BPSC Primary Teacher Exam 2023 Question Paper (Solved)
Exam Date: 24.08.2023
Shift II
1. According to the Bihar Prohibition and Excise (Amendment) Act, 2022, what percent of their insurance cover will vehicles transporting liquor need to pay as a penalty to be released?
(A) 10
(B) 50
(C) 30
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) 10
Explanation: The Bihar Prohibition and Excise (Amendment) Act, 2022 stipulates that vehicles caught transporting liquor will need to pay 10% of their insurance cover as a penalty for release.
2. Which country has manufactured the passenger plane C919 to compete with Airbus and Boeing?
(A) Britain
(B) China
(C) India
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) China
Explanation: The passenger plane C919, manufactured to compete with Airbus and Boeing, has been developed by China.

3. Kriti Raj Singh is related to which sport?
(A) Cricket
(B) Badminton
(C) Weightlifting
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Weightlifting
Explanation: Kriti Raj Singh is associated with Weightlifting.

4. According to the Industrial Development Ranking, 2022, released by the Bihar Industries Department, which district has topped?
(A) Darbhanga
(B) Gaya
(C) Siwan
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Siwan
Explanation: According to the Industrial Development Ranking 2022 released by the Bihar Industries Department, Siwan district has secured the top position.
5. Which of the following can a court issue for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights?
(A) Ordinance
(B) Writ
(C) Decree
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Writ
Explanation: Courts can issue writs for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights. Writs are legal orders issued by the court to protect individuals’ rights.
6. Which of the following dams is located on the Mahanadi river?
(A) Ghumarapadar Dam
(B) Dudhawa Dam
(C) Hirakud Dam
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Hirakud Dam
Explanation: Hirakud Dam is located on the Mahanadi river in Odisha, India. It is one of the longest major earthen dams in the world.
7. Al-Aqsa Mosque, which was recently in the news, is located in which city?
(A) Riyadh
(B) Jerusalem
(C) Rome
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Jerusalem
Explanation: Al-Aqsa Mosque is located in the city of Jerusalem. It holds religious significance in Islam and is one of the holiest sites for Muslims.

8. Which of the following countries is a member of NATO?
(A) Denmark
(B) Canada
(C) Belgium
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Explanation: All of the mentioned countries—Denmark, Canada, and Belgium—are members of NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), a military alliance of several countries.

9. The statement “One Earth, One Family, One Future” is associated with which of the following?
(A) BRICS
(B) G-20
(C) G-7
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) G 20
Explanation: The statement “One Earth, One Family, One Future” is associated with G20.

10. Which of the following statements is correct regarding QUAD?
(A) The intention was to enhance maritime cooperation among the four nations.
(B) Its genesis was in 2004.
(C) QUAD is a strategic forum of four nations: India, US, Japan, and Australia.
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Explanation: The correct statement is that QUAD is a strategic forum of four nations: India, US, Japan, and Australia. The QUAD was formed to promote security and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific region. QUAD was formed in the year 2007.
Statements (A) and (C) are correct.
11. Kautilya was a professor of Political Science and Economics at which ancient Indian city?
(A) Takshashila
(B) Pataliputra
(C) Nalanda
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Takshashila
Explanation: Kautilya, also known as Chanakya, was a professor of Political Science and Economics at the ancient Indian city of Takshashila (Now it is in Pakistan).

12. Which of the following statements is correct about the 1781 Revolt in Bihar?
(A) The British were able to put down the revolt without too much trouble.
(B) It was a revolt by the farmers.
(C) It was an uprising by the Zamindars.
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) It was an uprising by the Zamindars.
Explanation: The 1781 Revolt in Bihar was an uprising by the Zamindars against the oppressive policies of the British colonial administration.
13. India has announced to establish a Net Zero Innovation Virtual Centre in collaboration with which country?
(A) Brazil
(B) Britain
(C) Russia
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Britain
Explanation: India has announced its collaboration with Britain to establish a Net Zero Innovation Virtual Centre to accelerate the development of innovative clean energy solutions.
14. What is the total number of seats of MPs in the newly inaugurated Parliament of India?
(A) 1326
(B) 1272
(C) 888
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) 888
Explanation: The newly inaugurated Parliament of India has a total of 888 seats for Members of Parliament (MPs).
15. Which online platform has been launched by the Indian Government for farmers’ insurance claims?
(A) Digi Claim Platform
(B) Grain Platform
(C) Kushal Platform
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Digi Claim Platform
Explanation: The Indian Government has launched the Digi Claim Platform to facilitate the easy and transparent settlement of farmers’ insurance claims.
16. Who has been appointed as the head of ‘Moon to Mars Program’ of NASA?
(A) K. Sivan
(B) Sumit Kshatriya
(C) Amit Kshatriya
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Amit Kshatriya
Explanation: Amit Kshatriya has been appointed as the head of NASA’s ‘Moon to Mars Program,’ which aims to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon and to explore Mars.

