Demographic attributes are the statistical characteristics of a population that help in understanding its structure and dynamics. These attributes are essential tools for geographers, economists, and policymakers to analyze population trends and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, development planning, and public services.
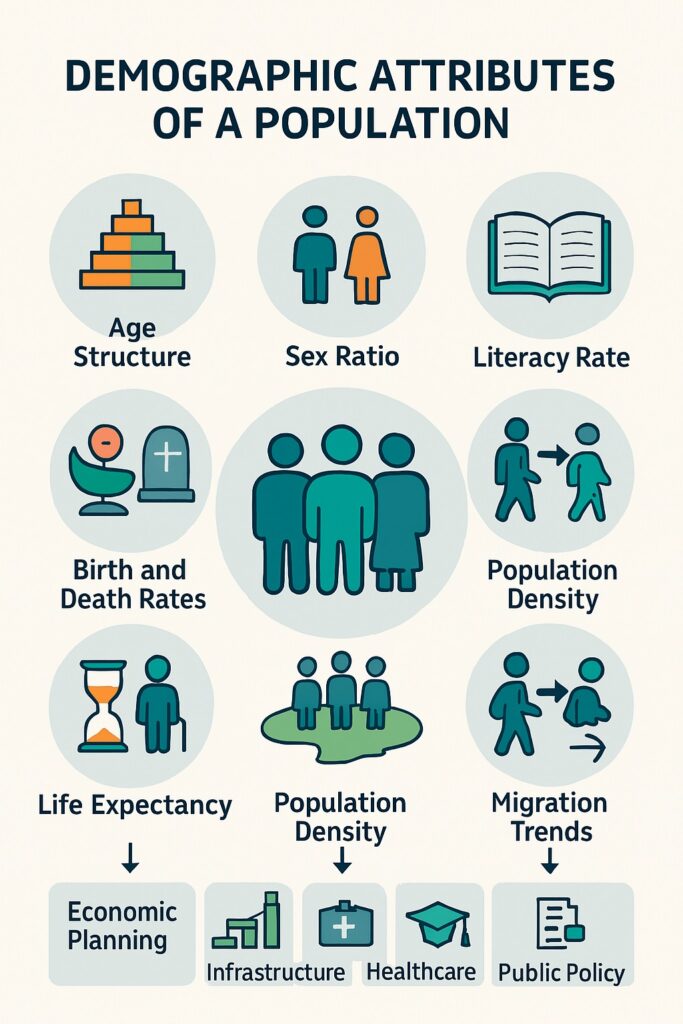
Table of Contents
Key Demographic Attributes
Population Size and Density
-
- Population size refers to the total number of people living in a specific area.
- Population density indicates the number of people per square kilometer and reflects how crowded or sparsely populated an area is.
- For example, India has a high population density, while countries like Canada and Australia have low densities.
Age Structure
-
- Age structure shows the proportion of different age groups within a population.
- It is generally divided into three groups: children (0–14 years), working-age population (15–64 years), and elderly (65+ years).
- A youthful population offers labor potential, while an aging population increases the need for healthcare and pensions.
Sex Ratio
-
- Sex ratio is the number of females per 1000 males in a population.
- It reveals the gender balance and reflects the social and cultural practices of a region.
- A balanced or higher sex ratio often indicates better gender equality and female health.
Literacy Rate
-
- Literacy rate measures the percentage of people aged 7 years and above who can read and write with understanding.
- It is a critical indicator of educational attainment and human development.
- Higher literacy rates are linked with lower birth rates, better health, and greater employment.
Life Expectancy
-
- Life expectancy is the average number of years a person is expected to live from birth.
- It reflects the standard of living, healthcare, nutrition, and public services available in a region.
- Developed countries generally have higher life expectancies than developing ones.
Birth Rate and Death Rate
-
- Birth rate is the number of live births per 1000 people in a year.
- Death rate is the number of deaths per 1000 people in a year.
- Together, they determine the natural growth rate of a population.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
-
- IMR is the number of infant deaths (under one year) per 1000 live births in a year.
- It serves as a measure of a country’s healthcare and nutritional standards.
- A high IMR indicates poor health facilities and maternal care.
Dependency Ratio
-
- The dependency ratio is the ratio of non-working (children and elderly) to working-age population.
- A high dependency ratio means more pressure on the working population to support dependents.
Occupational Structure
-
- This refers to the distribution of the population across various sectors: primary (agriculture), secondary (industry), and tertiary (services).
- In developing countries, a large portion of the population works in agriculture, while developed nations have more people in service and industrial sectors.
Importance of Demographic Attributes
- Provide crucial data for development planning and policy-making.
- Help in assessing the needs for infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
- Assist in understanding labor markets and economic productivity.
- Guide governments in managing migration, urbanization, and environmental issues.
- Aid in predicting future population trends and their implications.
Demographic attributes offer valuable insights into the social, economic, and political character of a population. By analyzing these attributes, countries can implement more effective development strategies and work toward sustainable population management.
Read: Geography Notes