1. Which of the following smart cities has become India’s first city to run on 100% renewable energy during the daytime?
A. Bengaluru
B. Jaipur
C. Indore
D. Diu
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: In the year 2016 Diu became the first city in India to run entirely on solar energy during the daytime.
2. Mahmoud Abu Zeid has won the 2018 UNESCO/ Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize He hails from which country?
A. Israel
B. Iraq
C. Iran
D. Egypt
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Mahmoud Abu Zeid is an Egyptian photojournalist. He is also known as Shawkan and has been in jail since 14 August 2013 when he was arrested while covering a demonstration at Rabaa Al-Adawiya Square in Cairo. The award is named in honor of Guillermo Cano Isaza, the Colombian journalist.
3. The bilateral military exercise ‘Harimau Shakti 2018’ has been conducted between India and which country?
A. Indonesia
B. Malaysia
C. New Zealand
D. South Korea
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The bilateral military exercise ‘Harimau Shakti 2018’ has been conducted between India and Malaysia in the dense forests of Sengai Perdik, Hulu Langat, Malaysia.
4. Which Union Ministry has launched the Second Edition of the ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’?
A. The Ministry of Home Affairs
B. The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
C. The Ministry of Human Resource Development
D. The Ministry of Rural Development
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The Ministry of human resource development has launched the second edition of the Unnat Bharat Abhiyan.
Unnat Bharat Abhiyan (UBA) is a flagship program launched by the Government of India in 2014. The aim of the program is to bring about the comprehensive transformation of rural India by enabling higher education institutions to work with the people of rural India in identifying development challenges and developing appropriate solutions.
The Unnat Bharat Abhiyan is implemented through a network of participating institutions, which includes Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), National Institutes of Technology (NITs), and other premier institutions of higher education in India.
The program has a two-fold objective. Firstly, it aims to create a sustainable and inclusive development framework that addresses the development challenges of rural India. Secondly, it seeks to create a vibrant relationship between higher education institutions and rural communities, with the latter being empowered through access to knowledge and resources.
Under the Unnat Bharat Abhiyan, participating institutions are required to adopt a village or a cluster of villages and conduct a comprehensive study of the development challenges and opportunities in the area. Based on the study, the institutions are expected to develop appropriate solutions and work towards their implementation in collaboration with the local communities and stakeholders.
5. Which Union Ministry in collaboration with Google India has launched a 360 Virtual Reality (VR) video of ‘Incredible India’?
A. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
B. The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
C. The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
D. The Ministry of Tourism
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The Ministry of Tourism in collaboration with Google India has launched a 360° virtual reality (V.R.) video of “Incredible India” by video capture technology including Google s Yi Halo camera and its music is inspired by the rhythms and melodies of the concerned regions.
6. Which city hosted India’s first ever nationwide food archaeology conference ‘ArchaeoBroma’?
A. Mumbai
B. New Delhi
C. Indore
D. Surat
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Mumbai hosted India’s first-ever nationwide food archaeology conference Titled “Archaeo Broma”. It was the first Nationwide conference held in India and discussed the history, archaeology, and sociology of food. Its aim was to change the viewpoint of food with respect to its history, social attachment, and different traditions.
7. What is India’s rank in the 2018 World Press Freedom Index [WPFI]?
A. 136th
B. 138th
C. 135th
D. 137th
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: India ranked 138th in the 2018 world press freedom Index (WPFI) amongst 180 countries and was released by the France-based international non-governmental organization reporter without borders (REB) or reporters sans frontiers. (RSF). Norway was ranked 1st. 3rd March is celebrated as WPF every year.
8. Which institute has been awarded the 2018 National Intellectual Property Award in the category Top R & D Institution / Organization for Patents and Commercialization?
A. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research
B. The Indian Space Research Organization
C. The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre
D. The Defence Research and Development Organization
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: It had been ranked 9th in the world amongst the 1207 government institutions & an overall global ranking of 75 in the world.
9. Which State has topped the list of States with the most number of beggars, as per data released by the Union Ministry of Social Justice?
A. West Bengal
B. Andhra Pradesh
C. Bihar
D. Uttar Pradesh
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: West Bengal is followed by Uttar Pradesh and Bihar at number two and three respectively.
10. Which district has become India’s first district to have 100% solar-powered health centers?
A. Kolkata
B. Chennai
C. Bengaluru
D. Surat
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Surat district has become India’s first district to have 100% solar-powered primary health centers. It will help bring down the electricity bill and also help to fight global warming.
11. Which Indian sportsperson bagged Gold in the Men’s 25 m Rapid Fire Pistol Event at the 2018 ISSF Junior Shooting World Cup in Sydney?
A. Rajkanwar Singh
B. Anhad Jawanda
C. Sainath
D. Anish Bhanwala
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Anish Bhanwala bagged gold in the men’s 25 m rapid-fire pistol event at the 2018 ISSF Junior Shooting World Cup in Sydney. He belongs to Karnal Haryana and became the youngest Indian to win a gold medal in the Commonwealth game at the early age of 15 years.
12. Which State Government has signed a pact with the Airport Authority of India (AAI) to develop villages in Kamrup?
A. West Bengal
B. Mizoram
C. Nagaland
D. Assam
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Assam has signed a pact with the Airport Authority of India [AAI] to develop villages in Kamrup. AAI would provide financial assistance under its CSR initiative.
13. Which State has the highest number of fully covered tribal habitations with safe drinking water?
A. Madhya Pradesh
B. Odisha
C. Rajasthan
D. Jharkhand
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Madhya Pradesh has the highest number of fully covered tribal habitations with safe drinking water with 55770 numbers of habitations, followed by Odisha (52427), and Jharkhand (53476).
14. ISRO has successfully launched GSAT– 6A satellite from which rocket vehicle?
A. GSLV – F07
B. GSLV – F09
C. GSLV – F05
D. GSLV – F08
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: ISRO successfully launched GSAT-6A geosynchronous satellite from GSLV- F08 on March 29, 2018, carrying an indigenously developed cryogenic upper stage.
15. What is the theme of the 2018 International Day of Forests?
A. Forests and Water
B. Forests and Energy
C. Forests and Sustainable Cities
D. Forests and Life
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: “Forests and Sustainable Cities” is the theme of 2018 the international day of Forest (IDF). The UN General Assembly proclaimed 21st March the International Day of Forest in 2012. The day celebrates and raises awareness of the importance of all types of forests.
16. Who has been elected as a new President of Egypt?
A. Moussa Mostafa Moussa
B. El-Sayyid el-Badawi
C. Abdel Fattah el-Sisi
D. Ahmed ShafiqSisi
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, an Egyptian military officer elected as the new President of Egypt. Abdel Fattah al-Sisi became Egypt’s de facto leader in July 2013, after the country’s military, removed President Mohammed Morsi from power following mass protests against his rule. Abdel Fattah el-Sisi was elected president in May 2014 and reelected to a second term in March 2018.
17. Who has been chosen for the prestigious J.C. Daniel Award for 2017?
A. Sathyan Anthikkad
B. K.G.Geogre
C. SreekumaranThampi
D. Adoor Gopalakrishnan
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Shreekumaran Thampi has been chosen for the prestigious J. C Daniel Award for 2017. The J.C Daniel Award is Kerala’s highest award in Malayalam cinema by the Kerala state.
18. According to recent data released by Indian Cellular Association [ICA], India acquired what position in the world in producing mobile phones?
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Fourth
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: According to data shared by ICA, the annual production of mobile phones in India has increased from 3 million units in 2014 to 11 million units in 2017. India replaced Vietnam to become the second-largest producer of mobile phones in 2017.
