Latitude and Longitude are imaginary lines used to locate places on the Earth’s surface. They form a coordinate system that helps in identifying the exact position of any place on Earth. Although latitude and longitude are used together, they refer to different aspects of a location.
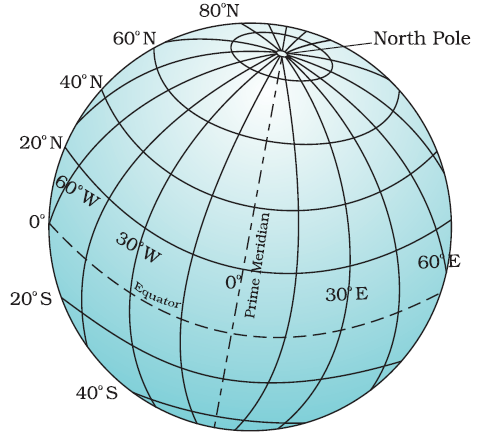
Table of Contents
What is Latitude?
Latitude is a measurement of a location’s distance from the Equator, which is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. Latitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds and ranges from 0 degrees at the Equator to 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
"Latitude of New Delhi is 28.61 Degree North".
-
Latitude lines are imaginary horizontal lines that run east to west around the Earth.
-
They measure the distance north or south of the Equator.
-
Important lines of latitude include:
-
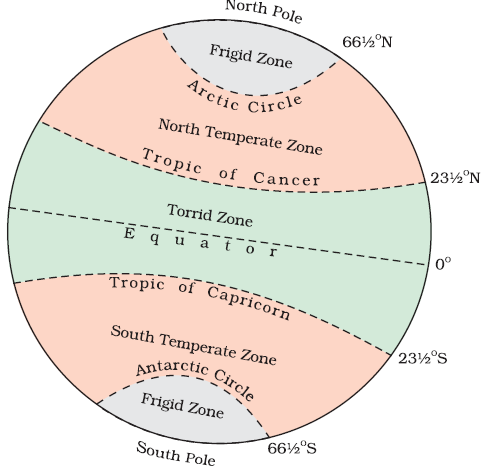
Equator (0°)
-
Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N)
-
Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S)
-
Arctic Circle (66.5° N)
-
Antarctic Circle (66.5° S)
-
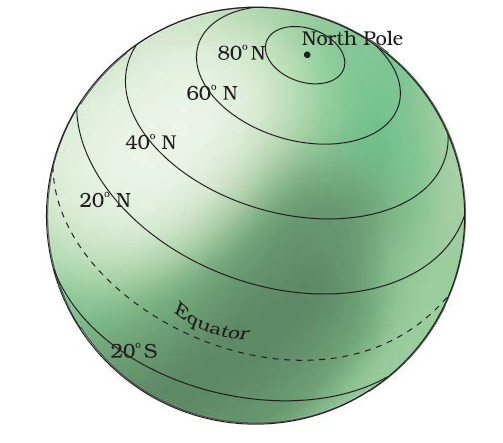
Latitude is usually denoted by the Greek letter phi (φ). The latitude of a location tells us its position in relation to the Equator. A location with a latitude of 0 degrees is on the Equator, while a location with a latitude of 90 degrees is at the North or South Pole.
What is Longitude?
Longitude is a measurement of a location’s distance from the Prime Meridian, which is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England, at 0 degrees longitude. Like latitude, longitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds and ranges from 0 degrees at the Prime Meridian to 180 degrees at the International Date Line.
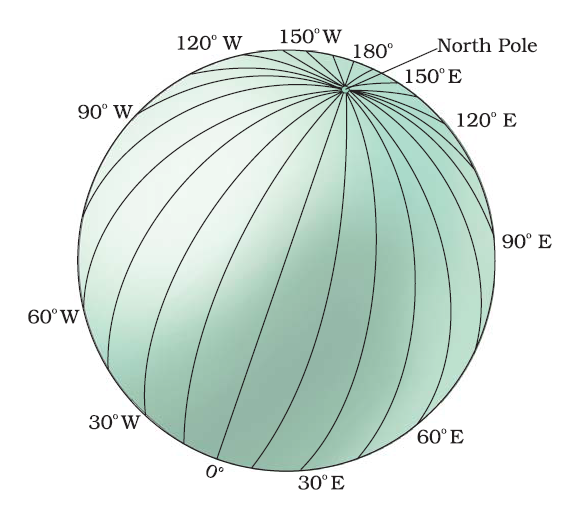
Longitude is usually denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). The longitude of a location tells us its position in relation to the Prime Meridian. A location with a longitude of 0 degrees is on the Prime Meridian, while a location with a longitude of 180 degrees is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Prime Meridian.
Differences between Latitude and Longitude
| Feature | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Runs East–West | Runs North–South |
| Measures | Distance North or South of the Equator | Distance East or West of the Prime Meridian |
| Reference Line | Equator (0° Latitude) | Prime Meridian (0° Longitude) |
| Range of Values | 0° to 90° North or South | 0° to 180° East or West |
| Lines Called | Parallels | Meridians |
| Are Lines Parallel? | Yes, all latitude lines are parallel | No, they meet at the poles |
| Total Number | 181 (including Equator) | 360 (from 180° E to 180° W) |
| Shape of Lines | Circles that get smaller toward poles | Semi-circles from pole to pole |
| Helps Locate | North or South position | East or West position |
What is Prime Meridian?
