
The tropical zone is divided into two sub-zones: the equatorial region and the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ). The equatorial region is located near the equator and is characterized by high temperatures and constant rainfall throughout the year. The ITCZ, on the other hand, is a region of low atmospheric pressure where the trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres meet. This convergence of winds results in heavy rainfall, thunderstorms, and the formation of hurricanes.
The Subtropical Zone
The subtropical zone is located between the tropical and temperate zones and extends from 23.5 degrees to 35 degrees north and south latitude. This region is characterized by warm temperatures, low humidity, and minimal rainfall.
"The subtropical zone is home to deserts, such as the Sahara and the Mojave, and to semi-arid regions, such as the Mediterranean."
The subtropical zone is also home to two distinct pressure belts: the subtropical high-pressure belts and the subtropical low-pressure belts. The subtropical high-pressure belts are located near 30 degrees north and south latitude and are characterized by high atmospheric pressure and clear skies. The subtropical low-pressure belts, on the other hand, are located near 25 degrees north and south latitude and are characterized by low atmospheric pressure and cloudiness.
The Temperate Zone
The temperate zone is located between the subtropical and polar zones and extends from 35 to 65 degrees north and south latitude. This region is characterized by moderate temperatures, varying humidity, and moderate rainfall. The temperate zone is home to a variety of ecosystems, including deciduous forests, grasslands, and temperate rainforests.
The temperate zone is divided into two sub-zones: the mid-latitude region and the polar front region. The mid-latitude region is characterized by westerly winds that bring moisture from the ocean, resulting in rainfall and the formation of storm systems. The polar front region is located near 60 degrees north and south latitude and is characterized by the convergence of polar and westerly winds, resulting in the formation of cold fronts and storms.
The Polar Zone
The polar zone is located between the Arctic and Antarctic Circles and extends from 65 to 90 degrees north and south latitude. This region is characterized by cold temperatures, low humidity, and minimal rainfall. The polar zone is home to the Arctic and Antarctic regions, which are covered by ice and snow.
The polar zone is also home to the polar high-pressure belt, which is characterized by high atmospheric pressure and clear skies. The polar high-pressure belt is formed by the descending air from the polar front, which cools and dries as it descends, resulting in the formation of high-pressure systems.
Impact on the Climate and Weather Patterns
The temperature and pressure belts of the world play a crucial role in determining the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. The equatorial region, for example, experiences high temperatures and constant rainfall due to its location near the equator and the presence of the ITCZ. The subtropical high-pressure belts, on the other hand, are characterized by high atmospheric pressure and clear skies, resulting in dry and arid conditions.
The polar zone, with its cold temperatures and low humidity, is also important in determining global weather patterns. The polar high-pressure belt, for example, affects the formation of storms and cold fronts in the mid-latitude and polar front regions.
Furthermore, the temperature and pressure belts also influence ocean currents and air masses, which in turn affect global climate patterns. For example, the equatorial trade winds and the prevailing westerlies play a critical role in transporting heat and moisture across the planet, influencing the climate patterns of the various regions.
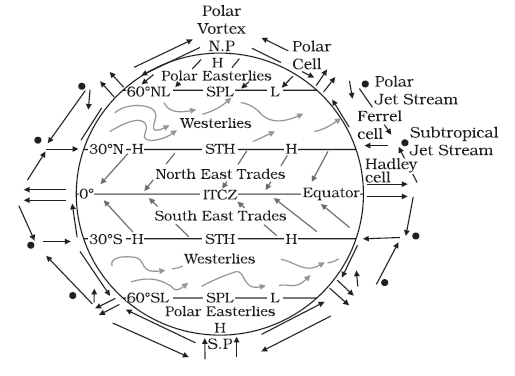
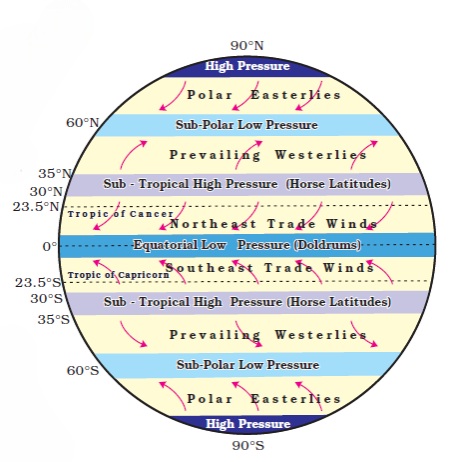
Pressure Belts of the World
Pressure belts are regions of the Earth characterized by uniform atmospheric pressure. They are formed due to differential heating of the Earth’s surface and the rotation of the Earth (Coriolis effect). These belts play a crucial role in the formation of global wind systems and precipitation patterns.