19. Which State Government has rolled out ‘Rupashree Scheme ‘ for the marriage of poor girls?
A. Tamil Nadu
B. Odisha
C. West Bengal
D. Assam
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: West Bengal has rolled out the ‘Rupashree Scheme’ for the marriage of poor girls started on the 1st of April 2018. It is a West Bengal state government initiative that provides a one-time financial grant of Rs. 25,000 and a scholarship of Rs.500 for economically stressed families at the time of their adult daughters’ marriages until they attain 18.
20. NITI Aayog has launched the ‘Atal New India Challenge’ that will provide grants of up to how much amount to innovative products and solutions?
A. Rs.2 crore
B. Rs.1 crore
C. Rs.1.5 crore
D. Rs.2.5 crore
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: NITI Aayog has launched the ‘Atal New India Challenge’ that will provide grants of up to Rs.1 crore. Atal New India Challenge is an initiative by the Atal Innovation Mission aimed at supporting innovators to create products/solutions based on advanced technologies in areas of national importance and social relevance through a grant-based mechanism.
21. Who chaired the first meeting of the think tank on the Framework for National Policy on E-commerce?
A. Narendra Modi
B. Arun Jaitley
C. Suresh Prabhu
D. Smriti Irani
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Suresh Prabhu chaired the first meeting of the think tank on the Framework for National Policy on E-commerce. An e-commerce framework refers to the type of software you’re using to build your e-commerce store. The IT Act 2000 is the sole cyber law in India that also governs, to some extent, the online issues of e-commerce in India.
22. Which of the following districts of Bihar does not share a border with Nepal?
A. Madhubani
B. Kishanganj
C. Sitamarhi
D. Purnia
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Following districts touch the boundary of Nepal in Bihar.
- West Champaran
- East Champaran
- Sithamarhi
- Madhubani
- Supaul
- ArariaKishanganj
23. Which of the following is the only UNESCO World Heritage Site present in Bihar State India?
A. Mahabodhi Vihar
B. Buddhist Monastery Nalanda
C. Ancient site of Vikramasila Monastery
D. Tomb of Sher Shah Sur
E. None of the above/More than one
Answer: E
Solution: Bihar has several UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex, Bodh Gaya: The Mahabodhi Temple Complex in Bodh Gaya is one of the most important Buddhist pilgrimage sites in the world. It is where Gautama Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment under the Bodhi tree.
- Nalanda Mahavihara: The Nalanda Mahavihara was a renowned Buddhist university in ancient India. It is located in the present-day district of Nalanda and was a center of learning from the 5th century CE to the 12th century CE.
- Vikramshila Mahavihara: The Vikramshila Mahavihara was another important Buddhist university in ancient India. It is located in the present-day district of Bhagalpur and was established in the 8th century CE.
- Archaeological Site of the Ancient Vikramshila University: This site includes the remains of the Vikramshila Mahavihara and surrounding areas.
- The Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area (partly in Bihar): This national park is located in the western part of the Himalayan Mountains and is known for its diverse flora and fauna.
24. The Union Cabinet has approved MoU between India and SACEP for cooperation on oil chemical pollution in the South Asian Sea region. What does SACEP stand for?
A. South Asia Compatibility Environment Programme
B. South Asia Cooperation Environment Programme
C. South Asia Connective Environment Programme
D. South Asia Coercive Environment Programme
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: SACEP Stands for South Asia Cooperation Environment Programme. The South Asia Co-operation Environment Programme, also known as SACEP was signed in 1982 by the governments of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka to enhance the environmental conditions in the South Asian region.
25. Which State Government has recently signed MoU with South Korea to enhance tourism cooperation?
A. Kerala
B. Mizoram
C. Tamil Nadu
D. Uttar Pradesh
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Uttar Pradesh has recently signed MoU with South Korea to enhance tourism cooperation. An agreement was signed in 2000 to develop Ayodhya and Gimhae as sister cities, following which a memorial was constructed in Ayodhya which is visited by a large number of tourists from South Korea every year.
26. The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education [ICFRE] has signed MoU with a TIFAC for supporting forest-based communities. Where is the headquarters of ICFRE located?
A. Hyderabad
B. Bengaluru
C. Allahabad
D. Dehradun
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Dehradun is the headquarters of the Indian Council of forestry research and Education (ICFRE). It is an autonomous organization or governmental agency under the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India. Its functions are to conduct forestry research, Transfer the technologies developed to the states of India and other user agencies, and impart forestry education.
27. Which of the following teams has won the Newton- Bhabha Fund for the project on Groundwater Atomic Research in Ganga River Basin?
A. India – Russia Joint Team
B. India – UK Joint Team
C. India – Japan Joint Team
D. India – Israel Joint Team
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: India – UK joint team, has won the Newton Bhabha fund for the project on groundwater arsenic research in the Ganga river basin.
28. The Barh Super Thermal Power Station [BSTPS] is located in which State?
A. Bihar
B. Karnataka
C. Rajasthan
D. Punjab
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: The Barh Super Thermal Power Station [BSTPS] is located in Bihar. Atal Bihari Vajpayee laid the foundation stone of the main plant of stage-1 of NTPC Barh in 1999. The 1,320 MW (2 x 660 MW) Barh Stage-2 built by BHEL is operational while the 1,980 MW (3 x 660 MW) Barh Stage-1 is being built by Russian firm Technopromexport (TPE).
29. The International Solar Alliance [ISA] has recently signed a pact with which international organizations to promote solar deployment in Asia and the Pacific.
A. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
B. New Development Bank
C. African Development Bank
D. Asian Development Bank
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The International Solar Alliance [ISA] has recently signed a pact with Asian Development Bank to promote solar energy in Asia and the Pacific. ADB’s ( Asian Development Bank ) headquarters is in Manila. Its main aim is to reduce poverty in Asia and the Pacific region.
30. India has signed a tripartite MoU with which countries civil nuclear cooperation?
A. USA and Nepal
B. Japan and Myanmar
C. Russia and Bangladesh
D. Germany and Sri Lanka
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: India has signed a tripartite MoU with Russia and Bangladesh for civil nuclear cooperation in the construction of the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant in Bangladesh. Nuclear Power Cooperation of India Limited (NPCIL) will play a key role in building a nuclear power plant on foreign soil with the proposed supply of equipment and material for the power station being built by Russia in Bangladesh. India is also extending support for capacity building and has been training Bangladeshi nuclear scientists for the project.
31. What is the most significant feature of the Indus Valley Civilization?
A. Burnt brick buildings
B. First true arches
C. Buildings of worship
D. Art and architecture
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Burnt brick buildings are the most significant feature of the Indian Valley civilization. Most of the houses in the Indus Valley civilization were made of Burnt bricks. The main features of town planning were the use of baked as well as sundried bricks, well-planned straight roads, and a system of drainage. Harappa Mohanjodaro, Lothal, and Dholavira are some Indus Valley sites famous for burnt brick buildings.

32. Megasthenes was the ambassador of
A. Seleucus
B. Alexander
C. Darius
D. The Greeks
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Megasthenes was the ambassador of Seleucus, the contemporary of Chandragupta Maurya, and wrote Indica which contains information about Indian society and culture.

33. Kautilya’s Arthashastra is a book on
A. Economic Relations
B. Principles and practice of Statecraft
C. Religious System
D. Wealth Accumulation
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: It is an ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, economic policy, and military strategy. Kautilya was the Prime minister in the court of Chandragupta Maurya.
34. Tripitakas are the sacred books of the:
A. Jains
B. Hindus
C. Parsees
D. Buddhists
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Tripitaka or Three Baskets is a traditional term used for various Buddhist scriptures. It is known as Pali Canon in English. The three pitakas are Sutta Pitaka, Vinaya Pitaka and Abhidhamma Pitaka.
35. The central point in Ashoka’s Dhamma is
A. Loyalty to the king
B. Peace and non-violence
C. Respects for elders
D. Religious toleration
E. None of the above/More than one
Answer: E
Solution: The Ashoka’s Dhamma (a Prakrit form of the Sanskrit word dharma) is a set of edicts that formed a policy of the Mauryan emperor Ashoka was not only the philosophical teaching of Buddha, but it contains the idea of humanism, the universal brotherhood and Ahimsa on pillar edicts. Dhamma Mahamatra was appointed to check out law and order in his kingdom.
36. The division of Maurya society into seven classes is particularly mentioned in
A. Kautilya’s Arthashastra
B. Ashokan edicts
C. The Puranas
D. The Indica of Megasthenes
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The division of Maurya society into seven classes particularly mentioned in the Indica of Megasthenes an ambassador of Seleucus who visited India in the time of Chandragupta Maurya.
The seven classes were 1. Brahmins 2. Farmers 3. Herdsmen 4. Artisans and Shopkeepers 5. Soldiers 6. Over-seers 7. seventh class was those who deliberate about public affairs with the king.
37. The famous Chinese pilgrim Fa-Hien visited India during the reign of
A. Chandragupta I
B. Chandragupta II
C. Ramagupta
D. Srigupta
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The famous Chinese pilgrim Fa-Hien visited India during the reign of Chandragupta II. Chandragupta II was also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya. Fa-Hein was the first traveler who visited India from China. He studied the Sanskrit language for about three years in Patliputra. He has written a book ‘Record of the Buddhistic Kingdoms’.
38. The Chola age was most famous for
A. Village assemblies
B. War with the Rashtrakutas
C. Trade with Ceylon
D. Advancement of Tribal culture
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: The Chola Age was famous for village assemblies. The most important feature of the Chola administration was the local administration at the districts, towns, and villages level. Uttaramerur inscriptions speak much about the Chola administration.
Village autonomy was the most unique feature of the Chola administrative system. They had a very strong naval base. Rajendra Chola 1 conquered northern India along the Ganga valley and built a new capital called “Gangaikonda Cholapuram”.
39. The mighty gateways found at the temples of South India are called?
A. Shikhars
B. Gopurams
C. Devalayas
D. Mandaps
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The mighty gateways found at the temples of the south Indian called Gopurams, huge size gates at the entrance of the south Indian temples. A gopuram or gopura is a monumental entrance tower, usually ornate, at the entrance of a Hindu temple, in the Tamil architecture of the Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, and Telangana states of Southern India.
40. The remains of the Vijayanagara Empire are found in:
A. Bijapur
B. Golconda
C. Hampi
D. Baroda
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Hampi is a very famous site for the remains of the Vijayanagara Empire. Hampi is located in Karnataka. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty.
41. Who was the first Muslim ruler to formulate the ‘theory of kingship’ similar to the ‘theory of the divine right of the kings’?
A. Aibak
B. Iltutmish
C. Balban
D. Alauddin
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The Theory of Kingship was formulated by Ghiyas-ud-din-Balban. He was the ninth sultan of the Mamluk Dynasty and he ruled from 1266 to 1287. The main principle was that the king was the representative of God on the earth and kingship is the divine institution. He was also famous for his policy on blood and iron.
42. The paper came to be used in the:
A. 12th century
B. 13th century
C. 14th century
D. 15th century
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Paper came to be used in India in the 12th century. The first papermaking process was seen in China during the Eastern Han period (25-220 AD).
43. European Paintings were introduced in the court of?
A. Humayun
B. Akbar
C. Jahangir
D. Shah Jahan
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Under European painting was introduced at the court of Akbar by the Portuguese priests. Under their influence, the principles of foreshortening, whereby near and distant people and things could be placed in perspective were very frequently adopted.
44. Who was the ruler of India when the English East India Company was formed?
A. Aurangzeb
B. Akbar
C. Jahangir
D. Humayun
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Akbar from 1556- 1605 was the ruler of India. The Company received a Royal Charters from Queen Elizabeth-I on 31 December 1600.
45. Which of the following Princely States was not annexed by the British?
A. Sind
B. Gwalior
C. Awadh
D. Satara
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Satara, Nagpur, and Sambalpur were the three princely states among the others to be annexed by the British reign through the policy of the Doctrine of Lapse under the pretext of not having an heir. The doctrine of lapse was given by Lord Dalhousie.
46. What was the ultimate goal of Gandhiji’s Salt Satyagraha?
A. Repeal of Salt laws
B. Curtailment of the government’s power
C. Economic relief to the common people
D. ‘PurnaSwaraj’ for India
E. None of the above/More than one
Answer: E
Solution: The Salt Satyagraha was a nonviolent civil disobedience campaign that aimed to force the British to repeal salt laws and recognize India’s right to produce and sell its own salt without being taxed by the British government. The campaign culminated in the famous Salt March, which drew international attention to India’s struggle for independence and ultimately led to the repeal of the Salt Laws in 1931.
Salt march is also known as a Dandi march. Gandhi Ji started the salt march from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi with 78 volunteers. This march had another goal of economic relief for coastal people.
47. The Moplah Rebellion of 1921 broke out in:
A. Assam
B. Kerala
C. Punjab
D. Bengal
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The Moplah rebellion of 1921 broke out in Kerala against the British and the Hindu landlords in Malabar (Northern Kerala). It was an armed revolt. It was led by Variyamkunnath Kunjahammed Haji.
48. The Swadeshi Movement took place in India during:
A. the Champaran Satyagraha of Gandhiji
B. the Anti-Bengal Partition agitation
C. the Protest against the Rowlatt Act
D. the Non-Cooperation Movement
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The Swadeshi movement took place in India during the anti-Bengal partition agitation. It was one of the most successful pre-Gandhian movements. It started after the partition of Bengal in 1905 by Lord Curzon. The main leaders were Arbindo Ghosh, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, etc. The Swadeshi Movement, now known as the ‘Make in India’ campaign was officially proclaimed on August 7, 1905, at the Calcutta Town Hall, in Bengal.
49. Bihar Provincial Kisan Sabha formed in:
A. 1929
B. 1930
C. 1931
D. 1932
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Bihar Provincial Kisan Sabha was formed in 1929 by Sahjanand Saraswati to mobilize peasant grievances against the Zamindari attacks on their occupancy right and thus sparking the farmer’s movement in India.
50. By which Act, Bihar became a separate province?
A. The Government of India Act of 1935
B. The Government of India Act of 1919
C. The Indian Councils of 1909
D. The Indian Independence Act of 1947
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Bihar became a separate province by the Government of India Act 1935. Before this Bihar, Orissa, and Bengal were one province and Orissa become a separate state in 1936.
51. Which one of the following Committees / Commissions recommended the creation of Nyaya Panchayats?
A. Balwant Rai Mehta Committee
B. Ashok Mehta Committee
C. G.V.K. Rao Committee
D. Sarkaria Commission
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Ashok Mehta Committee recommended the creation of Nyaya Panchayats in December 1977. This committee recommended that the three-tier system of the Panchayati Raj should be replaced by the two-tier system. For the demarcation of the exact jurisdiction of such Nyaya Panchayats, an officer in charge is appointed who in most cases is the Collector. A Nyaya Panchayat is empowered with both civil and criminal jurisdiction.
52. Which one of the following functions is not the concern of Local Self- Government?
A. Public Health
B. Sanitation
C. Public Utility Services
D. Maintenance of Public Order
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The Maintenance of Public Order is not the concern of Local- self Government (panchayat, municipality, etc). It has been mentioned in the state list under Schedule 7 of the constitution, so, it’s a concern of state governments.
Local self-government bodies are responsible for school and preschool education, primary healthcare (outpatient clinics, rural health posts), cultural institutions, amenities – street lighting, roads, cleaning, public order, and many other important day-to-day issues.
53. The system of Panchayati Raj is mentioned in –
A. The Union List
B. The State List
C. The Concurrent List
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The system of Panchayati Raj is mentioned in the state list under the 7th schedule of the Indian constitution. Article 246 defines three lists, state list union list & concurrent list.
54. 50% reservation for women Panchayati Raj Institutions is legalised in certain States such as
I. Bihar,
II. Uttarakhand,
III. Madhya Pradesh,
IV. Himachal Pradesh
A. Only III
B. Only II and III
C. II, III, and IV
D. I, II, III, and IV
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: 50% reservation for women Panchayati Raj institution is legalized in all four states.
55. Money Bill can be presented
A. Only in the Lok Sabha
B. Only in the Rajya Sabha
C. In both the Houses
D. In a joint meeting of both the Houses
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: A Bill may be introduced in either House of Parliament. However, a Money Bill can not be introduced in Rajya Sabha. Article 110 of the constitution talks about the money bill.
If any question arises about whether a bill is a money bill or not, the decision of the speaker of Lok Sabha shall be final. Rajya Sabha is required to return a Money Bill passed and transmitted by Lok Sabha within a period of 14 days from the date of its receipt.
Rajya Sabha may return a Money Bill transmitted to it with or without recommendations. It is open to Lok Sabha to accept or reject all or any of the recommendations of Rajya Sabha. However, if Rajya Sabha does not return a Money Bill within the prescribed period of 14 days, the Bill is deemed to have been passed by both Houses of Parliament at the expiry of the said period of 14 days in the form in which it was passed by Lok Sabha.
56. What is the nature of the Indian Constitution?
A. Federal
B. Unitary
C. Parliamentary
D. Federal in nature but unitary in spirit
E. None of the above
Answer : D
Solution: Constitutions are either unitary or federal. In the unitary government, the powers of the government are centralized in the central government & the states are subordinate to the center. In the federal constitution, there is a division of power between the states & the central government & both are independent in their own spheres.
57. Who appoints the Judges of the Supreme Court of India?
A. The Prime Minister
B. The President
C. The Chief Justice of India
D. The Ombudsman
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The Chief Justice of India and the Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President under Article 124 of the Constitution.
58. Who is the Ex Officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha?
A. The President
B. The Vice President
C. The Prime Minister
D. None of the above
E. More than one of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The vice president is the Ex-officio chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Article 63 of the Indian constitution states there shall be a vice president of India. He performs the duty of the president when the president is not present.
59. The Prime Minister of India is responsible to whom?
A. The Cabinet
B. The President
C. The Lok Sabha
D. The Rajya Sabha
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The Prime Minister of India is responsible to the Lok Sabha. Article 75 of the constitution of India says that the P.M. being the head of the council of ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
60. What is the minimum age for a Member of the Parliament?
A. 18 years
B. 21 years
C. 25 years
D. 30 years
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Important Age Limits in the Indian Constitution.
| Post | Minimum Age | Maximum Age |
|---|---|---|
| President | 35 years | None |
| Vice-President | 35 years | None |
| Governor | 35 years | None |
| MP (Lok Sabha) | 25 years | None |
| MLA | 25 years | None |
| MP (Rajya Sabha) | 30 years | None |
| MLC | 30 years | None |
| Supreme Court Judge | None | 65 years |
| High Court Judge | None | 62 years |
| Member of Union Commission | None | 65 years |
| Member of State Commission | None | 62 years |
| Member of Panchayat | 21 years | None |
| Member of Municipality | 21 years | None |
61. What is the retirement age of the Judges of the Supreme Court?
A. 60 years
B. 62 years
C. 65 years
D. 70 years
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The retirement age of the judges of the supreme court is 65 years, and for the judges of the High Court, it is 62 years.
62. Who is the highest Civil Service Office of the Central Government?
A. The Attorney General of India
B. The Cabinet Secretary
C. The Home Secretary
D. The Finance Secretary
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The highest Civil Service Office of the Central Government is the cabinet secretary. The highest post in the state is that of the chief secretary. The cabinet secretary is under the direct charge of the prime minister. They are ex-officio Chairman of the Civil Services Board; the chief of the Indian Administrative Service and head of all civil services under the rules of business of the Government of India.
63. One of the problems in calculating National Income of India is:
A. Underemployment
B. Inflation
C. Low level of savings
D. Non-organized sector
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: One of the problems in calculating the National Income in India is the non-organized sector. Six major difficulties faced in the measurement of national income are as follows: 1. problems of definition, 2. lack of adequate data, 3. non-availability of reliable information, 4. choice of method, 5. lack of differentiation in economic functioning, 6. double counting.
64. The apex bank for providing agricultural refinance in India
A. RBI
B. NABARD
C. SBI
D. Imperial Bank
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The apex bank for providing agricultural refinance in India is NABARD. NABARD came into existence on 12 July 1982 by transferring the agricultural credit functions of RBI and refinance functions of the then Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC). It is an apex regulatory body for the overall regulation of regional rural banks and apex cooperative banks in India. It is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance.
65. According to the 14th Finance Commission, the Percent share of States in the proceeds of the share central tax revenue should be:
A. 32 Percent
B. 35 Percent
C. 40 Percent
D. 42 Percent
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: According to the 14th Finance Commission, the Percent share of States in the proceeds of the share central tax revenue should be 42 Percent. The 14th Finance Commission was constituted in January 2014.
66. Which sector in India attracts the highest FDI equity flow?
A. Construction Sector
B. Energy Sector
C. Automobile Sector
D. Service Sector
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The service Sector attracted the highest percentage of FDI equity flow.
67. Who amongst the following is the present Governor of the RBI?
A. Bimal Jalan
B. Arvind Subramanian
C. Raghuram Rajan
D. Urjit Patel
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Urjit R Patel was the current governor of the RBI While Raghuram G Rajan was the predecessor of Patel.
68. The size of the marginal landholding in India is:
A. More than 5 hectares
B. 2 hectares to 4 hectares
C. 1 hectare to 2 hectares
D. Less than 1 hectare
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The Indian Government classifies land holdings into five groups: Marginal ( less than one hectare) Small (1-2 hectares) Semi-medium (2-4 hectares), Medium(4-10 hectares), Large(greater than 10 hectares).
69. Globalization does not include
A. Reduction in import duties
B. Abolition of import licensing
C. Free flow of FDI
D. Disinvestment of Public Sector Equity
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Globalisation doesn’t include the dis-investment of public sector equity. It is the sole decision of the domestic government to disinvest or nationalize.
70. The Prevention of Laundering Act came into India during the year:
A. 1998
B. 1999
C. 2001
D. 2005
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) came into force in India in 2005 to prevent money laundering and confiscation of property derived from money laundering.
71. TRIMS stands for
A. Trade-Related Income Measures
B. Trade-Related Incentive Measures
C. Trade-Related Investment Measures
D. Trade-Related Innovative Measures
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: TRIMS stands for Trade-Related Investment Measures. This Agreement, negotiated during the Uruguay Round, applies only to recognize that certain investment measures can restrict and distort trade. It states that WTO members may not apply any measure that discriminates against foreign products or that leads to quantitative restrictions, both of which violate basic WTO principles.
72. NITI Aayog came into existence on
A. 1st January 2014
B. 1st June 2014
C. 1st January 2015
D. 1st June 2015
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: National Institution for Transforming India, better known as NITI Aayog, was formed via a resolution of the Union Cabinet on 1 January 2015. NITI Aayog is the premier policy think tank of the Government of India, providing directional and policy inputs.
73. ‘Gullak Bachcha Bank’ is a bank based in:
A. Delhi
B. Patna
C. Bhopal
D. Jaipur
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The ‘Gullak Bacchcha Bank’ is based in Patna. Children can deposit up to a minimum of 1 rupee in the bank. There are about 3800 accounts in this bank.
74. The base year for Wholesale Price Index [WPI] has been changed by the Government of India from 2004-05 to
A. 2010-11
B. 2011-12
C. 2012-13
D. 2013-14
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The base year for All-India Whole Sale Price Index (WPI) in India has been changed by GOI from 2004-05 to 2011-12. In India, the Office of Economic Advisor (OEA), the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry calculate the WPI.
The index basket of the present 2011-12 series has a total of 697 items including 117 items for Primary articles, 16 items for Fuel & Power, and 564 items for Manufactured Products.
75. According to Indian Population Census, 2011, the percentage of literacy among males and females is lowest for the State of
A. Arunachal Pradesh
B. Andhra Pradesh
C. Bihar
D. Jammu and Kashmir
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: According to the Indian population census of 2011 the lowest literacy among males and females is in Bihar (61.82%) i.e Males (71.8%) and females (51.5%). Kerala has the highest percentage of literacy (93.74%).
76. The average size of landholdings in Bihar in comparison with other States is:
A. Lowest
B. Second lowest
C. Highest
D. Second highest
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The average size of landholdings in Bihar in comparison with other States is second lowest The average size of operational holdings is highest in Nagaland (5 hectares) and lowest in Kerala (0.18 hectares).
77. The latest per capita income at current prices is the lowest for the Indian State of:
A. Bihar
B. Uttar Pradesh
C. Odisha
D. Nagaland
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: The latest per capita income at current prices is the lowest for the Indian State of Bihar while it is highest for Goa. The per capita income measures the average income earned per person in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area’s total income by its total population. Data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), says that Bihar has the lowest NSDP per capita (INR at Current prices)Rs. 43,822 in FY 2018-19.
78. The latest annual per capita consumption of electricity in Bihar is:
A. Lowest
B. Second lowest
C. Highest
D. Second highest
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: The latest annual per capita consumption of electricity in Bihar is the lowest. It is 85% lower than the average Indian consumption. Goa has the highest per capita consumption of electricity. The per capita consumption of electricity in Bihar from 145 units in 2012-13 has now increased three times to more than 400 units.
79. The average yield of cotton is highest in India for the State of:
A. West Bengal
B. Bihar
C. Assam
D. Andhra Pradesh
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The average yield of cotton is the highest in India for the state of Andhra Pradesh 686kg/Hectare in 2017-18.
80. The road length per lakh of population in Bihar is:
A. Lowest
B. Second lowest
C. Highest
D. Second highest
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The road length per lakh of the population in Bihar is the second lowest. Road lengths per lakh population are the road density. It is highest for Arunachal Pradesh and lowest for Jammu & Kashmir due to hilly regions and disturbances caused by terrorism.
81. During 10000 BC, the population of the world was
A. 2 million
B. 3 million
C. 4 million
D. 5 million
E. None of the above
Answer: E
Solution: Estimates of the population of the world at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. The time taken by the earth to reach its 1st billion population was around 50,000 years, duration was around 1830 C.E. In the current time the human population is estimated to have reached 7.6 billion. It took only 200 years to reach 7 billion from 1 billion.
82. Cocos Plate lies between:
A. Central America and Pacific Plate
B. South America and Pacific Plate
C. Red Sea and Persian Gulf
D. Asiatic Plate and Pacific Plate
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Cocos plates lie between Central America and Pacific Plate. The worldwide famous Coco Island is rested upon it.
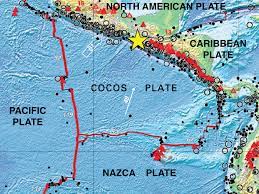
83. ‘Rust Bowl’ of the USA is associated with which one of the following regions?
A. Great Lakes region
B. Alabama region
C. California region
D. Pittsburg region
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The Pittsburg region of the USA is associated with the Rust Bowl of the USA. While a rust bowl can occur anywhere globally, it is most commonly used to refer to the U.S. Northeast and Midwest, which were previously dominant in automobile and steel manufacturing.
It is also known as the ‘Rust Belt’. The steel city of Pittsburgh has a sufficient number of industries located in this region.
84. Which one of the following approaches is associated with Prof. Amartya Sen?
A. Basic Needs Approach
B. Capability Approach
C. Income Approach
D. Welfare Approach
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The capability approach is associated with Prof. Amartya Sen in the measurement of absolute poverty in developing countries. It is an economic theory conceived in the 1980s as an alternative approach to welfare economics. The core focus of the capability approach is on what individuals can do (i.e., capable of ).
A. Basic Needs Approach is a development approach that focuses on fulfilling the basic needs of people, such as food, water, shelter, healthcare, and education. This approach is based on the idea that people have certain fundamental needs that must be met before they can pursue other goals or participate in society.
B. Capability Approach is a development approach that emphasizes the importance of individual freedom and capability. This approach recognizes that people have different abilities, resources, and opportunities, and that development should be about expanding the range of choices and opportunities available to individuals so that they can lead lives that they value.
C. Income Approach is an economic approach that focuses on the role of income and economic growth in development. This approach suggests that economic growth and increasing incomes are essential for development, as they create opportunities for investment, job creation, and poverty reduction.
D. Welfare Approach is an approach that aims to improve the well-being of individuals and communities. This approach can take many different forms, including social welfare programs, community development initiatives, and public health interventions. The focus is on improving people’s overall welfare and quality of life.
85. Which one of the following is known as the ‘Coffee Port’ of the world?
A. Sao Paulo
B. Santos
C. Rio de Janerio
D. Buenos Aires
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: “Santos” is known as the ‘Coffee Port’ of the world and is the outer port of Sao Paulo in Brazil which is the world’s largest producer of coffee.
86. Which one of the following States has the highest percentage of area under forests?
A. Himachal Pradesh
B. Assam
C. Andhra Pradesh
D. Arunachal Pradesh
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution:
• Largest forest cover in India: Madhya Pradesh > Arunachal Pradesh > Chhattisgarh > Odisha > Maharashtra
• Forest cover as a percentage of total geographical area: Mizoram (85.41%) > Arunachal Pradesh (79.63%) > Meghalaya (76.33%) > Manipur (75.46%) > Nagaland (75.31%).
87. Which one of the following soils is deposited by rivers?
A. Red Soil
B. Black Soil
C. Alluvial Soil
D. Laterite Soil
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Alluvial soil is deposited by the rivers. It is the most fertile soil dominated by the Northern plain of India.
88. What is the share of hydroelectric power in the total electricity produced in India?
A. 10 percent
B. 12 percent
C. 20 percent
D. 22 percent
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The share of hydroelectric power in the total electricity produced in India is 22 percent. The hydropower project at Siang at Arunachal Pradesh will alone generate between 10,000 and 12,000 MW, of hydroelectricity once it is completed and it will be the largest hydroelectric dam in South Asia.
89. Which Census year is called the ‘Demographic Divide’ in the population study of India?
A. 1911
B. 1921
C. 1931
D. 1941
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The year 1921 is known as the Demographic Divide in India because before this year, the population was not constant, sometimes it increased and at other times it decreased. After 1921, we can see a continuous increase in the population.
