Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environment. The principles of ecology provide a framework for understanding the complex relationships between organisms and their surroundings and how these relationships impact the functioning of ecosystems.

Table of Contents
Key Principles of Ecology
Interdependence of Organisms
All organisms are interconnected and dependent on one another for survival. This interdependence is seen in food webs, where species rely on each other for nutrients and energy.
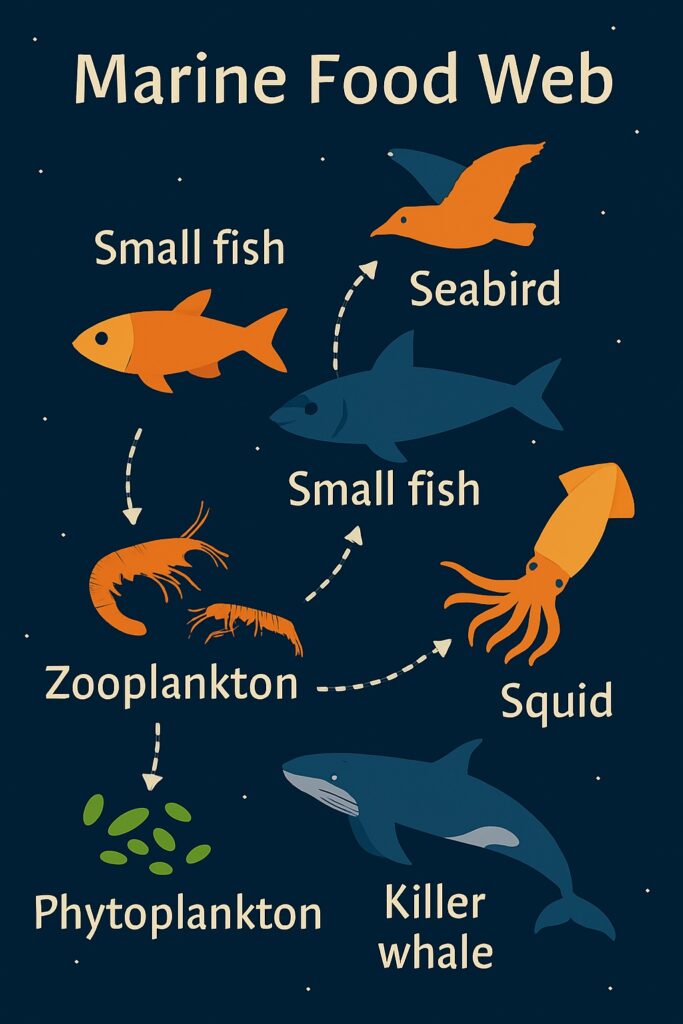
The interdependence of organisms in an ecosystem refers to the intricate web of relationships and interactions between different species within a given environment. These interactions can be categorized into three main types: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.

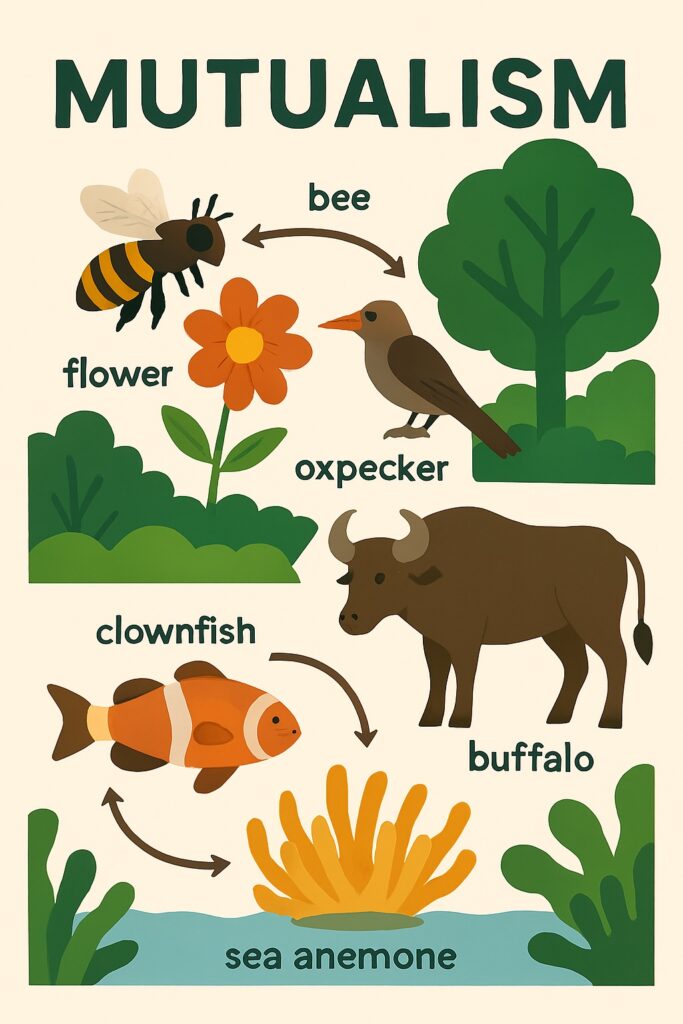
Mutualism
Mutualistic relationships occur when two or more species benefit from their interaction. For example, certain plants rely on animals for pollination, while the animals obtain nectar or pollen as a food source. Both parties benefit from this relationship, as the plants reproduce and the animals acquire sustenance.