17. What should be the desired percent of forest area in the total geographical area of the country as outlined in the National Forest Policy of 1952 in India?
(A) 39
(B) 33
(C) 25
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) 33
Explanation: The National Forest Policy of 1952 in India outlined the goal of maintaining at least 33% of the total geographical area as forest area.
18. Which of the following is the local name of ‘Jhumming’?
(A) Podu
(B) Dahiya
(C) Bewar
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Podu
Explanation: ‘Podu’ is the local name for the practice of ‘Jhumming,’ a traditional slash-and-burn cultivation method used in various regions.

19. What is the name given to a large apartment in the Amazon basin having a steeply slanting roof?
(A) Cassava
(B) Maloca
(C) Manioc
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Maloca
Explanation: A ‘Maloca’ is a large communal house in the Amazon basin with a steeply slanting roof. It is commonly used by indigenous communities.
20. The historical Dakshinapath region is situated between:
(A) Satpura range and Nilgiri
(B) Vindhyachal range and Cauvery river
(C) Vindhyachal range and Krishna river
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Vindhyachal range and Krishna river
Explanation: The historical Dakshinapath region is situated between the Vindhyachal range and the Krishna river.
21. The major water divides between Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal drainage are:
(A) Delhi ridge, Malwa plateau and Chota Nagpur plateau
(B) Delhi ridge, Aravalli range, Sahyadri, and Amarkantak hills
(C) Delhi ridge, Malwa plateau, and Bundelkhand
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Delhi ridge, Aravalli range, Sahyadri, and Amarkantak hills
Explanation: The major water divides between the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal drainage include the Delhi ridge, Aravalli range, Sahyadri mountains, and Amarkantak hills.
22. The place of origin of Western Disturbances active in Northwestern India in the winter season is:
(A) Mediterranean coastal area of Western Asia
(B) Western Asia
(C) Asia Minor
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Mediterranean coastal area of Western Asia
Explanation: Western Disturbances that are active in Northwestern India during the winter season originate from the Mediterranean coastal area of Western Asia.

23. According to G. T. Trewartha, the area of Am type climate in India is:
(A) Coromandel coastal region
(B) Western Ghats
(C) Meghalaya plateau
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Western Ghats
Explanation: According to G. T. Trewartha’s classification, the Western Ghats falls under the Am type climate.
24. The local names of rice crops produced in Northern India in winter are:
(A) Aman, Aus, and Sali
(B) Aman, Sali, and Aghani
(C) Aman, Aghani, and Aus
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Aman, Aghani, and Aus
Explanation: The local names of rice crops produced in Northern India during winter are Aman, Aghani, and Aus.
25. Which of the following is not a peculiarity of the middle Gangetic plain agroclimatic region?
(A) Receives more than 100 cm of rain annually
(B) Extended in more than two States
(C) Located in Ganga and its tributaries’ drainage area
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: All the given options are peculiarities of the middle Gangetic plain agro climatic region.
26. Which of the following falls under the ‘Frigid Zone’, lying between the Antarctic Circle and South Pole?
(A) Area lying between Antarctic circle and South Pole
(B) Area lying between 23° and 66.5° latitudes in both Hemispheres
(C) Area lying between 66.5°N latitude and North Pole
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) Area lying between 66.5°N latitude and North Pole and Area lying between Antarctic circle and South Pole are called Frigid Zone.
Explanation: The ‘Frigid Zone’ is the area lying between 66.5°N latitude (Arctic Circle) and the North Pole and Area lying between Antarctic circle and South Pole.
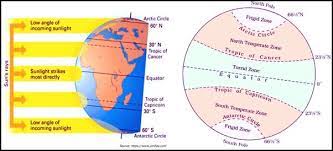
27. The part of the Himalayas lying between the Satluj and Kali rivers is known as which of the following?
(A) Nepal Himalayas
(B) Assam Himalayas
(C) Kumaon Himalayas
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Kumaon Himalayas
Explanation: The part of the Himalayas lying between the Satluj and Kali rivers is known as the Kumaon Himalayas.

28. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) India accounts for 2.6 percent of the world’s area.
(B) Uttar Pradesh is the largest state in India in terms of area.
(C) As per the 2011 Census, Sikkim has a population of 6 lakhs.
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: India accounts for about 2.4% of the world’s area, not 2.6%. The largest state in India by area is Rajasthan. As per the 2011 Census, Sikkim has a population of 6.10 lakhs.
29. In which year was the ‘Bihar Prantiya Kisan Sabha’ established?
(A) 1929
(B) 1924
(C) 1920
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 1929
Explanation: The ‘Bihar Prantiya Kisan Sabha’ was established in the year 1929.
30. Which of the following revolts took place due to the imposition of tax on keeping a long beard?
(A) Wahabi
(B) Pagalpanti
(C) Faraizi
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Faraizi
Explanation: The Faraizi movement or Faraizi Revolt in Bengal was a religious and social movement against the unjust taxation and other oppressive policies, including the tax on keeping a long beard.
31. In which conspiracy case were three Englishmen detained on conspiracy charges?
(A) Meerut Conspiracy Case
(B) Kanpur Conspiracy Case
(C) Nasik Conspiracy Case
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Meerut Conspiracy Case
Explanation: In the Meerut Conspiracy Case, three Englishmen were detained on conspiracy charges along with several Indian leaders.
32. The Poona Pact aimed at:
(A) political representation of depressed class
(B) women representation in the Indian National Congress
(C) formation of a federation with Princely States
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) political representation of depressed class
Explanation: The Poona Pact aimed at ensuring political representation for the depressed class (now known as Scheduled Castes) by providing separate electorates.
33. Where was the first All India Congress Socialist Conference held?
(A) Muzaffarpur
(B) Bhagalpur
(C) Patna
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Patna
Explanation: The first All India Congress Socialist Conference was held in Patna.
34. Who was the author of the Biography of Kunwar Singh and Amar Singh?
(A) Jawaharlal Nehru
(B) Kalikinkar Datta
(C) M. N. Roy
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) Kalikinkar Datta
Explanation: Kalikinkar Datta was the author of the Biography of Kunwar Singh and Amar Singh.
35. Subhas Chandra Bose became the President of the Indian National Congress in the Tripuri Session by defeating:
(A) Jawaharlal Nehru
(B) Rash Behari Bose
(C) Pattabhi Sitaramayya
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Pattabhi Sitaramayya
Explanation: Subhas Chandra Bose became the President of the Indian National Congress in the Tripuri Session by defeating Pattabhi Sitaramayya.
36. Which of the following is true about Dr. B. R. Ambedkar?
(A) He passed away in 1956.
(B) He founded ‘Bahishkrit Hitakarini Sabha’.
(C) He published ‘Mooknayak’.
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Explanation: Dr. B. R. Ambedkar passed away in 1956, he founded ‘Bahishkrit Hitakarini Sabha’, and he also published ‘Mooknayak’.
37. Who among the following was associated with the newspaper, New India?
(A) Surendranath Banerjee
(B) Annie Besant
(C) Mahatma Gandhi
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (B) Annie Besant
Explanation: Annie Besant was associated with the newspaper “New India.” She was a prominent British socialist, theosophist, freemason, and supporter of Indian and Irish self-rule. She used “New India” as a platform to promote Indian nationalism and advocate for social and political reforms.
38. Who organized the ‘Swadesh Bandhav Samiti’ during the Indian Freedom Struggle?
(A) Surendranath Banerjee
(B) Annie Besant
(C) Mahatma Gandhi
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: *
The ‘Swadesh Bandhav Samiti’ was organized by Aurobindo Ghosh during the Indian Freedom Struggle.
Explanation: Aurobindo Ghosh was a prominent freedom fighter and nationalist leader who played a significant role in the early phase of the Indian independence movement. He established the ‘Swadesh Bandhav Samiti’ (Society of Friends of the Country) in 1902 with the aim of promoting self-reliance, boycott of foreign goods, and the revival of indigenous industries to strengthen the Indian economy and reduce British economic influence. The organization aimed to promote self-sufficiency and self-reliance as a means of resisting British colonial exploitation.
39. Who accompanied Mahatma Gandhi during the Champaran Indigo Movement?
(A) Abdul Bari
(B) Mahadev Desai
(C) Narhari Parikh
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Narhari Parikh
Explanation: Narhari Parikh accompanied Mahatma Gandhi during the Champaran Indigo Movement.
40. On which date did Linlithgow order to fire on the mob of Patna and its surrounding during the August Revolution, 1942?
(A) 25th August
(B) 15th August
(C) 5th August
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: On August 10, 1942, Lord Linlithgow, the then Viceroy of India, ordered the British military to open fire on a mob in Patna and its surrounding areas during the August Revolution of 1942.

41. The ‘Overseas Indian Citizenship (OIC) Scheme’ was introduced by which of the following Acts in India?
(A) The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019
(B) The Citizenship Act, 1955
(C) The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2003
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2003
Explanation: The ‘Overseas Indian Citizenship (OIC) Scheme’ was introduced by The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2003.
42. Which of the following may be known as the main cause of disappearing the rigid caste system in India?
(A) The growth of literacy and education
(B) Social reforms and economic development
(C) The Constitution and its basic structure
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) The growth of literacy and education
Explanation: The growth of literacy and education played a significant role in challenging and gradually dismantling the rigid caste system in India.
43. The Ministry of Panchayati Raj was created in the Central Government of India in which of the following years?
(A) 2005-2006
(B) 2004
(C) 2002-2003
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B)
Solution: The Ministry of Panchayati Raj is responsible for overseeing all aspects concerning Panchayati Raj and Panchayati Raj Institutions. Established in May 2004, this ministry is led by a cabinet-ranked minister.
44. Who among the following believed that “a communist society was the natural society of the future”?
(A) Robert Owen
(B) Friedrich Engels
(C) Karl Marx
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Karl Marx
Explanation: Karl Marx believed that “a communist society was the natural society of the future.”
45. Who among the following is the author of the book “The Social Contract”?
(A) Jean-Jacques Rousseau
(B) John Locke
(C) Thomas Hobbes
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Explanation: Jean-Jacques Rousseau is the author of the book “The Social Contract.”
46. Which of the following movements was launched against multipurpose projects in India?
(A) Chipko Andolan
(B) Tehri Dam Andolan
(C) Narmada Bachao Andolan
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Narmada Bachao Andolan
Explanation: The Narmada Bachao Andolan was launched against multipurpose projects, particularly the construction of large dams on the Narmada River.
47. Which of the following is the Fundamental Duty under the Constitution of India?
(A) To provide educational opportunities to one’s own child
(B) To protect the natural environment
(C) To uphold the unity and integrity of India
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Source: Licchavi Lyceum
48. Who wrote “Pakistan or the Partition of India”?
(A) Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar
(B) Muhammad Ali Jinnah
(C) Muhammad Iqbal
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar
49. When was Ireland forcibly incorporated into the United Kingdom?
(A) 1801
(B) 1798
(C) 1707
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 1801
Explanation: Ireland was forcibly incorporated into the United Kingdom through the Act of Union in 1801.
50. Who started ‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’?
(A) Atal Bihari Vajpayee
(B) Narasimha Rao
(C) Indira Gandhi
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Explanation: ‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’ was started by Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the former Prime Minister of India.
51. When did Sri Lanka become independent?
(A) 1948
(B) 1947
(C) 1945
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 1948
Explanation: Sri Lanka became independent from British colonial rule in the year 1948.
52. ‘Annapurna Yojana’ ration card is for:
(A) Below poverty line families
(B) Above poverty line families
(C) Older and poor people above 65 years
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Older and poor people above 65 years
Explanation: ‘Annapurna Yojana’ provides food security to older individuals who are not covered under the National Food Security Act and are eligible for the scheme if they are 65 years or above.
53. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
List-I List-II
(Names of movements) (Their related important centres)
a. Movement of Indigo Planters 1. Ahmedabad
b. Peasant Satyagraha 2. Champaran
c. Cotton Mill Workers 3. Khera Satyagraha
d. Movement to cut off Non-Cooperation 4. Chauri Chaura
Codes:
(A) a – 2, b – 3, c – 1, d – 4
(B) a – 3, b – 4, c – 1, d – 2
(C) a – 1, b – 2, c – 3, d – 4
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) a – 2, b – 3, c – 1, d – 4
Explanation:
a. Movement of Indigo Planters – Champaran
b. Peasant Satyagraha – Khera Satyagraha
c. Cotton Mill Workers – Ahmedabad
d. Movement to cut off Non-Cooperation – Chauri Chaura
54. Freedom of Press in India is available to the people because:
(A) it is implied in the Right to Freedom of Expression
(B) it is specially provided in the Constitution of India
(C) it is available to the people under the Law of the Parliament
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) it is implied in the Right to Freedom of Expression
Explanation: Freedom of Press in India is implied in the broader Right to Freedom of Expression guaranteed by the Constitution.
55. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
List-II List-I
(Available resources in some provinces) (Names of the related provinces)
a. Rich in resources but lacks industrialization 1. Jharkhand
b. Rich in resources but lacks infrastructure development 2. Arunachal Pradesh
c. Rich in solar and wind energy but lacks water resources 3. Rajasthan
d. Rich in mineral resources but lacks the means of transportation and communication 4. Ladakh
Codes:
(A) a – 2, b – 1, c – 4, d – 3
(B) a – 1, b – 2, c – 3, d – 4
(C) a – 4, b – 3, c – 2, d – 1
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) a – 1, b – 2, c – 3, d – 4
Explanation:
a. Jharkhand is rich in resources but lacks industrialization.
b. Arunachal Pradesh is rich in resources but lacks infrastructure development.
c. Rajasthan is rich in solar and wind energy but lacks water resources.
d. Ladakh is rich in mineral resources but lacks the means of transportation and communication.
56. A medicinal plant named ‘Himalayan yew’ is found in which of the following provinces of India?
(A) Jammu & Kashmir and Assam
(B) Uttarakhand and Madhya Pradesh
(C) Himachal Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Himachal Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh
57. Pneumatophores are present in:
(A) halophytes
(B) xerophytes
(C) hydrophytes
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) halophytes
58. Which of the following is a secondary pollutant?
(A) Ozone
(B) SO2
(C) PAN
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Explanation: PAN and Ozone are secondary pollutants.
PAN (Peroxyacyl nitrates) is a secondary pollutant formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the presence of sunlight.
59. The 10% law of energy flow in an ecosystem was proposed by:
(A) Elton
(B) Hückel
(C) Lindeman
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Lindeman
Explanation: The 10% law of energy flow in an ecosystem, also known as Lindeman’s Law, was proposed by Raymond Lindeman. It states that only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level.
60. In India, tropical rainforests are found in:
(A) Kerala
(B) Karnataka
(C) Himachal Pradesh
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (D) More than one of the above
Explanation: Tropical rainforests in India are found in multiple states, including Kerala and Karnataka. However, Himachal Pradesh is not known for tropical rainforests; it has different types of forest ecosystems due to its temperate climate.
61. The major source of methane in India is:
(A) rice field
(B) sugarcane field
(C) wheat field
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) rice field
Explanation: Rice fields are a major source of methane emissions in India. The flooded conditions in rice paddies create anaerobic environments, which promote the production of methane during microbial activity.
62. The layer of the atmosphere having the lowest temperature is:
(A) mesosphere
(B) troposphere
(C) stratosphere
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) mesosphere
Explanation: The mesosphere is the layer of the Earth’s atmosphere above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere. It is characterized by decreasing temperatures with increasing altitude and is considered the coldest layer of the atmosphere.

