The fiscal deficit of India has been a topic of discussion among economists and policymakers for many years. In simple terms, fiscal deficit refers to the difference between the government’s total expenditure and its total revenue. The fiscal deficit indicates the amount of borrowing required by the government to meet its expenses. In this article, we will explore the fiscal deficit of India, its causes, and its implications.
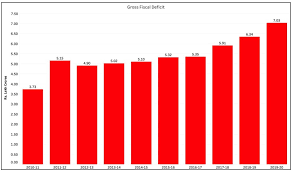
Table of Contents
Overview of Fiscal Deficit of India
The fiscal deficit of India has been a cause for concern for many years. In the financial year 2020-21, India’s fiscal deficit was estimated to be 9.5% of the country’s GDP. This was primarily due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the government’s efforts to mitigate its impact on the economy. The fiscal deficit for the financial year 2021-22 has been estimated to be 6.8% of GDP, which is still high, but lower than the previous year.
Causes of Fiscal Deficit
There are several causes of fiscal deficit in India. One of the main reasons is the government’s inability to generate sufficient revenue through taxes and other sources. India’s tax-to-GDP ratio is lower than that of other developing countries, which means that the government is not able to collect enough revenue to meet its expenses.
Another reason for the fiscal deficit is the government’s expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes. These schemes are necessary to provide support to the poor and underprivileged sections of society, but they also put a strain on the government’s finances.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to the fiscal deficit, as the government had to spend a significant amount of money on healthcare, vaccination drives, and relief measures for the affected population.
Implications of Fiscal Deficit
The fiscal deficit has several implications for the economy of India. One of the most significant consequences is the inflationary pressure it creates. When the government borrows money to finance its expenses, it increases the money supply in the economy. This, in turn, can lead to inflation, as there is more money chasing the same amount of goods and services.
Another implication of the fiscal deficit is the impact it has on interest rates. When the government borrows money, it competes with the private sector for the available funds. This can lead to an increase in interest rates, which can make it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money.
The fiscal deficit also affects the country’s credit rating, which can have a significant impact on foreign investment. A high fiscal deficit can lead to a downgrade in the country’s credit rating, which can make it more expensive for the government to borrow money from international markets.
Measures to Reduce Fiscal Deficit
There are several measures that the government can take to reduce the fiscal deficit. One of the most effective ways is to increase revenue through taxes and other sources. This can be done by broadening the tax base and reducing tax exemptions and incentives.
The government can also reduce its expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes. This can be done by targeting these schemes to the most vulnerable sections of society and reducing leakage and inefficiencies in their implementation.
Another way to reduce the fiscal deficit is to promote economic growth. When the economy grows, it generates more revenue for the government through taxes and other sources. This can be achieved by implementing structural reforms and promoting investment in infrastructure and other sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fiscal deficit of India has been a cause for concern for many years. While it has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, it is also a result of the government’s inability to generate sufficient revenue and its expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes. The fiscal deficit has several implications for the economy, including inflationary pressure, higher interest rates, and a lower credit rating. However, there are several measures that the government
Summary
- Fiscal deficit refers to the difference between the government’s total expenditure and total revenue.
- India’s fiscal deficit was 9.5% of GDP in the financial year 2020-21 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The government’s inability to generate sufficient revenue through taxes and subsidies are causes of fiscal deficit.
- The fiscal deficit creates inflationary pressure and affects interest rates and the country’s credit rating.
- Increasing revenue through taxes, targeting subsidies to the most vulnerable, and promoting economic growth can help reduce the fiscal deficit.
Questions
Q. What is fiscal deficit?
a. The difference between total expenditure and total revenue of a business
b. The difference between total expenditure and total revenue of a government
c. The difference between total revenue and total profit of a government
d. The difference between total revenue and total expenditure of a business
Answer: b. The difference between total expenditure and total revenue of a government.
Explanation: Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government’s total expenditure and total revenue.
Q. What was India’s fiscal deficit in the financial year 2020-21?
a. 6.8% of GDP
b. 9.5% of GDP
c. 3.2% of GDP
d. 5.0% of GDP
Answer: b. 9.5% of GDP.
Explanation: India’s fiscal deficit was 9.5% of GDP in the financial year 2020-21 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Q. What is one of the causes of fiscal deficit in India?
a. The government’s ability to generate sufficient revenue through taxes
b. The government’s expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes
c. Decreasing economic growth
d. Lower interest rates
Answer: b. The government’s expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes.
Explanation: One of the causes of fiscal deficit in India is the government’s expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes.
Q. What is one of the implications of fiscal deficit?
a. Lower inflationary pressure
b. Lower interest rates
c. Higher credit rating
d. Inflationary pressure
Answer: d. Inflationary pressure.
Explanation: One of the implications of fiscal deficit is inflationary pressure due to increased money supply in the economy.
Q. How can the government reduce fiscal deficit?
a. Increase revenue through taxes
b. Decrease revenue through taxes
c. Increase expenditure on subsidies and social welfare schemes
d. Decrease economic growth
Answer: a. Increase revenue through taxes.
Explanation: One way the government can reduce fiscal deficit is by increasing revenue through taxes.
Note: The other options in the MCQs are incorrect and can be eliminated based on the information provided in the article.
Important Links