90. The largest number of cotton mills in Tamil Nadu are found in:
A. Chennai
B. Coimbatore
C. Madurai
D. Salem
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The largest number of cotton mills in Tamil Nadu are found in Coimbatore. Coimbatore is often referred to as the Manchester of South India due to its cotton production and textile industries.’
91. Which one of the following States is the leading producer of rubber in India?
A. Tamil Nadu
B. Kerala
C. Karnataka
D. Andhra Pradesh
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Kerala is the leading producer of rubber in India. Almost 90% of the rubber produces in Kerala alone. This crop was brought to India during British rule.
92. National Waterway 1 connects:
A. Kottapuram to Kollam
B. Sadiya to Dhubri
C. Haldia to Allahabad
D. Haldia to Kolkata
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: National Waterway 1 runs from Prayagraj in Uttar Pradesh to Haldia in West Bengal via Patna and Bhagalpur in Bihar across the Ganges River. It runs across the Ganges, Bhagirathi, and Hoogli river systems. It is the longest waterway in India (1,620km).
93. Khetri Belt of Rajasthan State is famous for:
A. Copper mining
B. Gold Mining
C. Mica mining
D. Iron ore mining
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Khetri Belt of Rajasthan is famous for copper mining. Khetri region is known for copper since the Indus Valley civilizations are located in Jhunjhunu of the district of Rajasthan.
94. Which one of the following rivers joins the Ganga at Fatuha?
A. Son
B. Punpun
C. Sakri
D. Balan
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Punpun River joins Ganga at Fatuha. Punpun River is a tributary of the Ganga. It originates in the Palam district of Jharkhand.
95. According to Koppen’s climatic classification, the climate of North Bihar may be explained as:
A. Cwg
B. Aw
C. CA’w
D. CB’w
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: According to Koppen’s climatic classification, the climate of North Bihar may be explained as Cwg. The climate is warm and temperate in North Bihar.
96. Which soil is predominantly found in the districts of Muzaffarpur, Darbhanga, and Champaran?
A. Black Soil
B. Newer Alluvium
C. Older Alluvium
D. Red Soil
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Newer alluvium is predominately found in the districts of Muzaffarpur, Darbhanga, and Champaran.
The alluvium soil is the most fertile soil, and it is predominantly found in the northern plain of India, and it is divided into two varieties viz khadar and banger. The Khadar is composed of newer alluvium and form most of the fertile Ganges plain. The Banger is the older one and is less fertile as compared to Khadar.
97. The largest jute-producing district of Bihar is:
A. Siwan
B. Gaya
C. Vaishali
D. Purnia
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The largest jute-producing district of Bihar is Purina. It provides the climatic condition for the production of jute in a particular region. India’s first jute park named Punrasar Jute Park is coming up in the Purina district of Bihar.

West Bengal is the largest jute producer in India, while India is the largest jute producer in the world followed by China.
98. Triveni Canal has been constructed on the river:
A. Kosi
B. Son
C. Gandak
D. Kamla
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Triveni canal has been constructed on the river Gandak which is the left bank tributary of Ganga. It has been constructed for the irrigation in Champaran district of Bihar. It was started in 1979. Gandak River is also called the ‘Narayani’ River. It originates from Nhubine Himal Glacier located in Mustang District, Nepal.
99. The salvation place of Mahavirji, the originator of the Jain religion, is located at
A. Maner
B. Rajgir
C. Pavapuri
D. Jalan Fort
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The salvation place of Mahavir Ji, the originator of the Jain religion is Pavapuri. Pavapuri is located in the Nalanda district of Bihar. Pavapuri is a sacred place in Jainism as it was the cremation area of Mahavir Ji.
100. Kaimur Plateau is famous for:
A. Copper
B. Limestone
C. Lithium
D. Bauxite
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Kaimur plateau is famous for limestone. The Kaimur Plateau is situated in Bihar. It extends into the eastern zone of the Vindhya Range. A type of hard white sedimentary rock is used for making cement. Its major materials are the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate.
101. Swami Sahajanand Saraswati published a journal named:
A. Jankranti
B. Hunkar
C. KrishakSamachar
D. Vidrohi
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: Swami Sahajanand Saraswati published a journal called “Hunkar”. Sahajanand Saraswati is considered a peasant leader of India.
102. Who established a branch of Anushilan Samiti at Patna in 1913?
A. Rewati Nag
B. Yadunath Sarkar
C. Sachindra Nath Sanyal
D. Mazharul Haque
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Anushilan Samiti was a revolutionary organization in Bengal that was established in 1900. It was led by Sri Aurobindo Ghosh with the help of other prominent members. Sachindra Nath Sanyal established a branch of Anushilan Samiti at Patna in 1913. Bankimchandra Mitra of BN College was given responsibility to lead the organization.
103. Who organized Kisan Sabha at Munger in 1922-23?
A. Swami SahajanandSaraswati
B. Shri Krishna Singh
C. Mohammed Jubair
D. K.N.Singh
E. None of the above
Answer: E
Solution: Kisan Sabha was organised in 1922 by Mohammad Zubair and Sri Krishna Singh in Munger. Zubair was the Sardar of Kisan Sabha while krishna singh was the naib Sardar of the Kisan Sabha. This organization was made for poor peasants.
104. Bihar Socialist Party was born in 1934 with its Secretary?
A. Acharya Narendra Dev
B. Jayaprakash Narayan
C. Rambriksh Benipuri
D. Kapoor Thakur
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Bihar socialist party was born in 1934 with its secretary Jayprakash Narayan. Rambriksh Benipuri & Narayan in a meeting at Patna on 17 may 1934 founded the Bihar Congress socialist party. Acharya Narendra Dev became president.
105. Who was the member of the Constituent Assembly of India from Bihar?
A. A. N. Sinha
B. Rajendra Prasad
C. Jagjivan Ram
D. Shyam Nandan Prasad Mishra
E. None of the above
Answer: E
Solution: Anugrah Narayan Sinha, Jagjivan Ram, Sachchidanand Sinha, Raghunandan Prasad, Rajendra Prasad, Shyam Nandan Mishra were some of the prominent members of the constituent assembly from Bihar.
106. The first Indian Ministry in Bihar in 1937 came into existence under whose leadership?
A. Shri Krishna Singh
B. Md. Yunus
C. G.S. Lal
D. Wahab Ali
D. Wahab Ali E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Mohammad Yunus was the leader of Bihar province in British India for three months in 1937, during the state’s first democratic election. However his minority government had already resigned when the session began.
107. Whom did Rajendra Prasad consider as the father of Pakistan?
A. Md. Jinnah
B. Lord Mountbatten
C. Lord Minto
D. Liaquat Ali Khan
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Rajendra Prasad considered Lord Minto as the father of Pakistan which is also known as the father of communal electorate.
- Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a lawyer, politician, and the founder of Pakistan.
- Lord Mountbatten was the last viceroy of British India. Liaquat Ali Khan was the first prime minister of Pakistan.
108. When was Patna Lawn renamed as Gandhi Maidan?
A. During Quit India Movement
B. During Anti-Simon Commission Rally
C. During Champaran Satyagraha
D. On the eve of Independence
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Patna Gandhi Maidan was used as Golf course & horse racing track and called as Patna Lawn. But when Mahatma Gandhi came to this place to launch the Champaran satyagraha (1917), a huge crowd gathered here to hear his speech, and it was the first time when the ordinary Indian people entered the ground. Thus the park was re-named as Gandhi Maidan in honour of the Mahatma Gandhi.
109. Bombay Presidency Association was established by:
A. Ferozshah Mehta
B. K.T. Tailang
C. W. C. Banerjee
D. Tayabjee
E. None of the above
Answer: E
Solution: Bombay Presidency Association was established by Badruddin Taiyabjee, Pherozshah Mehta and K. T. Telang in 1885.
110. Who established Imperial Commission Corps?
A. Lord Minto
B. Lord Curzon
C. Lord Lytton
D. Lord Ripon
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Lord Curzon established imperial cadet corps in 1901 to provide military education and special officer commissions to Indian princes and aristocrats.
111. The Declaration of Partition of Bengal was done on:
A. 19th July, 1905
B. 7th August, 1905
C. 15th August, 1905
D. 16th October, 1905
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: It was announced on 19 July 1905 by Lord Curzon, the then Viceroy of India, and implemented on 16 October 1905, it was undone a mere six years later.
112. Who was given life punishment for the murder of Colonel Wyllie?
A. Madan Lal Dhingra
B. Udham Singh
C. Bhagat Singh
D. Manmathanath
E. None of the above
Answer: A
Solution: Madan Lal Dhingra was given life punishment for the murder of Colonel Wyllie. Dhingra’s suicide attempt failed and he was overpowered.
113. The post of the Indian High Commission was created by which Act?
A. The Indian Councils Act, 1909
B. The Government of India Act, 1919
C. The Government of India Act, 1935
D. The Indian Independence Act, 1947
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: The post of the Indian High Commission was created by the Government of India Act,1919. The first high commissioner for India was Indian civil service officer sir William Stevenson Meyer, and the first of Indian origin was sir Dadiba Merwanji Dalal.
114. The Indian National Congress did not take part in which of the following Round Table Conferences?
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Participated in all
E. None of the above
Answer: E
Solution: The First Round Table Conference was conducted between November 1930 and January 1931. Neither Indian National Congress nor any prominent political or business leaders from India participated in it because most of them were lodged into jails.
Second Round Table Conference was held between September and December 1931. In this conference, INC took part and Mahatma Gandhi was appointed as sole representative of Indian National Congress.
Third Round Table Conference was held in London on November 17, 1932 which Congress refused to attend it.
115. Mahatma Gandhi presided over which Session of the Indian National Congress?
A. 1922
B. 1924
C. 1928
D. 1930
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: W.C Bannerjee presided over the first session of the Indian National Congress which was held at Bombay in 1885 from 28 Dec to 31 Dec.
Mahatma Gandhi chaired over 1924 session of the Indian National Congress which was held at Belgaum.
116. Who was not a member of the Cabinet Mission?
A. Pethick Lawrence
B. Wavell
C. Stafford Cripps
D. A.V. Alexander
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: Wavell was not a member of the Cabinet Mission. The Cabinet mission of 1946 aimed to discuss the transfer of power from the British government to the Indian leadership.Members of the mission are : Lord Pethick – Lawrence, the secretary of state for India, Sir Stafford Cripps, president of the board of trade, and A V Alexander, the first Lord of the Admiralty.
117. Who wrote the pamphlet ‘Now or Never’?
A. Md. Jinnah
B. Md. Iqbal
C. Rahmat Ali
D. Khafi Khan
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: The Pakistan declaration (Now or Never) was a pamphlet written and published by Chaudhary Rahmat Ali, on 28 January 1933, in which the word Pakistan was used for the first time and was presented in the third round table conference in 1933.
118. Who declared ‘Sati’ illegal?
A. Warren Hastings
B. William Bentinck
C. Cornwallis
D. Curzon
E. None of the above
Answer: B
Solution: ’Sati’ is declared illegal by Lord William Bentinck on 4 December 1829 on the request of Raja Rammohan Roy.
119. When was the Punjab Land Alienation Act passed?
A. 1850
B. 1895
C. 1900
D. 1905
E. None of the above
Answer: C
Solution: Punjab Land Alienation Act was passed in 1990. The Punjab Land Alienation Act of 1900 was a piece of legislation introduced by the British Raj with the aim of limiting the transfer of land ownership in Punjab. It put a 15 years limitation for purchases and mortgage and prevented urban landers from any kind of land transaction.
120. The Department of State was established under whose headship?
A. Mahatma Gandhi
B. J.L. Nehru
C. G.B. Pant
D. Sardar Patel
E. None of the above
Answer: D
Solution: The department of state was established under Sardar Patel to deal with princely states and relationship with independent India.
121. A number, when divided by 342, gives a remainder 47. When the same number is divided by 19, what would be the remainder?
A. 0
B. 9
C. 18
D. 8
E. None of the above
Ans: B
Solution: Let the number be x
when x is divided by 342 gives the remainder 47.
It means, x= 389 (just make the sum)
So, when 389 is divided by 19, it will give the remainder is 9.
122. A person who spends 66 2/3% of his income is able to save Rs.1,200 per month. His monthly expenses (in Rs.) are
A. 2,400
B. 3,000
C. 2,000
D. 3,600
E. 2,800
Ans: A
Solution: The person spends 66 2/3% of his income
i.e. He spends 2/3rd of his income, it means he saves 1/3rd of his income.
So, 1/3rd is equal to 1200.
His Expenses will be 2/3rd, i.e. 2400.
123. A man gains 20% by selling an article for a certain price. If he sells it at the double the price, the percentage of profit will be
A. 140
B. 200
C. 100
D. 160
E. 120
Ans: A
Solution: Let Cost Price be Rs. 100 and Selling Price be Rs. 120
Now, the New selling price will be 120X2= 240 Rupees.
So, Profit Percentage will be ((240-100)/100)X100 %
= 140 %
124. 10 women can complete a work in 7 days, and 10 children take 14 days to complete the work. How many days will 5 women and 10 children taken to complete the work?
A. 6
B. 5
C. 3
D. 7
E. 4
Ans: D
Solution: 10 women take 7 days, so, 1 woman will take 70 days.
so, per day work of women will be 1/70.
Similarly,
per day work of children will be 1/140
Now, 5 women and 10 children will do (5/70) plus (10/140) work daily.
i.e. 20/140 work daily
or, 1/7 work daily.
So Total Time Taken will be 7 days.
125. How many numbers between 11 and 90 are divisible by 7?
A. 10
B. 9
C. 13
D. 12
E. 11
Ans: E
Solution: Between 11 and 90, divisible by 7 is 14,21,28,35,42,49,56,63,70,77,84
Total: 11
126. A man can row 7.5 Km per hours in still water. If in a river running at 1.5 Km an hour, it takes him 50 minutes to row to a place and back, how far off is the place?
A. 3 Km
B. 4 Km
C. 2 Km
D. 5 Km
E. 7 Km
Ans: A
Solution: Let the width of the river be x
Speed of Travel in the upward journey will be 7.5 Plus 1.5 = 9 Km/h
Speed of Travel in the downward journey will be 7.5 Minus 1.5 = 6 Km/h
Total Time Taken will be x/9 Plus x/6
=5x/18
Now, it is given that the total time taken is 50 minutes.
So, 5x/18 = 50/60
So, x= 3 Km.
127. A sum of money invested at compound interest amounts to Rs 4624 in 2 years and to Rs 4913 in 3 years. The sum of money is
A. Rs 4240
B. Rs 4280
C. Rs 4096
D. Rs 4346
E. Rs 4406
Ans: E
Solution:
4624=P(1 Plus r/100)^2
4913=P(1 Plus r/100)^3
Just divide the above equations.
r= 6.25 %
Now, Put the value of r in any equations to get P.
P = 4096 Rs.
128. A man buys Rs 20 shares paying 9% dividend. The man wants to have an interest of 12% on his money. The market value of each share is:
A. Rs 18
B. Rs 15
C. Rs 21
D. Rs 25
E. Rs 20
Ans: (B)
Solution: Dividend on Rs. 20 = 9X20/100=9/5 Rupees.