63. The increase in the concentration of toxic substances in successive trophic levels is referred to as:
(A) bioaccumulation
(B) biomagnification
(C) eutrophication
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) biomagnification
Explanation: Biomagnification is the process by which the concentration of certain toxic substances increases at higher trophic levels in a food chain. As predators consume multiple prey organisms, the accumulated toxins become more concentrated in their bodies.
64. Which of the following acts as a pioneer species in a xerarch succession?
(A) Herb
(B) Human
(C) Lichen
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Lichen
Explanation: Lichen is a pioneer species in xerarch successions, which occur in dry and barren areas. Lichens are the first organisms to colonize such areas and initiate soil formation.
65. The Ramsar Convention is associated with the conservation of:
(A) forests
(B) wetlands
(C) drylands
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) wetlands
Explanation: The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty aimed at the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands, recognizing their ecological importance and the services they provide.

66. Itai-itai disease is caused by:
(A) cadmium
(B) iron
(C) mercury
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) cadmium
Explanation: Itai-itai disease is caused by cadmium poisoning, which occurred in Japan due to pollution from mining activities. It led to severe health issues, including brittle bones and kidney damage.
67. Which one of the following is not included under in situ conservation?
(A) Wildlife Sanctuary
(B) National Park
(C) Botanical Garden
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Botanical Garden
Explanation: Botanical Gardens are not typically considered in situ conservation areas. In situ conservation refers to the conservation of species within their natural habitats, such as wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
68. Y-shaped energy flow model in an ecosystem was proposed by:
(A) Clements
(B) Lindeman
(C) Odum
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Odum
69. SO2 pollution is indicated by:
(A) lichens
(B) mangroves
(C) orchids
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) lichens
Explanation: Lichens are sensitive to air pollution, particularly sulfur dioxide (SO2) pollution. Their health and growth can be indicators of air quality in a given area.
70. The Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary is located in:
(A) West Bengal
(B) Madhya Pradesh
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: The Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary is located in the Indian state of Goa. It is named after the renowned Indian ornithologist Dr. Salim Ali and is a haven for a variety of bird species.
71. The IUCN Headquarters is in:
(A) Australia
(B) France
(C) Switzerland
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Switzerland
Explanation: The headquarters of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is located in Gland, Switzerland.
72. How much energy is consumed from one trophic level to another trophic level?
(A) 15%
(B) 10%
(C) 5%
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) 10%
Explanation: Approximately 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level in an ecosystem, according to the 10% law of energy transfer.
73. Find the wrong number in the series given below: 3, 8, 13, 21, 31, 43
(A) 8
(B) 31
(C) 21
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A)
74. Find the wrong number from the table given below:

