The jute industry is one of the oldest traditional industries in India, known for producing eco-friendly and biodegradable fiber products like bags, sacks, ropes, mats, and carpets. India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods in the world. The location of the jute industry in India is heavily influenced by a set of geographical, economic, and infrastructural factors.
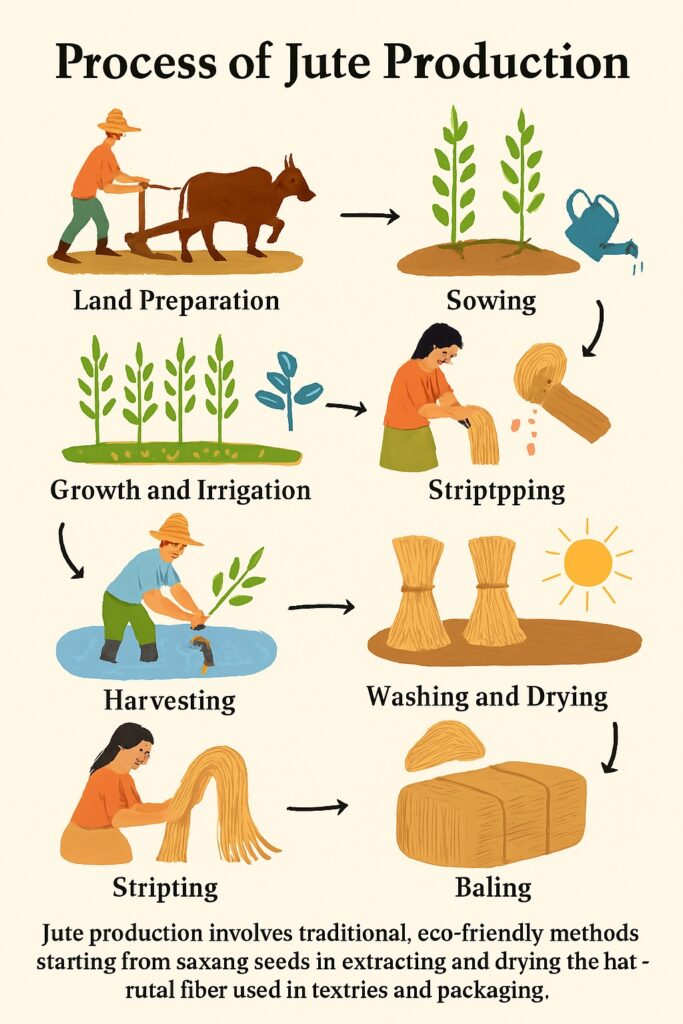
Table of Contents
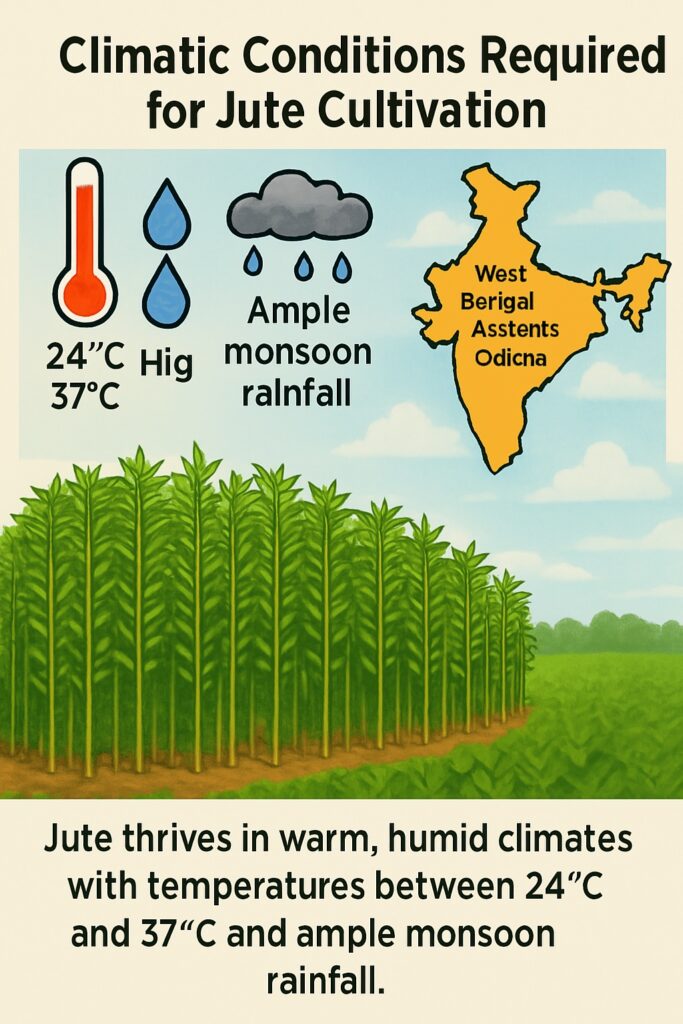
Climate
Jute is a crop that requires specific climatic conditions to grow successfully. The ideal temperature for jute cultivation is between 24 to 37 degrees Celsius. The crop also requires high humidity levels and adequate rainfall. The states of West Bengal, Bihar, and Assam in India have suitable climatic conditions for jute cultivation.
