The Balance of Payment (BOP) is a record of all economic transactions made between a country and the rest of the world in a given time frame. It includes trade in goods and services, as well as financial transactions such as investments and loans. Understanding the BOP is important for policymakers, businesses, and individuals, as it can provide insight into a country’s economic health and competitiveness.
Table of Contents
Structure of the Balance of Payment
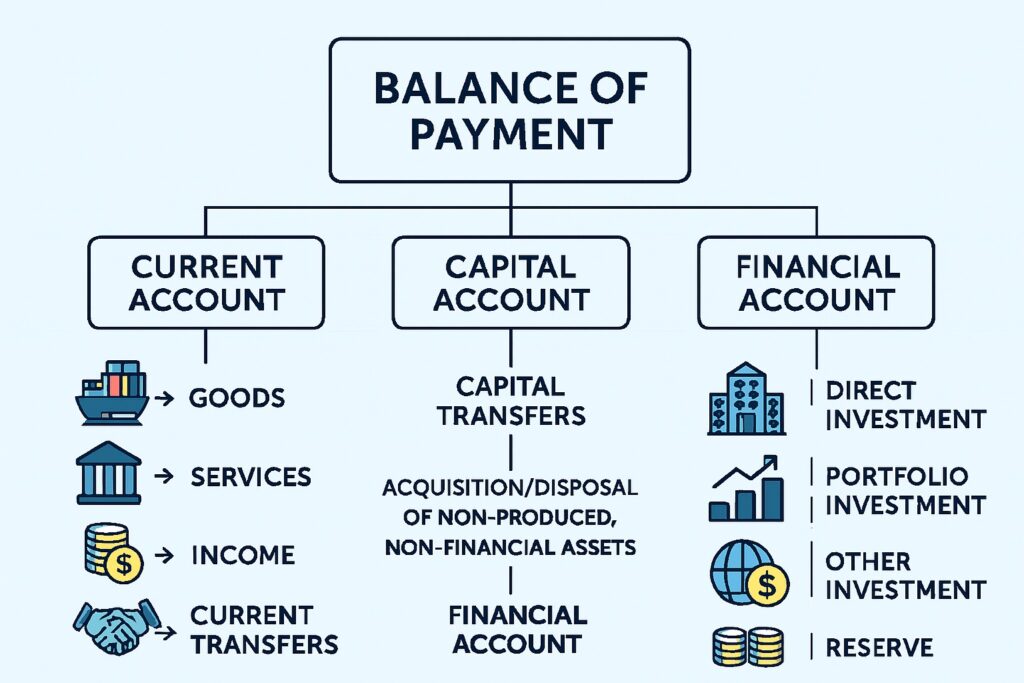
The BoP is broadly divided into three main components:
Current Account
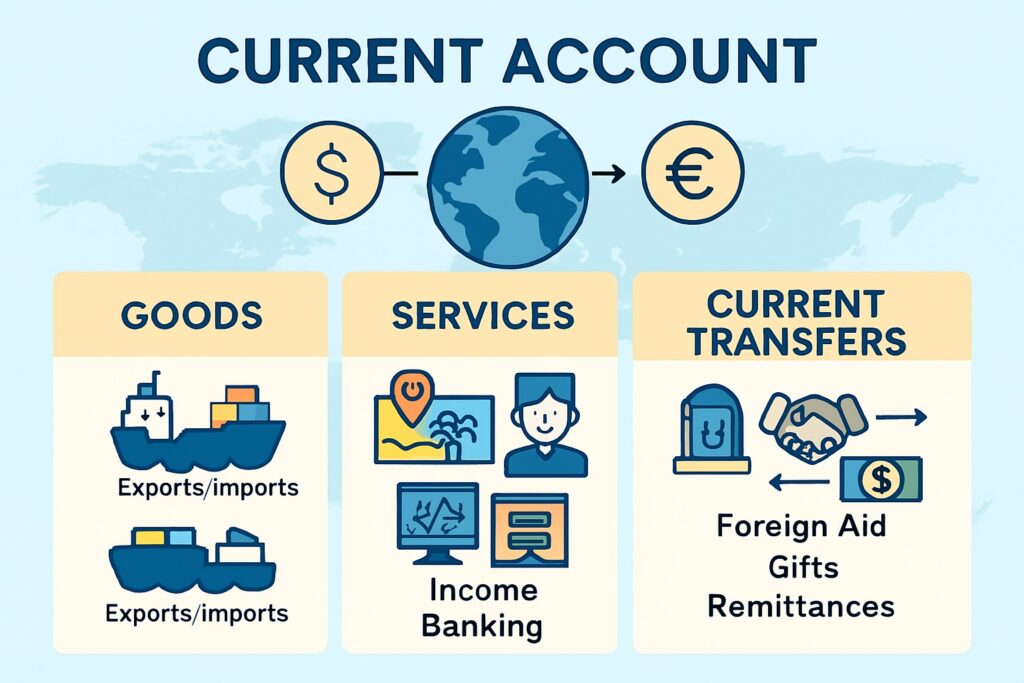
This section records the flow of goods, services, income, and current transfers. It records the flow of goods, services, income, and current transfers between a nation and the rest of the world over a specific period, typically a year. It reflects whether a country is a net lender or borrower in the global economy.
-
Trade Balance: Exports and imports of goods. A surplus occurs when exports exceed imports; a deficit when the reverse happens.
-
Services: Includes transactions like tourism, banking, and consulting.
-
Income: Earnings from foreign investments and wages.
-