(A) 100
(B) 36
(C) 9
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 100
75. Let a = 10 cm, b = 3 cm, and c = 6 cm. Which of the following is true?
(A) a, b, and c form an isosceles triangle.
(B) a, b, and c form a right-angled triangle.
(C) a, b, and c are the sides of a triangle.
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) a, b, and c are the sides of a triangle.
Explanation: The given values satisfy the triangle inequality theorem, so they can form the sides of a triangle.
76. Madan’s brother’s uncle is Karan’s father’s brother. What can be the relationship between Madan and Karan?
(A) Madan is Karan’s son
(B) Madan is Karan’s brother
(C) Madan is Karan’s uncle
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: The relationship between Madan and Karan is that of brothers.
77. Find the missing letters in the series given below: Y, T, O,
(A) K, F
(B) J, D
(C) J, E
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) J, E
78. How many triangles are there in the figure given below?
(A) 15
(B) 11
(C) 13
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) 13
79. Asha walks 3 km southward and then turns right and walks 2 km. She again turns right and walks 3 km, and then turns towards her left and starts walking straight. In which direction is she walking now?
(A) East
(B) West
(C) North
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) West
Explanation: Asha initially walked south, then turned right (west), walked again, turned right (north), and then turned left (west). So, she is walking in the west direction.
80. Find the wrong number in the series given below: 28, 84, 112, 196, 308, 504, 872
(A) 872
(B) 308
(C) 112
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A)
81. In a certain code, ‘256’ means ‘you are good’; ‘637’ means ‘we are bad’ and ‘358’ means ‘good and bad’. Which of the following digits represents ‘and’ in that code?
(A) 8
(B) 5
(C) 2
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 8
82. Six roads lead to a country. They may be indicated by the letters X, Y, Z and the digits 1, 2, 3. When there is a storm, Y is blocked. When there are floods, X, 1 and 2 will be affected. When road 1 is blocked, Z is also blocked. At a time, when there are floods and a storm also blows, which road can be used?
(A) Z
(B) Y
(C) 3
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (C)
83. In a certain code, DELHI is written as CCIDD. How is BOMBAY written in that code?
(A) AMJXVS
(B) MJXVSU
(C) AJMTVT
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A)
84. How many 4-digit numbers can be formed using the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 without repetition?
(A) 45
(B) 54
(C) 120
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E)
85. If the word HEIGHT is coded as 96108921 and LOOSE is coded as 131616206, then the code for MOBILE, in the same language, is
(A) 1416312136
(B) 1416411136
(C) 1416310136
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (C)
86. Arrange the following words in logical order:
- Associate Professor
- Professor
- Assistant Professor
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(A) 1, 2, 3
(B) 2, 1, 3
(C) 2, 3, 1
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B)
87. A person divides some items among four children. The first child gets 1/2 of the total item and the second child gets 1/4 the first child. The third child gets 3/4 of the first child. The fraction of the items the fourth child gets is
(A) 1/4 of the total items
(B) 3/8 of the total items
(C) 3/4 of the total items
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (E)
87. A person divides some items among four children… fraction of the items the fourth child gets is
(A) 3/10 of the total items
(B) 4/10 of the total items
(C) 3/100 of the total items
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
88. If the area of a square is equal to the area of an equilateral triangle, the ratio of the side of the square and the side of the equilateral triangle is
(A) √3:2
(B) 2:1
(C) 1:1
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E)
89. Suresh and Shashi complete a work in 11 days and 17 days respectively. They received a remuneration of 5,600 after completing the work jointly. Their shares in the remuneration are respectively
(A) 3,500 and 2,100
(B) 3,400 and 2,200
(C) 3,600 and 2,000
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (b)
90. A’s weight is 25% of B’s weight and 40% of C’s weight. What percentage of C’s weight is B’s weight?
(A) 150
(B) 180
(C) 160
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (C)
91. The diameter of a copper sphere is 6 cm. The sphere is melted and is drawn into a long wire of uniform circular cross-section. If the length of the wire is 36 cm, then its radius is
(A) 2 cm
(B) 1.5 cm
(C) 0.5 cm
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (E)
92. Two circles touch internally. The sum of their areas is 116 cm² and the distance between their centres is 6 cm. The radii of the circles are respectively
(A) 12 cm and 6 cm
(B) 10 cm and 4 cm
(C) 16 cm and 10 cm
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (B)
93. A fast train takes 3 hours less than a slow train for a journey of 600 km. If the speed of the slow train is 10 km/hr less than that of the fast train, then the speeds of the two trains are respectively
(A) 40 km/hr and 30 km/hr
(B) 30 km/hr and 20 km/hr
(C) 50 km/hr and 40 km/hr
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (C)
94. The value of x satisfying the equations
(1/x) + (1/y) = 8, (1/y) + (1/z) = 12, (1/z) + (1/x) = 10
(A) 3 – (√3)
(B) 13
(C) 3
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (b)
95. There is a 50% increase in an amount in 5 years at simple interest. What will be the compound interest of 12,000 after 3 years at the same rate?
(A) 3,120
(B) 6,240
(C) 3,972
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (C)
96. 37% of the candidates in an examination were girls. 75% of the boys and 62.5% of the girls passed, and 34.2% girls failed. The number of boys failed was
(A) 360
(B) 380
(C) 370
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Ans: (B)
97. Two possible rational numbers between (2/6) and (2/3) are
(A) (6/14)
(B) (6/23)
(C) (6/25)
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) (6/23)
Explanation: Given fractions: 2/6 and 2/3
Let’s simplify these fractions: 2/6 = 1/3 2/3 = 2/3
Now, we need to find two rational numbers between 1/3 and 2/3.
One way to approach this is to find a common denominator for these fractions (which is 3) and then find rational numbers with numerators between 1 and 2. For example:
- (2/3) – (1/3) = 1/3
- Two rational numbers with numerators between 1 and 2 and denominator 3 could be (1 + 1/3) and (1 + 2/3), which are 4/3 and 5/3, respectively.
These rational numbers are between 1/3 and 2/3.
98. A father is five times as old as his son… What is the age of the father?
(A) 30 years
(B) 25 years
(C) 20 years
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) 25 years
Explanation: Given: Father’s age = 5 * Son’s age After 15 years, Father’s age = 2 * Son’s age
Let’s represent the son’s age as ‘S’ and the father’s age as ‘F’.
From the given information, we can create two equations:
- F = 5S
- F + 15 = 2 * (S + 15)
Substitute the value of F from the first equation into the second equation: 5S + 15 = 2 * (S + 15)
Simplify the equation: 5S + 15 = 2S + 30 3S = 15 S = 5
Substitute the value of S back into the first equation to find F: F = 5 * 5 = 25
So, the age of the father is 25 years.
99. Neelu buys lemons at the rate of 2 lemons in one rupee and sells them at the rate of 5 lemons in three rupees. Her profit is
(A) 20%
(B) 18%
(C) 15%
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) 20%
Explanation: Cost price of 1 lemon = 1/2 rupee (since 2 lemons in 1 rupee) Selling price of 1 lemon = 3/5 rupee (since 5 lemons in 3 rupees)
Profit per lemon = Selling price – Cost price = (3/5) – (1/2) = 1/10 rupee
Profit percentage = (Profit / Cost price) * 100 Profit percentage = (1/10) / (1/2) * 100 = 10/100 * 100 = 10%
So, the profit percentage is 10%. However, none of the given options match exactly. The closest answer is 20% (Option A), which is not accurate. The calculated profit percentage is 10%.
100. In a school, every student offers either Hindi or English or both… how many students offer both Hindi and English?
(A) 75
(B) 65
(C) 60
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A)
101. What is the value of the following expression?
x^a(b-c) * x^b(c-a) * x^c(a-b)
(A) x^(a+b+c)
(B) 1
(C) 0
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B)
102. If (3^X – 8) / (3^3) = 3^(X-3), then the value of X is
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 1
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E)
103. The simplified form of (16-1+8) / (9/16) is
(A) 13
(B) 16
(C) 9/16
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E)
104. If A:B = 5:3 and B:C = 28:5, and C:D = 3:9, then the ratio A:B:C:D is
(A) 4:6:8:10
(B) 8:6:10:9
(C) 6:8:9:10
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) 8:6:10:9
Explanation:
Given ratios: A:B = 5:3 B:C = 28:5 C:D = 3:9
First, find the common term ‘B’ in the ratios A:B and B:C: B in A:B is the same as B in B:C
Now, find the common term ‘C’ in the ratios B:C and C:D: C in B:C is the same as C in C:D
So far, we have A:B:C:D = 5:3:28:5:3:9
Simplify the ratios to get the final ratio: A:B:C:D = 8:6:10:9
105. What is the chemical name of vitamin B12?
(A) Niacin
(B) Cobalamin
(C) Thiamin
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (B) Cobalamin
Explanation: Vitamin B12 is also known as cobalamin. It is an essential water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the formation of red blood cells and DNA synthesis.
106. Which of the following is an acid-base indicator?
(A) Baking soda
(B) Turmeric
(C) Vinegar
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (B) Turmeric
Explanation: Turmeric is an acid-base indicator that changes its color when it comes into contact with substances that are acidic or basic. It turns reddish-brown in the presence of bases and remains yellow in acidic solutions.