Equatorial Low Pressure Belt
The Equatorial Low Pressure Belt is a prominent atmospheric zone that encircles the Earth near the equator, typically lying between 5° North and 5° South latitude. It is characterized by consistently high temperatures and intense solar heating throughout the year due to the direct overhead sun. This intense heat causes the air to warm, expand, and rise, resulting in a zone of low atmospheric pressure at the surface. As the warm, moist air ascends, it cools and condenses, forming thick clouds and producing heavy, convectional rainfall almost daily.
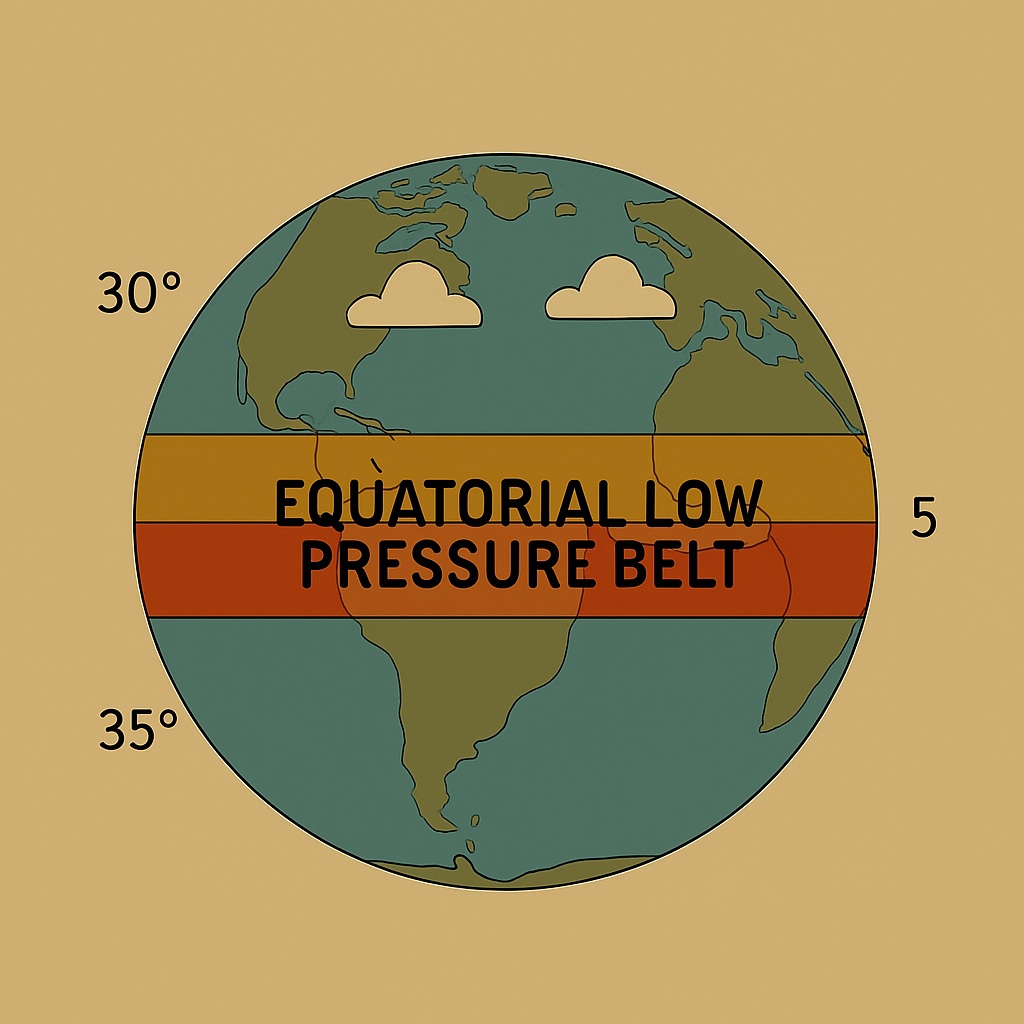
This belt is also known as the Doldrums, a name derived from the calm and windless conditions experienced here, as the vertical movement of air inhibits the development of strong surface winds. The rising air from the equatorial region eventually moves toward higher latitudes in the upper atmosphere, contributing to the formation of the Hadley Cell and playing a crucial role in the global circulation system. The Equatorial Low Pressure Belt is also associated with the world’s tropical rainforests, such as the Amazon and Congo basins, which thrive in its hot and humid climate.
Subtropical High Pressure Belts
The Subtropical High Pressure Belts are important zones in the Earth’s atmospheric circulation system, found roughly between 23.5° and 35° latitude in both hemispheres. These belts are formed by the descending air from the upper branches of the Hadley Cell. After rising at the Equator, the warm moist air moves poleward in the upper atmosphere, cools down, and then descends around these latitudes. This sinking air results in high atmospheric pressure at the surface, creating conditions that are typically dry, stable, and cloudless.