Current Transfers: Unilateral transfers such as foreign aid, remittances, and gifts.
Main Components of the Current Account
1. Trade in Goods (Merchandise Trade)
- Involves exports and imports of physical goods.
- When a country exports goods, it earns foreign exchange (credit).
- When it imports goods, it pays foreign exchange (debit).
- The difference is called the trade balance (surplus or deficit).
2. Trade in Services
- Covers intangible products, such as:
- Tourism
- Banking
- IT and software services
- Transport and insurance
- Like goods, export of services brings in money (credit), while import results in payment (debit).
3. Income
- Includes earnings from foreign investments:
- Wages and salaries sent by residents working abroad.
- Interest, dividends, and profits from foreign assets.
- Outflows happen when foreign investors in the country earn income and repatriate it.
4. Current Transfers
- These are one-way transactions with no exchange of goods or services, such as:
- Remittances sent by workers to their home country.
- Foreign aid and grants.
- Donations and gifts.
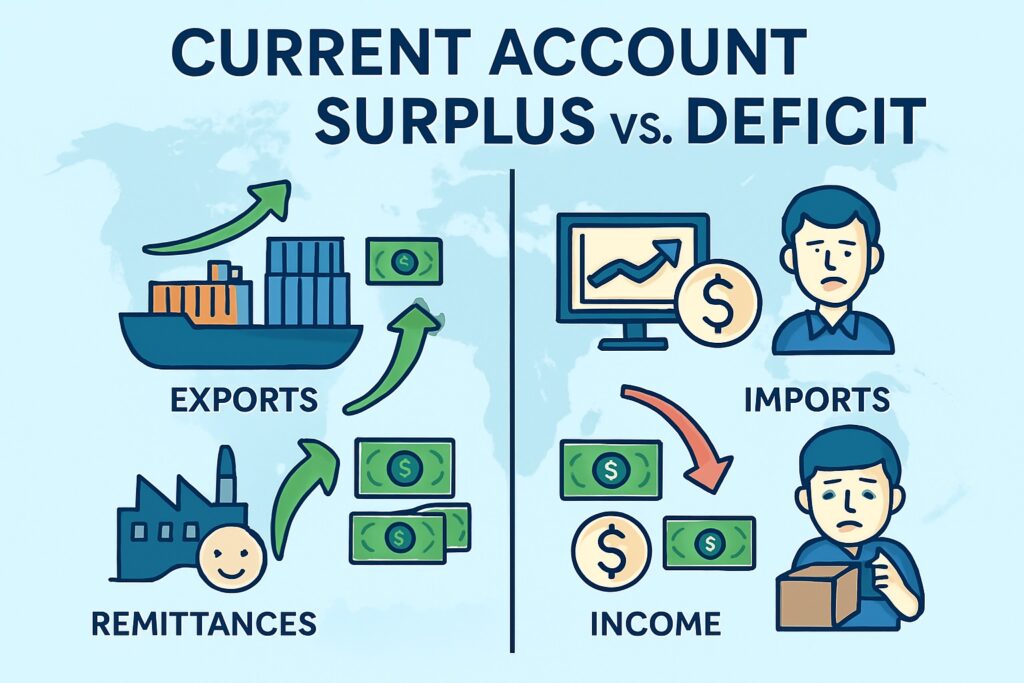
Current Account Surplus vs. Deficit
-
Surplus: When a country earns more from exports and income than it spends on imports and transfers.
