Migration is the movement of people from one place to another, either within a country (internal migration) or across national borders (international migration). It is a major demographic process that influences population distribution, economic activities, urbanization, and social change. People migrate for a variety of reasons, and this movement has both positive and negative consequences for the areas of origin and destination.

Table of Contents
Causes of Migration
Migration is generally driven by a combination of push factors (which compel people to leave their place of origin) and pull factors (which attract people to a new location).
- Economic Causes
- Lack of employment opportunities in the home region.
- Better job prospects and higher wages in cities or foreign countries.
- Economic disparities between rural and urban areas or between nations.
- Social Causes
- Desire for better educational facilities, healthcare, and quality of life.
- Migration for marriage or family reunification.
- Urban lifestyle and social freedom attracting rural youth.
- Political Causes
- Political instability, violence, or persecution in home regions.
- Migration due to war, internal conflict, or oppressive regimes.
- Refugees fleeing from human rights violations or civil unrest.
- Environmental Causes
- Natural disasters such as floods, droughts, earthquakes, and cyclones.
- Degradation of land and water resources due to overuse or climate change.
- Rising sea levels or desertification forcing people to relocate.
- Cultural and Aspirational Causes
- Influence of urban culture, media, and the desire for a modern lifestyle.
- Aspirations to live in more developed or cosmopolitan regions.
- Students moving for higher education abroad or in cities.
Consequences of Migration
Migration has far-reaching impacts on both the source region (place of origin) and the destination region (place of settlement). These can be positive or negative depending on the context.
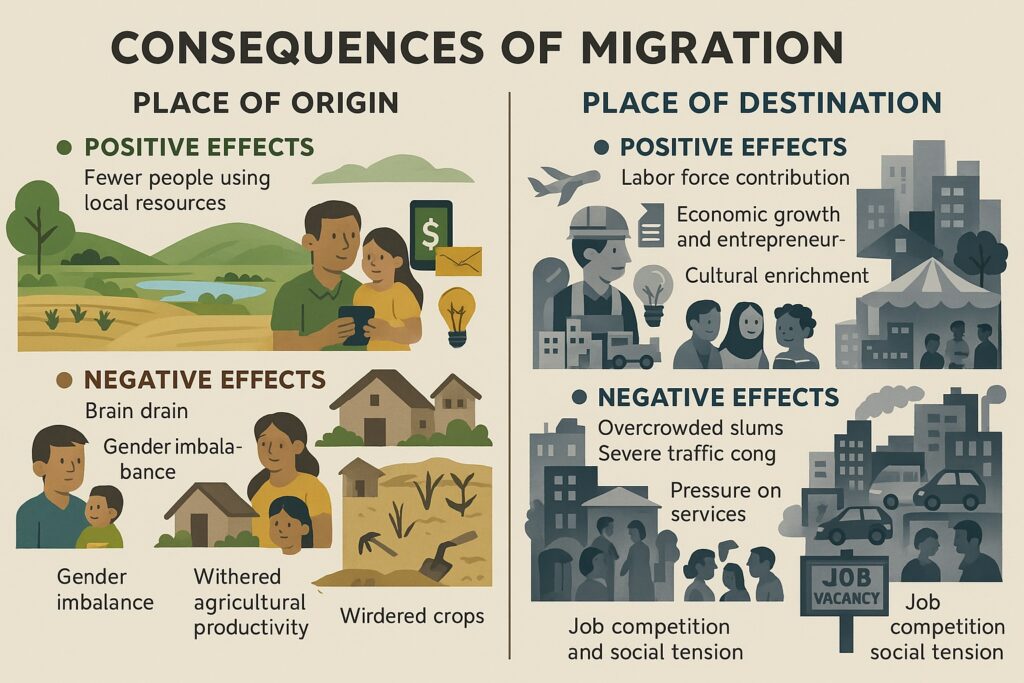
A. Consequences for the Place of Origin
- Positive Effects
- Reduction in pressure on local resources and employment.
- Remittances sent by migrants help improve family income and local economy.
- Exposure to new ideas and lifestyles can lead to social development.
- Negative Effects
- Loss of productive labor force, especially young and educated people (brain drain).
- Gender imbalance due to male-dominated migration.
- Decline in agricultural productivity and rural development.
B. Consequences for the Place of Destination
- Positive Effects
- Availability of labor for industries, construction, and services.
- Contribution to the economy through taxes, consumption, and entrepreneurship.
- Cultural diversity and social enrichment in urban areas.
- Negative Effects
- Overcrowding in cities, leading to slums and inadequate housing.
- Pressure on urban infrastructure, healthcare, water, and sanitation.
- Rise in unemployment, competition for jobs, and sometimes social tensions.
Conclusion
Migration is a natural and ongoing process that reflects human aspirations for a better life. While it brings economic and social opportunities, it also creates challenges in terms of resource management, urban planning, and social cohesion. Effective migration policies, rural development, skill training, and inclusive urban governance are essential to harness the benefits and minimize the adverse impacts of migration.
Read: Geography Notes