The Prime Meridian is the imaginary line of longitude that is defined as 0° longitude. It is the starting point for measuring longitude east and west around the Earth.
-
The Greenwich Meridian was officially adopted as the Prime Meridian at the International Meridian Conference in 1884.
-
Before that, different countries used their own meridians (like Paris or Rome) for mapping.
-
Greenwich was chosen because the Royal Observatory in Greenwich had been widely used for navigation and maps.
"Just as the Equator is the reference line for measuring latitude, the Prime Meridian is the reference line for measuring longitude".
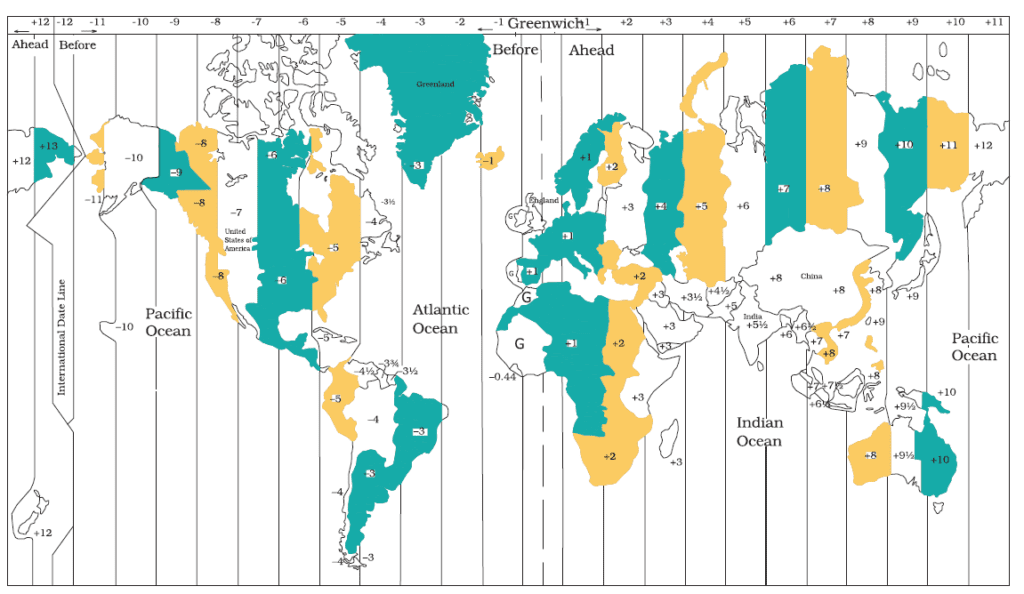
Longitude and Time
- Local time varies with longitude due to Earth’s rotation from west to east.
- Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, meaning:
- 15° = 1 hour time difference
- 1° = 4 minutes time difference
Example:
-
- At 15° east of Greenwich, time is 1 hour ahead
- At 15° west, time is 1 hour behind
- All places on the same longitude (meridian) share the same local time.
- A watch set to noon when the Sun is overhead gives the local time of that location.
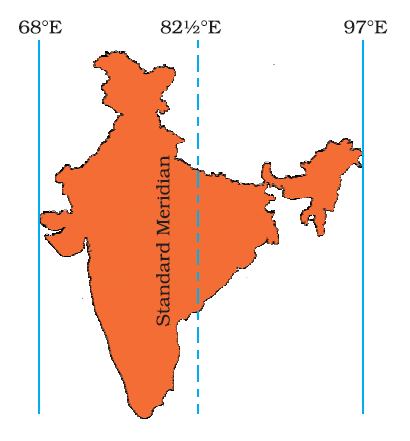
Standard Time of India
-
Local time varies from place to place because different longitudes experience sunrise and noon at different times.
-
This variation causes practical problems, especially in planning activities like train schedules across a country.
-
For example, Dwarka (Gujarat) and Dibrugarh (Assam) have a time difference of about 1 hour 45 minutes due to their longitudinal positions.
-
To avoid confusion, countries adopt a Standard Time based on the local time of a central meridian.
-
The Standard Meridian of India is 82½° East (82°30′ E).
-
This meridian passes near Mirzapur, a city in Uttar Pradesh.
-
The local time at this meridian is followed across the country and is known as Indian Standard Time (IST).
"India spans nearly 30° of longitude, which could cause up to 2 hours of local time difference between its easternmost and westernmost regions".
What is International Date Line?
The International Date Line (IDL) is an imaginary line on the Earth’s surface that plays a critical role in keeping global time and calendar dates organized.
-
The IDL runs roughly along the 180° longitude, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, opposite the Prime Meridian (0°).
-
It is not a straight line — it zigzags to avoid dividing countries and islands into different calendar days.
-
It passes around places like Fiji, Samoa, and Kiribati, adjusting its path to suit political and practical needs.
-
The IDL marks the place where each calendar day begins.
-
When you cross the IDL from west to east (e.g., from Asia to America), you go back one day.
-
When you cross from east to west (e.g., from America to Asia), you go forward one day.
Read: Geography Notes