-
Deficit: When the country spends more on imports, foreign income, and transfers than it earns.
Significance of the Current Account
-
Indicates a country’s international economic health.
-
A surplus may reflect strong exports or high foreign income.
-
A deficit may signal high dependence on foreign goods or need for external borrowing.
-
Policymakers use current account data to guide trade policy, exchange rate management, and monetary decisions.
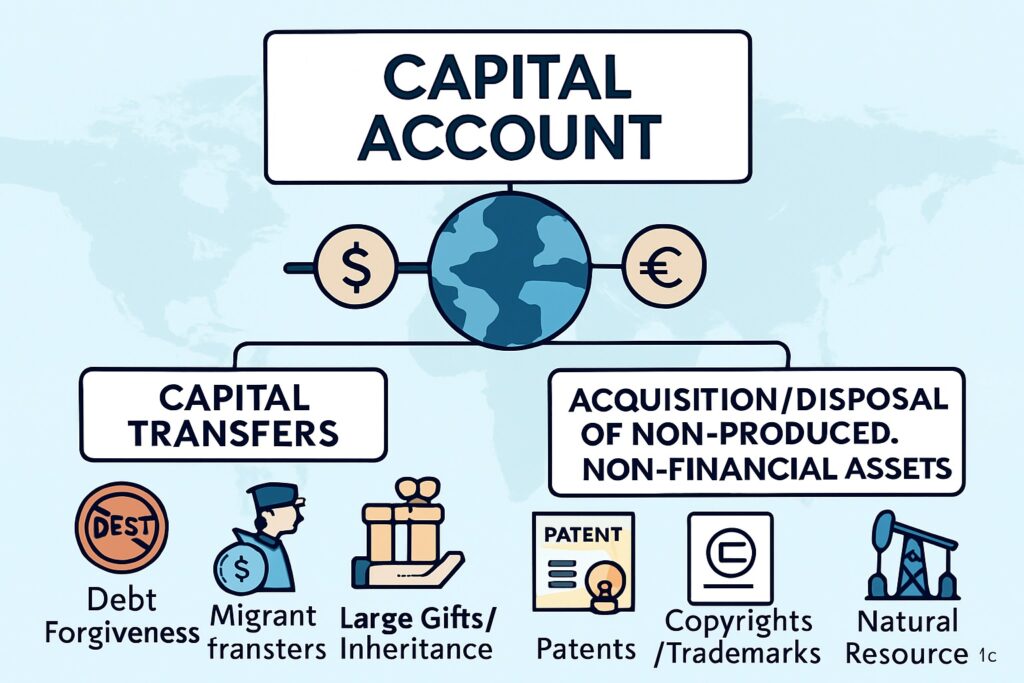
Capital Account
This account records capital transfers and acquisition/disposal of non-produced, non-financial assets such as patents, trademarks, or rights.
-
It is usually a smaller component in the BoP.
-
Includes debt forgiveness, transfers of ownership of fixed assets, and migrant transfers.
