Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) are some of the most marginalized and vulnerable communities in India. These are the indigenous communities who have been identified as being at the lowest rungs of the social ladder and are particularly vulnerable to exploitation and oppression. In this article, we will explore the concept of PVTGs, their status in India, and the government’s initiatives to improve their well-being.
Definition of PVTGs
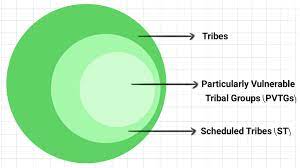
The PVTGs are communities that have been identified by the government as particularly vulnerable due to their unique cultural and social practices, their low population numbers, and their extreme poverty. The term was first introduced by the Dhebar Commission in 1960 to identify and address the problems of these communities. Today, there are 75 PVTGs identified in various states across India, with a total population of around 5 million.
Status of PVTGs in India
PVTGs are among the most vulnerable and marginalized communities in India, facing multiple forms of discrimination and exploitation. These communities often live in remote and isolated areas, with limited access to basic amenities like healthcare, education, and clean drinking water. They are also vulnerable to land grabbing, displacement, and forced assimilation.
Due to their unique cultural and social practices, PVTGs are also at risk of losing their traditional knowledge, skills, and way of life. This can have a profound impact on their sense of identity, social cohesion, and well-being.
Government Initiatives for PVTGs
The Indian government has taken several initiatives to improve the well-being of PVTGs. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs is responsible for implementing policies and programs for the welfare of these communities. Some of the key initiatives include:
- Forest Rights Act (2006): This act recognizes the traditional rights of forest-dwelling communities, including PVTGs, over forest land and resources. It seeks to address the historical injustices done to these communities and empower them to manage their own resources.
- Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana: This is a scheme launched by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs to improve the socio-economic status of tribal communities, including PVTGs. It aims to provide basic amenities like housing, water supply, and electricity to these communities, and to promote their livelihoods through skill development and employment opportunities.
- Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP): The TSP is a planning mechanism that aims to ensure that a minimum proportion of the total plan outlay of the government is earmarked for the welfare of tribal communities, including PVTGs. This ensures that these communities receive a fair share of the government’s resources and that their specific needs are addressed.
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) are some of the most marginalized and vulnerable communities in India, facing multiple forms of discrimination and exploitation. The Indian government has taken several initiatives to improve their well-being, including the Forest Rights Act, the Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana, and the Tribal Sub-Plan. However, much more needs to be done to ensure that these communities are empowered to manage their own resources, preserve their cultural heritage, and achieve their full potential. As such, the government and civil society must work together to address the challenges faced by PVTGs and promote their inclusion and empowerment in the broader society.