Global Climate Change is one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. The term refers to the long-term shift in average global temperatures caused by the increased emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The main drivers of this change are the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which have caused the concentration of these gases to rise dramatically in recent decades.

Table of Contents
What Causes Climate Change?
The primary cause of modern climate change is the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, especially:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) from fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
-
Methane (CH₄) from agriculture and livestock
-
Nitrous Oxide (N₂O) from fertilizers and industry
These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, creating the “greenhouse effect”—which leads to global warming and shifts in climate patterns.
Global Warming
Global warming means the Earth is getting warmer. Scientists say this is happening because of two main reasons:
- Ozone layer is getting thinner
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the air is increasing
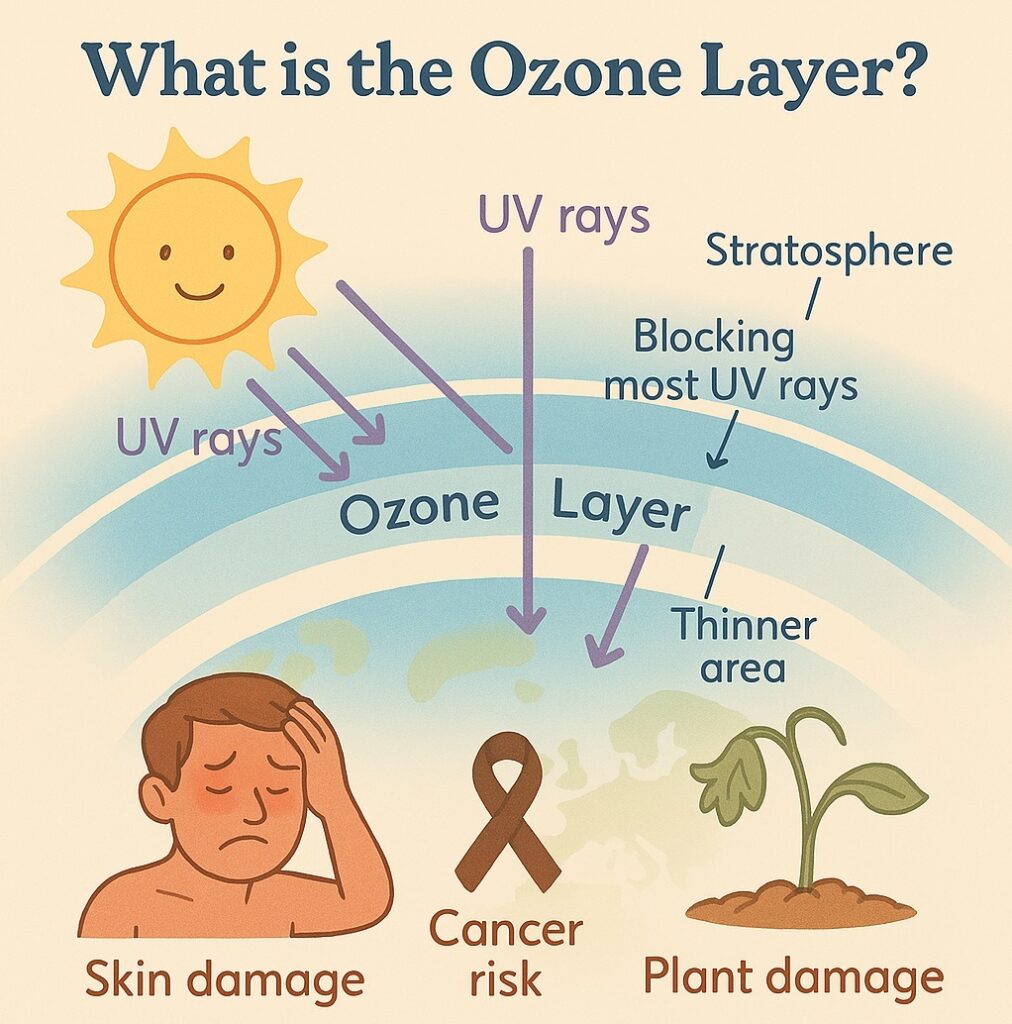
What is the Ozone Layer?
- It’s a layer of gas high up in the stratosphere
- It blocks harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun
- If the ozone layer gets thinner, more UV rays reach Earth, which:
- Increases Earth’s temperature
- Can cause skin burns and skin cancer
- Harms tiny life forms and plants
What is Carbon Dioxide Doing?