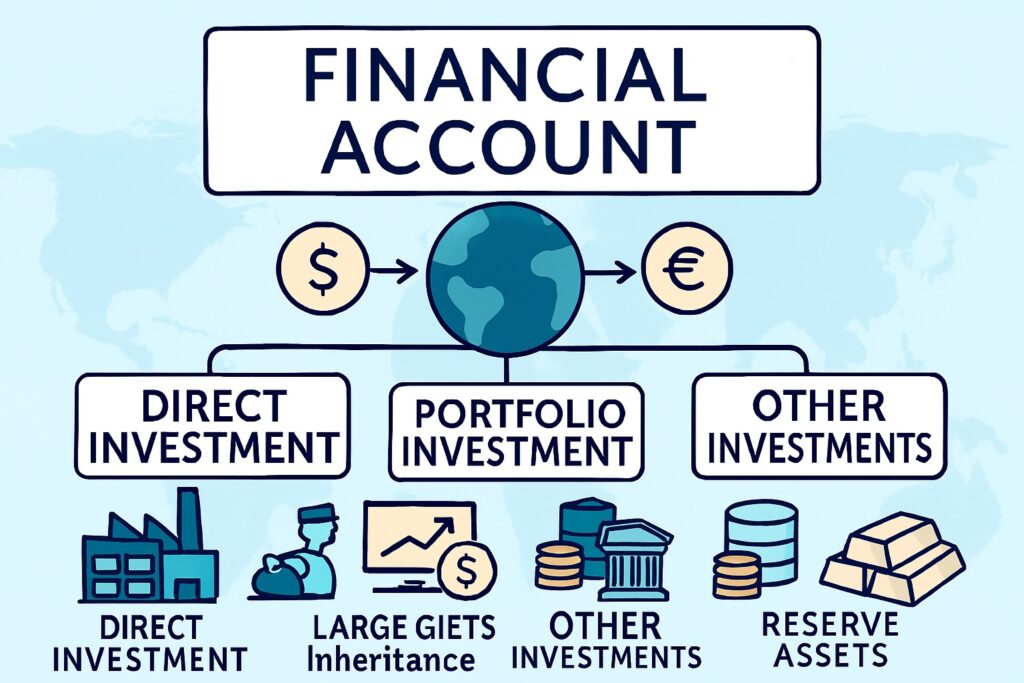
Financial Account
This tracks investments in financial instruments and real estate.
-
Direct Investment: Long-term investments like buying a foreign company or establishing business operations abroad.
-
Portfolio Investment: Short-term investments in shares, bonds, etc.
-
Other Investments: Includes loans, currency deposits, and trade credits.
-
Reserve Assets: Managed by the central bank, such as foreign currency reserves, gold, and SDRs (Special Drawing Rights).
"India has been experiencing a persistent current account deficit (CAD) for several years."
Relationship between Current and Capital Account
The relationship between the current account and the capital account is often referred to as the “twin deficits” or “twin surpluses”. A deficit in the current account often leads to a surplus in the capital account, as foreign investors seek to invest in the country to take advantage of its lower currency value. Similarly, a surplus in the current account can lead to a deficit in the capital account, as domestic investors seek to invest abroad to take advantage of higher returns.
Implications of Balance of Payment
The BOP has important implications for a country’s economic policy and growth. A large deficit in the current account can be a sign of a lack of competitiveness in the economy, as domestic businesses struggle to compete with foreign producers. This can lead to pressure to devalue the currency, which can make exports more competitive but can also lead to inflation and a decrease in purchasing power for consumers.
On the other hand, a large surplus in the current account can also have negative implications, as it can lead to an overvalued currency and a decrease in competitiveness. This can lead to a decrease in exports and a shift towards domestic consumption, which can lead to inflation and other economic problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the balance of payment is an important tool for understanding a country’s economic health and competitiveness. It is composed of two main components, the current account and the capital account, and can provide insights into a country’s trade relationships, investments, and economic policies. Understanding the BOP can help policymakers, businesses, and individuals make informed decisions about investments, trade, and other economic activities.
Read: Economy