Chinook wind is a warm and dry wind that occurs in regions close to the Rocky Mountains. It is also known as “snow-eater” because of its ability to melt snow rapidly. In this article, we will discuss everything you need to know about Chinook wind, including its characteristics, causes, and effects.
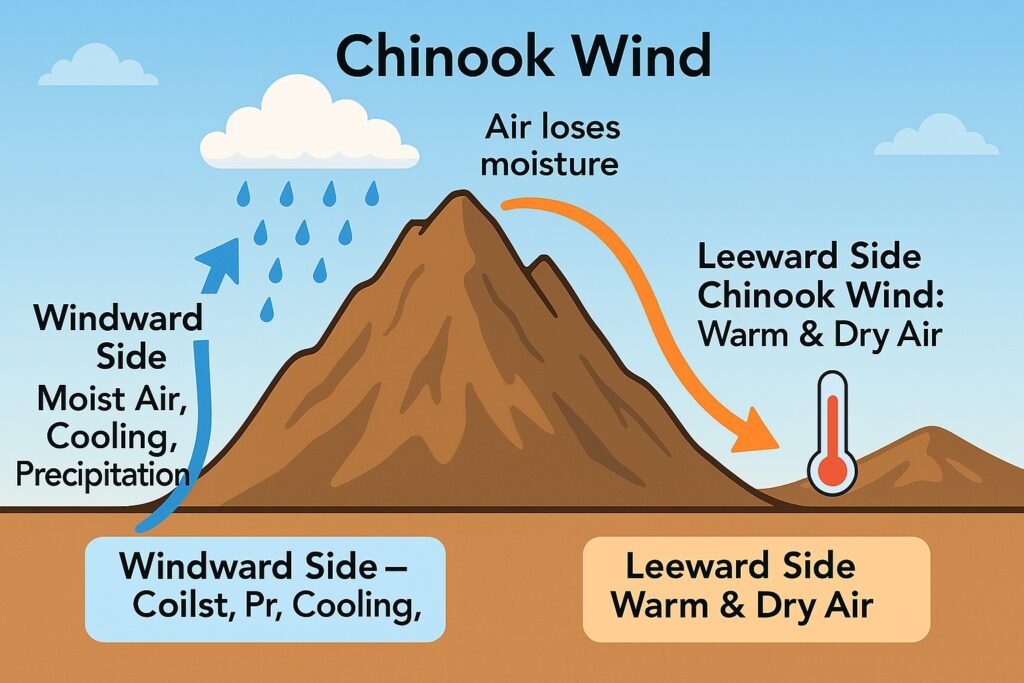
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Chinook wind
It is a warm and dry wind that originates from the Pacific Ocean and moves towards the Rocky Mountains. The wind is warm because it passes over the mountains and gains heat due to compression. It is characterized by a sudden increase in temperature, usually by 20 degrees Celsius or more, within a few hours.
Causes of Chinook wind
It is caused by a meteorological phenomenon called “foehn effect.” The foehn effect occurs when air is forced to rise over a mountain range, causing it to cool and release moisture. As the air descends on the leeward side of the mountain, it is compressed and heats up rapidly. This causes the air to become dry and warm, resulting in the Chinook wind.
Effects of Chinook wind
It has various effects on the environment and human life. One of its significant effects is the rapid melting of snow, which can cause flooding and landslides. The wind also dries out vegetation, increasing the risk of wildfires. On the positive side, Chinook wind provides relief from the cold weather and can increase agricultural productivity.
Chinook wind and culture
It has been a significant part of the culture of people living in the Rocky Mountains region. Native Americans have various legends and stories related to Chinook wind. Some tribes consider the wind as a spiritual force that brings change and renewal.
Conclusion
It is a warm and dry wind that occurs in regions close to the Rocky Mountains. It is caused by the foehn effect and has significant effects on the environment and human life. Understanding Chinook wind and its characteristics can help us prepare and mitigate its effects.
Read: Geography Notes