Khadar and Bhangar are terms used to describe the two types of soil found in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of northern India. Khadar refers to the new alluvial soil that is deposited by the rivers during floods, while Bhangar is the older alluvial soil that is found at a higher elevation than khadar. In this article, we will discuss the characteristics of khadar and Bhangar, their importance, and how they relate to agriculture in the region.
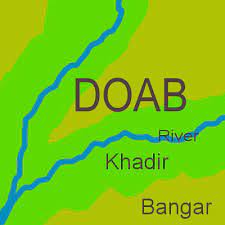
Table of Contents
Khadar Soil
Khadar soil is formed by the deposition of new alluvial material during floods. This soil is characterized by its high fertility and moisture content. It is dark in color, fine-grained, and rich in organic matter, making it highly suitable for agriculture. Khadar soil is found in the low-lying areas of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, where floods are a common occurrence. The regular flooding of the rivers helps to replenish the soil with nutrients, which makes it highly productive.
Bhangar Soil
Bhangar soil is formed by the deposition of older alluvial material. This soil is found at a higher elevation than khadar and is characterized by its relatively low fertility and high clay content. Bhangar soil is often pale in color and has a coarse texture. Due to its relatively low fertility, Bhangar soil is not as suitable for agriculture as Khadar soil. However, it is still used for growing crops in some parts of the region.
Importance of Khadar and Bhangar Soils
The Indo-Gangetic Plain is one of the most fertile agricultural regions in the world, and the presence of khadar and Bhangar soils is one of the main reasons for this. Khadar soil is highly productive and is used to grow a variety of crops, including wheat, rice, and sugarcane. Bhangar soil, on the other hand, is less fertile but is still used for growing crops such as mustard, gram, and lentils.
The fertility of khadar soil is due to its high organic matter content, which helps to retain moisture and nutrients. The regular flooding of the rivers also helps to replenish the soil with nutrients, making it highly productive. Bhangar soil, on the other hand, is less fertile due to its high clay content, which makes it less porous and less able to retain moisture and nutrients.
In Conclusion
Khadar and Bhangar are two types of soil found in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of northern India. Khadar is the new alluvial soil deposited by the rivers during floods, while Bhangar is the older alluvial soil found at a higher elevation.
Khadar soil is highly fertile and is used to grow a variety of crops, while Bhangar soil is less fertile but is still used for growing some crops. The presence of khadar and Bhangar soils is one of the main reasons for the high agricultural productivity of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
Important Links