These belts are associated with clear skies, low humidity, and minimal precipitation, which is why many of the world’s largest deserts—such as the Sahara, Arabian, Kalahari, and Australian deserts—are located within this zone. The descending air suppresses cloud formation and limits vertical air movement, leading to stable weather patterns. This region is also known as the Horse Latitudes, a historical term referring to the calm seas that often stranded ships during the age of sail.
The subtropical high pressure zones play a critical role in driving global wind systems. Winds blowing outward from these high pressure areas curve due to the Coriolis effect, forming the trade winds that blow toward the Equator and the westerlies that move toward the mid-latitudes. Overall, the Subtropical High Pressure Belts are vital for understanding global climate, ocean currents, and atmospheric dynamics.
Subpolar Low-Pressure Belts
The Subpolar Low-Pressure Belts are significant components of Earth’s global atmospheric circulation, located approximately between 60° and 70° latitude in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Unlike the thermally induced Equatorial Low or Polar Highs, the subpolar lows are primarily dynamically induced. They form where the cold, dense air flowing out from the poles (polar easterlies) meets the warmer, relatively lighter air moving poleward from the mid-latitudes (westerlies). This convergence forces the warmer air to rise. This convergence forces the warmer air to rise. This rising air leads to lower atmospheric pressure at the surface.
Polar High Pressure Belts
The Polar High-Pressure Belts are key components of Earth’s global atmospheric circulation, representing the cold, dense extremes of our planet’s weather engine. They are situated at the very highest latitudes, specifically over the North Pole and the South Pole, generally between 80° and 90° latitude.
-
Found over the poles where cold, dense air sinks, creating high pressure.
-
Characterized by dry and stable air.
-
Winds blow outward from the poles as polar easterlies.
What Is Air Pressure?
- The air around us has weight, and it presses down on the Earth’s surface — this is called air pressure.
- It’s measured using a barometer.
- Air pressure is measured in units called millibar (mb) or hectopascal (hPa) — 1 mb = 100 pascals.
- At sea level, the average pressure is about 1030 mb, but it normally ranges from 950 to 1050 mb.
- One millibar is about the force of one gram over one square centimeter!
- Air pressure is not the same everywhere. It changes from place to place (horizontal change) and from the ground up into the sky (vertical change).
- These changes affect weather, wind, and climate patterns across the globe.
Vertical Distribution of Air Pressure
Air is made up of different gases and can be compressed — that means it gets packed tighter when pressure is applied. When air is packed more tightly, it becomes heavier (denser), which increases air pressure.
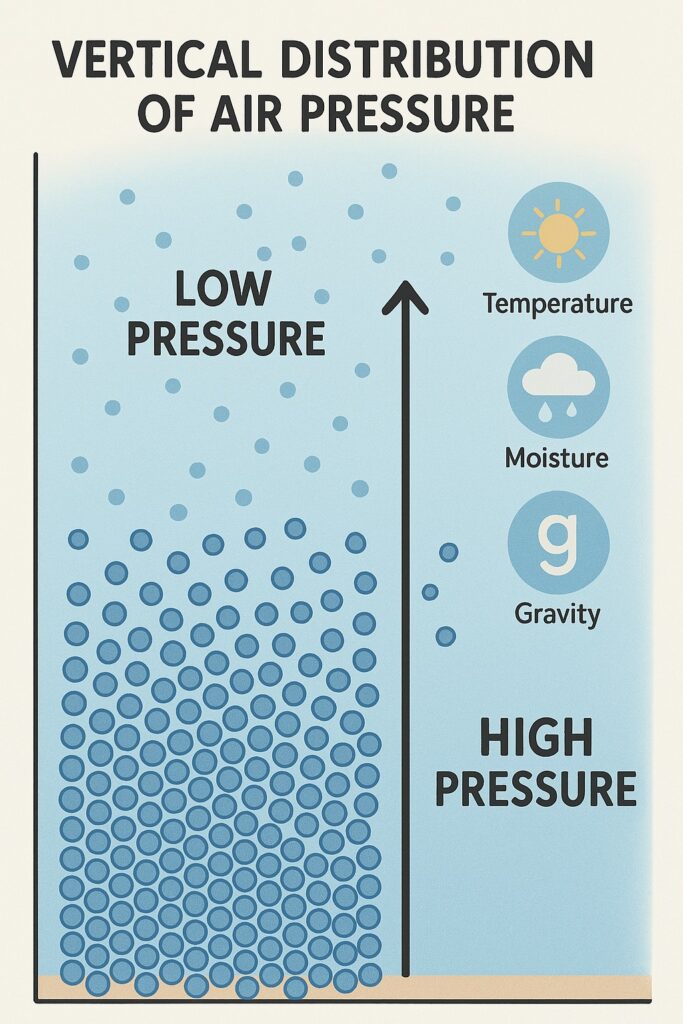
Think of it this way: the layers of air at the bottom get pressed by the layers above them. So the lower layers have more pressure, and the higher layers have less because they’re not pressed as much.
This vertical layering of pressure from bottom to top is called vertical distribution of pressure.
Air pressure decreases as we go higher up, but not always at the same rate. Close to sea level, the air is denser and thicker. Several things affect air pressure — such as temperature, moisture (water vapor), and Earth’s gravity — and these keep changing with height.
On average, air pressure drops by 34 millibars for every 300 meters you go up.
In high mountains, people feel the effects of low pressure more — water takes longer to boil, people get tired quickly, and may even feel dizzy or get nosebleeds because the air is thin and has less oxygen.
Horizontal Distribution of Air Pressure
Now let’s look at how pressure changes from place to place across the Earth — this is called horizontal distribution of pressure.
We show it on maps using lines called isobars. An isobar connects places that have the same air pressure when measured at sea level.
The space between isobars tells us how fast pressure changes over an area. This is known as the pressure gradient:
- If isobars are close together, the pressure changes fast — this means stronger winds.
- If they’re far apart, the pressure changes slowly — which means gentler winds.
Seasonal Distribution of Pressure
Pressure on Earth isn’t the same everywhere, and it changes with the seasons. This affects the weather and climate in each region.
To study this, we use isobar maps — special maps that show air pressure. But to make these maps fair for comparison, we adjust all air pressure readings to sea level (since pressure changes with height).
January Conditions
- In January, the Sun appears to move southward, so the equatorial low-pressure belt also shifts slightly south.
- Land heats up faster than oceans, so areas like South America, Southern Africa, and Australia develop low pressure zones.
- Over oceans in the Southern Hemisphere, large high-pressure cells form, especially where cold ocean currents are present.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, land cools faster than water, so big high-pressure areas form over places like Eurasia.
- The sub-polar low-pressure belt in the Southern Hemisphere forms a full ring because there’s almost no land to interrupt it.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, we see two low-pressure zones:
- Iceland Low (North Atlantic)
- Aleutian Low (North Pacific)
July Conditions
- In July, the Sun appears to move north, so all pressure belts — including the equatorial low — shift northward.
- This shift changes wind patterns and affects the climate in both hemispheres.
- In July, the Sun is overhead in the Northern Hemisphere, so pressure belts shift northward.
- Land areas become very hot, creating low pressure zones — especially over Asia.
- The Aleutian Low and Icelandic Low seen in winter disappear, because ocean areas in the north are now relatively warm.
- The Pacific and Atlantic Oceans in the Northern Hemisphere have well-formed sub-tropical high pressure cells.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the sub-tropical high pressure belt stays steady and continuous — it circles the globe.
- A belt of sub-polar low pressure also forms continuously in the Southern Hemisphere, since there’s hardly any land to block it.
- In contrast, the Northern Hemisphere shows only faint low-pressure zones
Types of Winds
Winds are divided into three main types based on how often they blow and what causes them:
Planetary Winds (Permanent Winds)
-
- These blow all year round in a fixed direction.
- They move from high-pressure belts to low-pressure belts across large areas of land and sea.
The main types are:
Trade Winds (Easterlies): These blow from sub-tropical high pressure to the equatorial low pressure.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, they blow from the northeast.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, they blow from the southeast. Because they mostly blow from the east, they’re also called tropical easterlies.
Westerlies: These blow from sub-tropical highs toward the poles.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, they blow from the southwest due to Earth’s rotation.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, they come from the northwest.
Polar Easterlies: These come from the polar high pressure areas and move toward sub-polar lows.
Periodic Winds
These are winds that change direction with the seasons. The most important example is the monsoon.
Monsoon Winds
- The word Monsoon comes from the Arabic word ‘Mausim’, which means season.
- Monsoon winds reverse direction based on the time of year:
- In summer, they blow from sea to land (bringing rain).
- In winter, they blow from land to sea (dry season).
- Earlier, people thought monsoons were just large-scale land and sea breezes, but now we know they’re much more complex.
- Today, scientists understand monsoons as a seasonal change in the global wind system, shaped by both:
- Planetary wind patterns, and
- Regional factors — like the shape of land, height of mountains, and air movement in the upper atmosphere.
Mountain and Valley Breezes
- Daytime (Valley Breeze): The sun heats up mountain slopes more than valleys. So, air over the slopes gets warm and rises, creating low pressure there. Cooler air from the valley below moves up to take its place. This upward flow is called a valley breeze or anabatic wind.
- Nighttime (Mountain Breeze): After sunset, mountain slopes cool down quickly. The air becomes cold and heavy, leading to high pressure. This heavy air flows downhill into the valley. This is the mountain breeze, also called katabatic wind.
Read: Geography