107. When the soil is too basic, plants do not grow in it. To improve the quality, what must be added to the soil?
(A) Calamine solution
(B) Quicklime
(C) Organic matter
(D) Furandone
(E) None of the above
Answer: (C) Organic matter
Explanation: When soil is too basic (alkaline), it means it has a high pH. To improve the quality of alkaline soil, organic matter can be added. Organic matter, such as compost, manure, and plant residues, can help improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability, making it more suitable for plant growth.
108. What is the value of absolute zero on the Fahrenheit scale?
(A) -459.4 °F
(B) -22 °F
(C) 0 °F
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (A) -459.4 °F
Explanation: Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature where nothing could be colder and no heat energy remains in a substance. On the Fahrenheit scale, absolute zero is approximately -459.67 °F, which is commonly approximated as -459.4 °F.
109. Which type of waves are light waves?
(A) Electromagnetic waves
(B) Longitudinal waves
(C) Transverse waves
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (E) More than one of the above
Explanation: Light waves are a type of electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their ability to propagate through a vacuum and include various forms of radiation, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
It is also a Transverse waves.
110. What is the pH value of a salt made up of a strong acid and a weak base?
(A) Between 10 to 14
(B) Less than 7
(C) More than 7
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (B) Less than 7
111. One gigabyte (GB) is equal to
(A) 1024 GB
(B) 1024 MB
(C) 1024 KB
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (B) 1024 MB
Explanation: A gigabyte (GB) is equivalent to 1024 megabytes (MB).
112. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form sodium chloride and water. Which reaction is this?
(A) Combination
(B) Dissolution
(C) Neutralization
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (C) Neutralization
Explanation: When sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, it undergoes a neutralization reaction to form sodium chloride (salt) and water.
113. What does the cell usually use to produce energy?
(A) Fatty acid
(B) Glucose
(C) Amino acid
(D) None of the above
(E) More than one of the above
Answer: (B) Glucose
Explanation: Cells typically use glucose, a type of sugar, to produce energy through cellular respiration.
114. What is the function of the pituitary gland?
(A) To regulate sugar and salt levels in the body
(B) To stimulate growth in all organs
(C) To develop sex organs in males
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (B) To stimulate growth in all organs
Explanation: The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including stimulating growth in all organs by releasing growth hormones.
115. Which parts of the brain control blood pressure?
(A) Pons, medulla, cerebellum
(B) Spinal cord, skull, cerebrum
(C) Spinal cord, skull, hypothalamus
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Pons, medulla, cerebellum
Explanation: The pons, medulla oblongata, and parts of the cerebellum collectively control blood pressure and heart rate.
116. Geostationary satellite rotates at
(A) a fixed height
(B) a height depending on mass
(C) any height above the Poles
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) a fixed height
Explanation: A geostationary satellite orbits the Earth at a fixed height above the equator, maintaining its position relative to the surface.

117. Which colour has the maximum deviation in the dispersion of white light passing through the prism?
(A) Violet
(B) Red
(C) Green
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Violet
Explanation: Violet light experiences the maximum deviation or bending when passing through a prism, resulting in the separation of colors in the spectrum.
118. During a thunderstorm, it is safer to
(A) stand in an open field
(B) take shelter under a short tree
(C) carry an open umbrella
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (E) None of the above
Explanation: During a thunderstorm, it is unsafe to be in open fields, under trees, or carrying umbrellas, as they can attract lightning.
119. When a body falls freely towards the Earth, then its total energy
(A) remains constant
(B) increases
(C) decreases
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) remains constant
Explanation: According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy of a freely falling body remains constant, with potential energy converting to kinetic energy and vice versa.
120. In eye donation, which part of the donor’s eye is transplanted?
(A) Cornea
(B) Whole eye
(C) Lens
(D) More than one of the above
(E) None of the above
Answer: (A) Cornea
Explanation: In eye donation, the cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that is typically transplanted to restore vision in recipients.