Flyash is a fine, powdery material that is a byproduct of burning coal in thermal power plants. When coal is burned to produce electricity, it produces a large amount of fly ash, which is carried away by the flue gases and released into the atmosphere. Fly ash contains several harmful substances, including heavy metals, such as mercury, lead, and arsenic, that can pose a threat to human health and the environment.

Thermal power plants are the primary source of fly ash pollution, as they produce a large amount of fly ash during the coal combustion process. According to estimates, India produces about 180 million tonnes of fly ash per year, with thermal power plants contributing about 80-85% of the total.
Fly ash pollution is a severe environmental problem, as it can contaminate soil, water, and air. The fine particles of fly ash can easily become airborne and travel long distances, leading to respiratory problems and other health issues. The toxic heavy metals present in fly ash can also enter the food chain and accumulate in plants and animals, leading to serious health hazards.
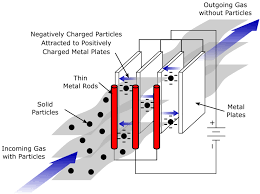
To reduce fly ash pollution, thermal power plants can adopt measures such as installing electrostatic precipitators (ESP) and bag filters to capture fly ash and reduce its emission into the atmosphere. The use of fly ash in the construction industry as a substitute for cement can also help to reduce fly ash pollution by reducing the amount of fly ash that needs to be disposed of. Additionally, the government can enforce regulations and set emission standards for thermal power plants to reduce fly ash pollution.
Important Links