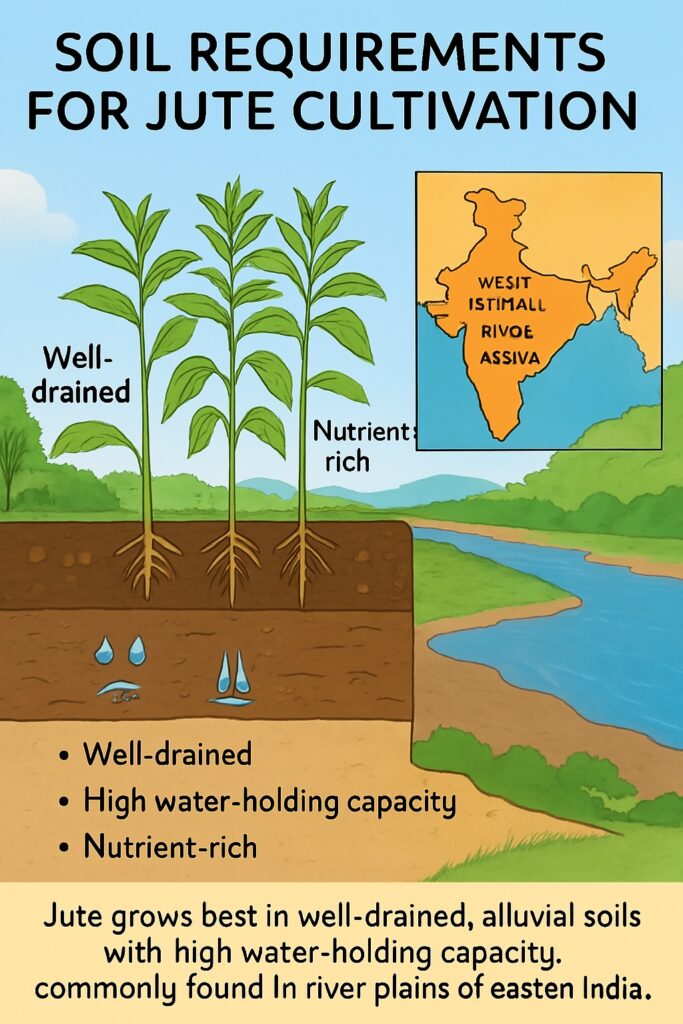
Soil
The quality of the soil is another crucial factor that determines the success of jute cultivation. Jute requires well-drained soil with a high water-holding capacity. The alluvial soil found in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta in West Bengal and Bangladesh is considered to be the most suitable for jute cultivation.
Availability of water
Jute requires a significant amount of water to grow. The availability of water, therefore, plays a critical role in jute cultivation. Regions with access to a regular supply of water are ideal for jute cultivation. The Ganges-Brahmaputra delta in West Bengal and Bangladesh has a network of rivers and canals, which provide irrigation facilities to jute cultivators.
Proximity to markets
The proximity to markets is a critical factor in the jute industry, as jute is a highly perishable commodity. Regions with easy access to markets are ideal for jute cultivation, as they ensure that the jute can be transported quickly and efficiently to the markets. The jute-growing regions of West Bengal and Bihar in India are located near major cities and towns, such as Kolkata, Delhi, and Mumbai.
Transportation
The transportation infrastructure also plays a key role in the jute industry. Regions with well-developed transportation networks, such as railways, roads, and ports, are ideal for jute cultivation. The jute-growing regions of West Bengal and Bihar in India have access to major transportation hubs, such as Kolkata port and the national highways.
In conclusion, the jute industry in India is influenced by a number of locational factors, including climate, soil, availability of water, proximity to markets, and transportation infrastructure. Understanding these factors is essential for the success and growth of jute production and trade in India.
Read: Geography Notes