- CO₂ lets sunlight in but traps heat (like a blanket)
- More CO₂ = more heat stays in the atmosphere
- In the last 100 years, CO₂ has increased by 25%
- This has raised Earth’s temperature by about 0.5°C
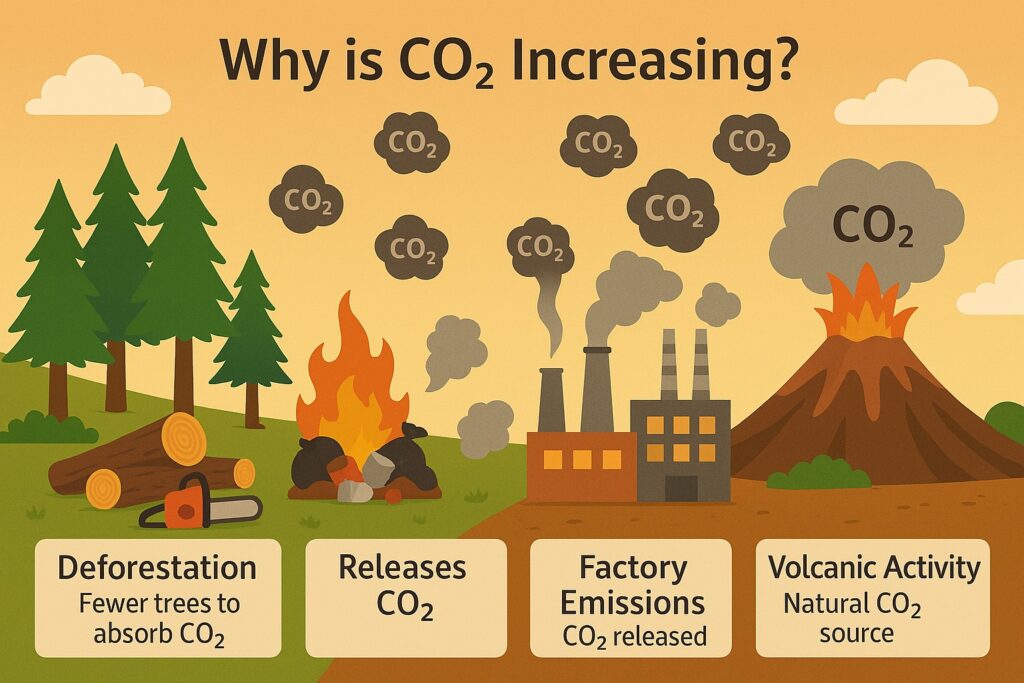
Why is CO₂ increasing?
- Cutting down forests (deforestation)
- Burning garbage
- Factory smoke
- Volcanic eruptions
What Could Happen If This Continues?
- Polar ice will melt
- Sea levels will rise
- Coastal areas and islands may flood
This whole process of Earth getting warmer due to ozone loss and CO₂ increase is called global warming.
What are the Consequences of Global Climate Change?
The effects of Global Climate Change are far-reaching and have the potential to impact every aspect of life on Earth. Some of the most significant consequences of this change include:
- Rising sea levels: As the global temperature increases, the polar ice caps are melting, causing sea levels to rise and threatening coastal cities and low-lying areas with flooding.
- Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events: As the Earth’s temperature continues to rise, the frequency and intensity of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, are likely to increase.
- Changes in precipitation patterns: The increase in temperature is also causing changes in precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and intense droughts in some areas and increased flooding in others.
- Impacts on biodiversity: Climate Change is causing shifts in the ranges of plants and animals, altering ecosystems and threatening the survival of many species.
- Impacts on agriculture and food security: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are affecting the productivity of agriculture, putting food security at risk in many parts of the world.

The Role of Human Activities in Global Climate Change
The majority of the scientific community agrees that human activities are the primary cause of Global Climate Change. This includes the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and land use changes. These activities have caused the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to rise dramatically, trapping more heat and causing the Earth’s temperature to rise.
Responding to Global Climate Change
The impacts of Global Climate Change are already being felt around the world, and it is essential that action is taken to reduce its severity and mitigate its impacts. Some of the key strategies for addressing this issue include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: This can be achieved through the transition to renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, and the adoption of energy-efficient technologies.
- Protecting and restoring forests: Forests are important sinks for carbon dioxide, and protecting and restoring them can help to mitigate the impacts of Global Climate Change.
- Adaptation: As the impacts of Global Climate Change become more severe, it will be important to develop strategies for adapting to these changes, including improving the resilience of infrastructure and communities.
- International cooperation: Addressing Global Climate Change requires cooperation at the international level, including the development of agreements such as the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature increases to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Global Climate Change is a complex and far-reaching issue that has the potential to impact every aspect of life on Earth. While the impacts of this change are already being felt, it is not too late to take action to reduce its severity and mitigate its impacts. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting and restoring forests, and developing strategies for adaptation, we can help to ensure a sustainable future for our planet. As a global community, it is our responsibility to take action to address this critical issue and ensure a future that is safe and sustainable for all.
Read: Geography Notes