He gets 12 Rs. income on Rs 100
So 9/5 Rs income = (100*9)/(12*5) = 15 Rs.
129. The following pie chart shows the spending of the country on various sports during the particular year. Study the chart carefully and answer the question (Note: Refer your question paper for chart) How much percent less is spent on football than that of cricket?
A. 35.5
B. 29
C. 32.5
D. 31
E. 33.33
Ans: E
Solution: Percentage decrease will be
= (81-54)/81X100
=33.33%
Hence, 33.33% less will be spent on football than that on cricket.
130. A invested Rs 76,000 in a business. After few months, B joined him with Rs 57, 000. At the end of the year, the total profit was divided between them in the ratio 2:1, After how many months did B join?
A. 6
B. 4
C. 3
D. 8
E. 5
Ans: D
Solution: Let B join after x months,
So the fraction will be (76000*12)/(57000*x) = 2/1
just, solve it, you will get x=8 months
131. Quartz crystals used in clocks are?
A. Sodium silicate
B. Silicon dioxide
C. Germanium dioxide
D. Titanium dioxide
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: B
Solution: Quartz crystal used in the clock is compound of silicon dioxide. This crystal forms a signal with a very accurate frequency so that quartz watches can give accurate precision as compared to at least mechanical or spring watches.
132. Bromine is a
A. Colorless gas
B. Brown solid
C. Highly inflammable gas
D. Red liquid
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: D
Solution: Bromine is a red liquid element. It is a fairly abundant element but has a rare property it is the only non-metal to exist in liquid form at room temperature. It is toxic and flame retardants.
133. Gases used in welding are
A. Oxygen and hydrogen
B. Oxygen and nitrogen
C. Oxygen and acetylene
D. Hydrogen and acetylene
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: C
Solution: Gases used in welding are, Oxygen and acetylene.
134. Galvanised iron pipes have a coating of
A. Zinc
B. Mercury
C. Lead
D. Chromium
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: A
Solution: Galvanised iron pipes have a coating of zinc. Galvanisation is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting.

135. The wavelength of the visible spectrum is in the range:
A. 1300 A-3900 A
B. 3900 A-7600 A
C. 7800 A-8200 A
D. 8500 A-9800 A
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: B
Solution: The wavelength of the visible spectrum is in the range of 3900A-7600A which is visible to human eye.

136. Detergents used for cleaning clothes are:
A. Carbonates
B. Bicarbonates
C. Bismuthates
D. Sulfonates
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: D
Solution: Detergents used for cleaning clothes are Sulfonates. A detergent is a soapless soap usually Alkylbenzene sulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are more soluble in hard water.
137. The element excreted through human sweat is
A. Sulfur
B. Iron
C. Magnesium
D. Zinc
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: E
Solution: The elements excreted through human sweat are more than one above. Sweat is mostly water. Dissolved in the water are trace amounts of minerals, lactic acid ,urea and measured concentrations of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
138. Blue vitriol is chemically
A. Sodium sulphate
B. Nickel sulphate
C. Copper sulphate
D. Iron sulphate
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: C
Solution: Blue vitriol is chemically copper Sulphate. Vitriol is an archaic name for a sulphate. Copper sulphate, blue stone, blue vitriol are all common names for pent hydrate cupric sulphate, CuSo4.5H20.

139. The positively charged part at the centre of the atom is called
A. Proton
B. Neutron
C. Electron
D. Nucleus
E. None of the above/More than one above

Answer: D
Solution: The positively charged part at the centre of atoms is called Nucleus. All substances are made from atoms. Each atom is made of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons.
140. The conversation of solid directly into gas
A. Sublimation
B. Condensation
C. Evaporation
D. Boiling
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: A
Solution: The conversation of solid directly into gas is called as sublimation. A substance changes from a solid to a gas without even passing through a liquid phase such as dry ice, solid Co2.

141. In the human system, insulin controls the metabolism of
A. Fats
B. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins
D. Nucleic acids
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: B
Solution: In the human system, insulin controls the metabolism of carbohydrates which is an essential source of energy in our body. Insulin is secreted by the pancreatic beta-cell a crucial hormone in the adaptions of metabolic pathway linked to glucose control i.e. diabeties.
142. The antibiotic among the following is:
A. penicillin
B. aspirin
C. Paracetamol
D. sulfadiazine
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: E
Solution: Among the above more than one above is antibiotics.
Antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial drug used in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection and the growth of bacteria. Penicillin V potassium is used to treat certain infections caused by bacteria.
Aspirin is an antipyretic and analgesic used to reduce fever and relieve mild to moderate pain from conditions such as muscle aches, toothaches, common cold, and headaches.
Paracetamol is an antipyretic and NSAID used to treat pain and fever.
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic.
143. Which of the following is mostly carbohydrate:
A. Wheat
B. Barley
C. Rice
D. Maize
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: C
Solution: Rice is mostly carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are the sugars, starches and fibres found in fruits, grains, vegetables and milk products. They are a source of energy for the body. Wheat, Maize, Barley subsequently contain carbohydrate after rice.
144. The heaviest metal among the following is
A. Gold
B. Silver
C. Mercury
D. Platinum
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: C
Solution: Mercury (Hg), (Atomic mass: 200.59 amu) is the heaviest metal among the following and is followed by Gold, Platinum and silver subsequently.
145. Stainless steel is an alloy of:
A. Iron and nickel
B. Iron and chromium
C. Copper and chromium
D. Iron and zinc
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: B
Solution: Stainless steel is an alloy of iron and chromium. An alloy is a combination of metals or a metal and another element. Chromium is critical in the manufacturing of stainless steel. Most stainless steel contains about 18 percent chromium; it is what hardens and toughens steel and increases its resistance to corrosion, especially at high temperatures.
146. To protect broken bones, plaster of Paris is used. It is:
A. Slaked lime
B. Calcium carbonate
C. Calcium oxide
D. Gypsum
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: D
Solution: To protect broken bones, plaster of Paris is used. Plaster of Paris is a quick-setting gypsum which hardens when moistened and allowed to dry.The chemical formula of plaster of Paris is CaSO4.1/2H2O. The chemical formula of gypsum is represented as CaSO4.2H2O.
147. A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond is called as an:
A. Alkane
B. Alkene
C. Alkyne
D. Ionic bond
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: B
Solution: A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond is called as an Alkene. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are made of only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkanes (CnH2n 2) single bond ,Alkenes (CnH2n) double bond and Alkyne(CnH2n-2)have at least one triple bond.
148. The chemical name of vinegar is
A. methanol
B. ethanol
C. acetic acid
D. ethyl acetate
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: C
Solution: The chemical name of vinegar is Acetic acid (CH3COOH). Vinegar is now mainly used as a cooking ingredient, or in pickling.
149. The acid used in a car battery is:
A. Acetic acid
B. Hydrochloric acid
C. Nitric acid
D. Sulfuric acid
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: D
Solution: The acid used in a car battery is sulfuric acid. Each cell of a lead storage battery consists of alternate plates of lead (cathode) and lead coated with lead dioxide (anode) immersed in an electrolyte of the sulfuric acid solution.
150. The gas, which comes out on opening a soda water bottle is
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Hydrogen
C. Nitrogen
D. Sulfur dioxide
E. None of the above/More than one above
Answer: A
Solution: The gas, which comes on opening a soda water bottle is carbon dioxide. Soda water, like other carbonated beverages, contains carbon dioxide that has dissolved under pressure. When the pressure is released by opening the soda container, the liquid cannot hold as much carbon dioxide, so the excess bubbles come out of the solution.
Read: BPSC Notes

