Drought is a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a shortage of water. It is one of the most devastating natural disasters affecting India due to its large dependence on the monsoon system. Droughts impact agriculture, water supply, power generation, and the overall economy, especially in rural areas.

Droughts are a major natural disaster in India, affecting millions of people every year. In this article, we will explore the causes and impacts of droughts in India, and discuss some of the measures that can be taken to cope with their effects.
Table of Contents
Types of Droughts
-
Meteorological Drought: When rainfall is significantly below normal (usually 75% or less of the average).
-
Agricultural Drought: When soil moisture is insufficient to meet the needs of crops during the growing season.
-
Hydrological Drought: When water reserves in lakes, reservoirs, and aquifers fall below average.
-
Socio-economic Drought: When the drought impacts the supply and demand of economic goods, especially food and water.
Causes of Droughts in India
-
Monsoon Failure: The Indian economy heavily depends on the southwest monsoon. A delay or failure can cause widespread drought.
-
Climatic Variability: Changes in atmospheric circulation, such as El Niño, influence rainfall patterns.
-
Deforestation: Reduces rainfall and increases run-off, decreasing groundwater recharge.
-
Overexploitation of Water Resources: Excessive use of groundwater and surface water leads to scarcity during dry periods.
-
Soil Degradation: Poor agricultural practices reduce the water-holding capacity of soil.
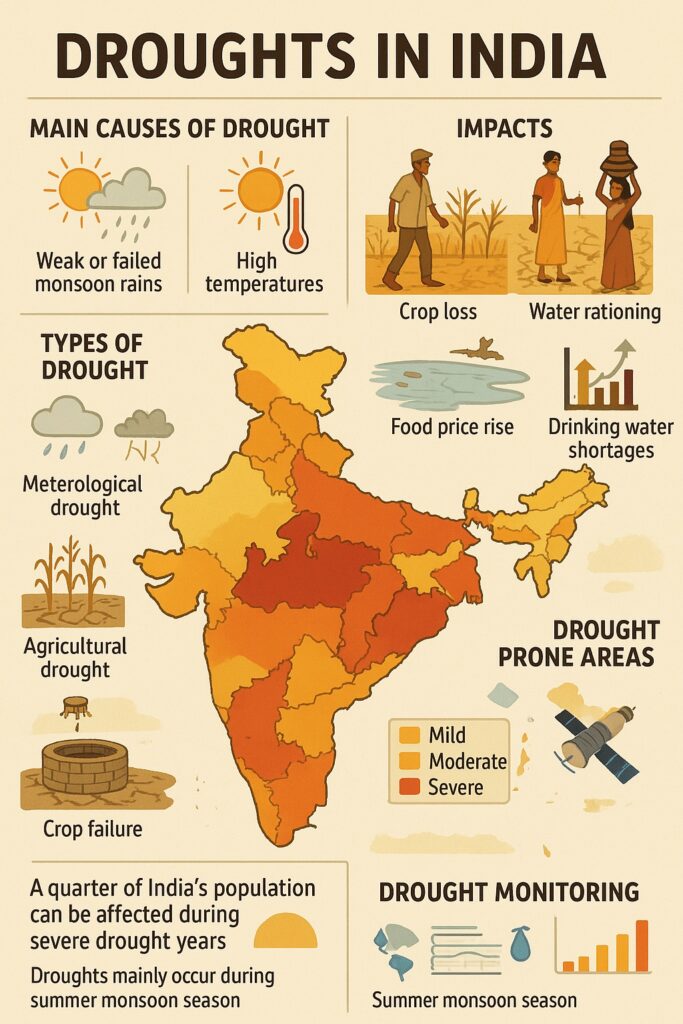
Drought-Prone Areas in India
India has about 68% of its net sown area prone to drought. The most affected regions include:
-
Western Rajasthan
-
Gujarat
-
Telangana
-
Maharashtra (Marathwada and Vidarbha)
-
Karnataka (north interior region)
-
Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh (parts)
Impact of Droughts
-
Agricultural Loss: Crop failure due to lack of water affects farmers’ income and food security.
-
Water Scarcity: Reduced availability for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use.
-
Migration: People move from rural to urban areas in search of livelihood.
-
Livestock Loss: Shortage of fodder and water affects cattle health and productivity.
-
Economic Impact: Affects GDP growth, especially in agrarian states.
-
Environmental Degradation: Loss of vegetation cover, soil erosion, and desertification.
Measures to Mitigate Droughts
Short-term Measures
-
Water Tankers and Wells: Emergency supply in affected areas.
-
Crop Insurance: Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) supports farmers.
-
Relief Employment: MGNREGA provides work during drought periods.
Long-term Measures
-
Rainwater Harvesting: To improve groundwater levels.
-
Drought-resistant Crops: Promoting millets and less water-intensive crops.
-
Watershed Management: Conserving water through natural drainage basins.
-
Irrigation Projects: Expanding drip and sprinkler systems for efficient water use.
-
Afforestation and Reforestation: Helps restore soil moisture and climate balance.
Government Initiatives
-
National Agricultural Drought Assessment and Monitoring System (NADAMS): Uses satellite data to assess drought.
-
Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP): Focuses on rain-fed areas.
-
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): Promotes climate-resilient farming.
Conclusion
Droughts in India are a recurring phenomenon with serious socio-economic consequences. With climate change increasing the frequency and intensity of such events, sustainable water management and agricultural practices are crucial. A combination of scientific planning, community participation, and effective government policies can help reduce the vulnerability of people and ecosystems to drought.
Read: Geography Notes