Table of Contents
Chapter 1: The Earth in the Solar System
1. Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 2: Tick the correct answer.
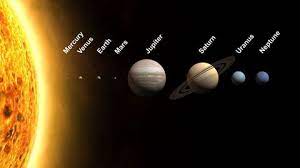
(a) The planet known as the “Earth’s Twin” is
(i) Jupiter (ii) Saturn (iii) Venus
Answer: (iii) Venus
Explanation: Venus is often referred to as Earth’s twin because of its similar size and composition. Both planets are rocky and have a comparable mass and density.


(b) Which is the third nearest planet to the sun
(i) Venus (ii) Earth (iii) Mercury
Answer: (iii) Mercury
Explanation: The order of planets from the sun, starting with the closest, is Mercury, Venus, Earth. So, Mercury is the third nearest planet.


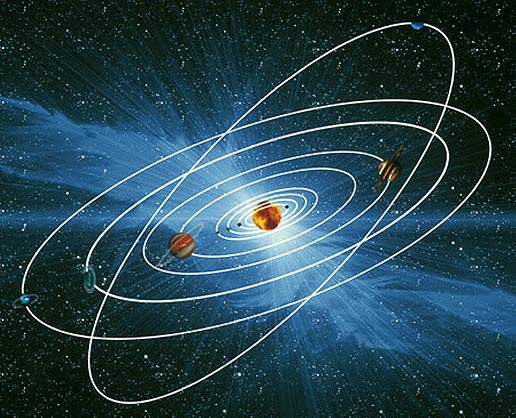
(c) All the planets move around the sun in a
(i) Circular path (ii) Rectangular path (iii) Elliptical path
Answer: (iii) Elliptical path
Explanation: Planets orbit the sun in elliptical paths. An elliptical orbit is a stretched-out circle, and this is the shape of the paths that planets follow as they go around the sun.

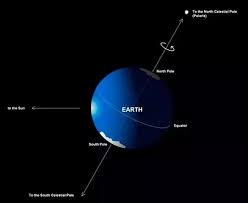
(d) The Pole Star indicates the direction to the
(i) South (ii) North (iii) East
Answer: (ii) North
Explanation: The Pole Star, also known as Polaris, indicates the direction towards the North. It is a reliable reference point for navigation in the Northern Hemisphere.

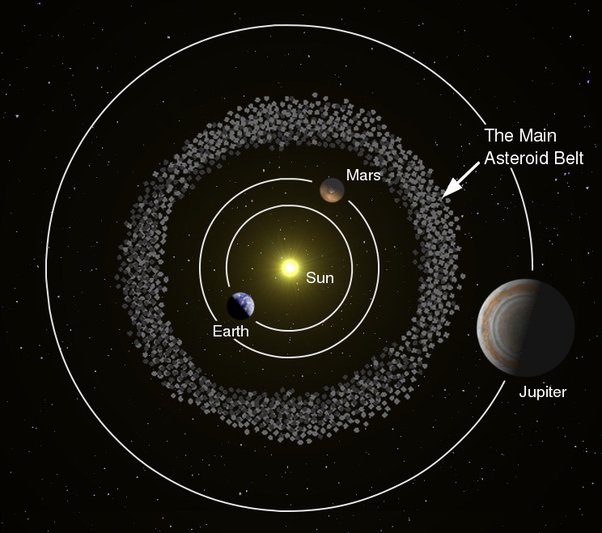
(e) Asteroids are found between the orbits of
(i) Saturn and Jupiter (ii) Mars and Jupiter (iii) The Earth and Mars
Answer: (ii) Mars and Jupiter
Explanation: Asteroids are primarily found in the asteroid belt, which is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This region is populated with numerous small rocky bodies known as asteroids.

Question 3: Fill in the blanks.
(a) A group of ________ forming various patterns is called a ________.
Answers: (a) stars, constellation
Explanation: A group of stars forming patterns is known as a constellation.
(b) A huge system of stars is called________.
Answer: (b) galaxy
Explanation: A huge system of stars, along with gas, dust, and dark matter, is called a galaxy. The Milky Way is an example of a galaxy.
(c) ________is the closest celestial body to our earth.
Answer: (c) Moon
Explanation: The Moon is the closest celestial body to Earth.
(d) ________is the third nearest planet to the sun.
Answer: (d) Earth
Explanation: Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
(e) Planets do not have their own________ and ___________________.
Answers: (e) light, heat source
Explanation: Planets do not have their own light and heat source; they receive light and heat from the Sun, which is a star.
Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
Question 1: Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) What is the true shape of the earth?
Answer: The true shape of the Earth is an oblate spheroid or geoid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. It is like the shape of orange.


(b) What is a globe?
Answer: A globe is a spherical representation of the Earth, providing a three-dimensional and accurate portrayal of its features.


(c) What is the latitudinal value of the Tropic of Cancer?
Answer: The latitudinal value of the Tropic of Cancer is approximately 23.5 degrees north.


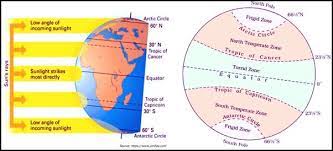
(d) What are the three heat zones of the Earth?
Answer: The three heat zones of the Earth are the Torrid Zone (tropical), the Temperate Zones (subtropical and polar), and the Frigid Zones (polar).

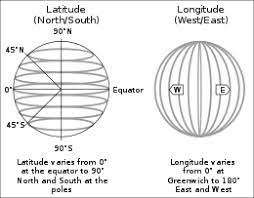
(e) What are parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude?
Answer: Parallels of latitude are imaginary lines running east-west around the Earth, measuring the distance north or south of the equator. Meridians of longitude are imaginary lines running north-south from pole to pole, measuring the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.


(f) Why does the torrid zone receive the maximum amount of heat?
Answer: The torrid zone receives the maximum amount of heat because it is situated near the equator, where the Sun’s rays are more direct throughout the year, leading to higher temperatures.
(g) Why is it 5.30 p.m. in India and 12.00 noon in London?
Answer: The time difference is due to the Earth’s rotation. India is ahead of London in time zones. As the Earth rotates from west to east, places to the east experience time ahead of locations to the west.
Question 2: Tick the correct answers.
(a) The value of the prime meridian is
(i) 90° (ii) 0° (iii) 60°
Answer: (ii) 0°
(b) The frigid zone lies near
(i) the Poles (ii) the Equator (iii) the Tropic of Cancer
Answer: (i) the Poles
(c) The total number of longitudes are
(i) 360 (ii) 180 (iii) 90
Answer: (i) 360



(d) The Antarctic circle is located in
(i) the Northern hemisphere (ii) the Southern hemisphere (iii) the Eastern hemisphere
Answer: (ii) the Southern hemisphere
(e) Grid is a network of (i) parallels of latitudes and meridians of longitudes (ii) the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn (iii) the North Pole and the South Pole
Answer: (i) parallels of latitudes and meridians of longitudes
Question 3: Fill in the blanks.
(a) The Tropic of Capricorn is located at _________________.
Answer: The Tropic of Capricorn is located at approximately 23.5 degrees south latitude.
(b) The Standard Meridian of India is ____________________.
Answer: The Standard Meridian of India is 82.5 degrees east longitude.
(c) The 0° Meridian is also known as ____________________.
Answer: The 0° Meridian is also known as the Prime Meridian.
(d) The distance between the longitudes decreases towards___________.
Answer: The distance between the longitudes decreases towards the poles.
(e) The Arctic Circle is located in the ____________ hemisphere.
Answer: The Arctic Circle is located in the Northern hemisphere.
Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth