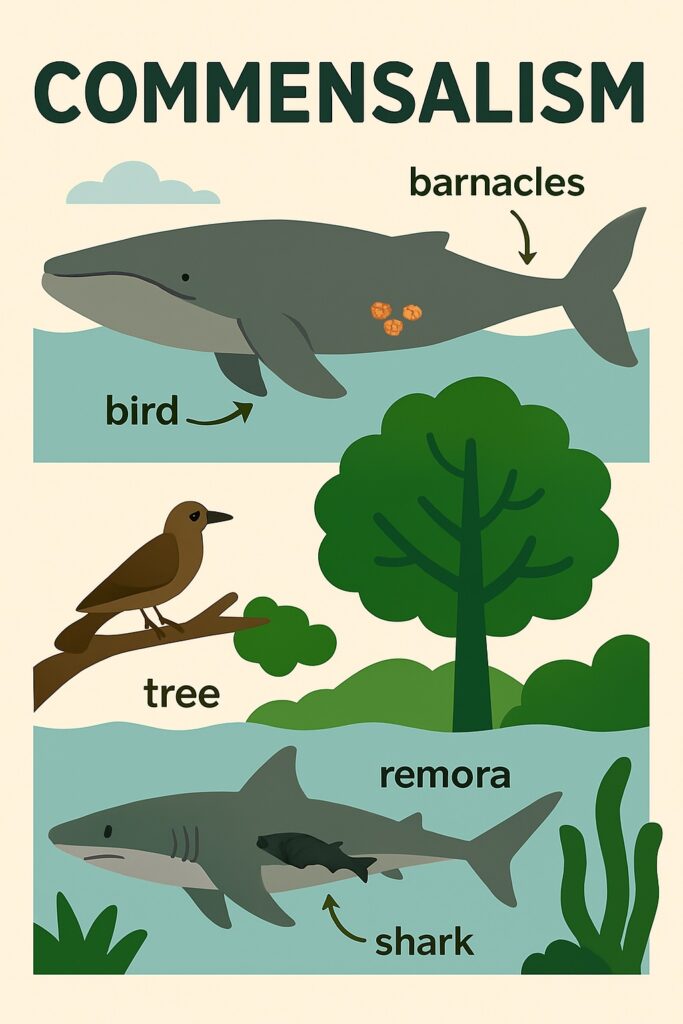
Commensalism
Commensalism describes a relationship where one species benefits while the other remains unaffected. For instance, epiphytic plants such as orchids attach themselves to trees to access sunlight, without harming or benefiting the host tree. The orchids benefit, but the trees are not significantly impacted.
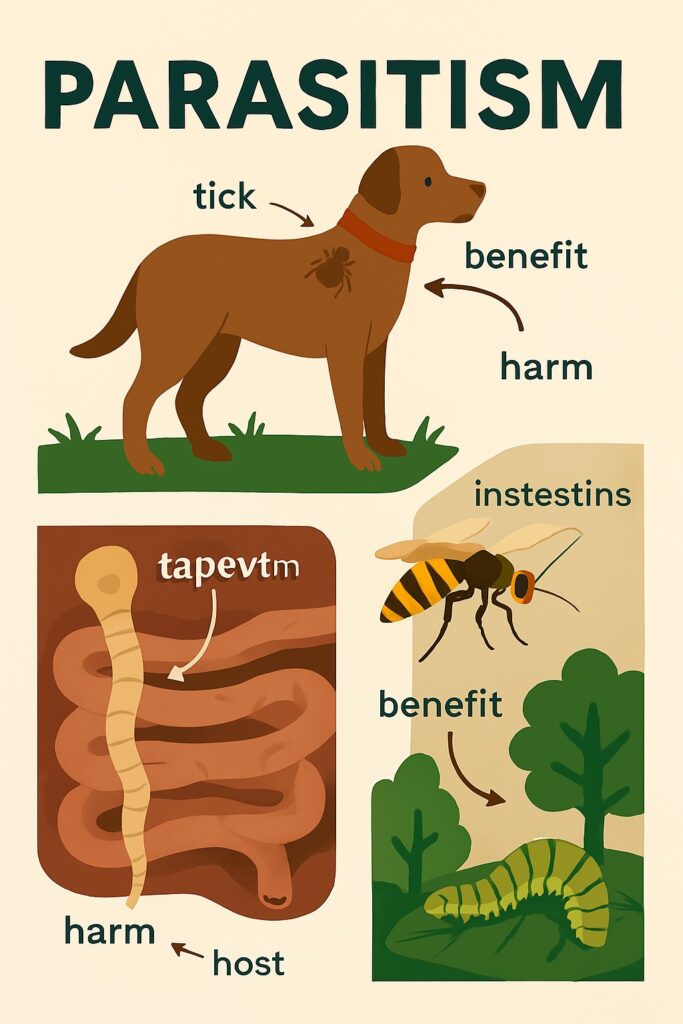
Parasitism
Parasitic relationships involve one organism (the parasite) benefiting at the expense of another organism (the host). Parasites derive nutrients or resources from the host, potentially causing harm or even death. Examples include fleas on dogs and ticks on humans. The parasite benefits, while the host is negatively affected.
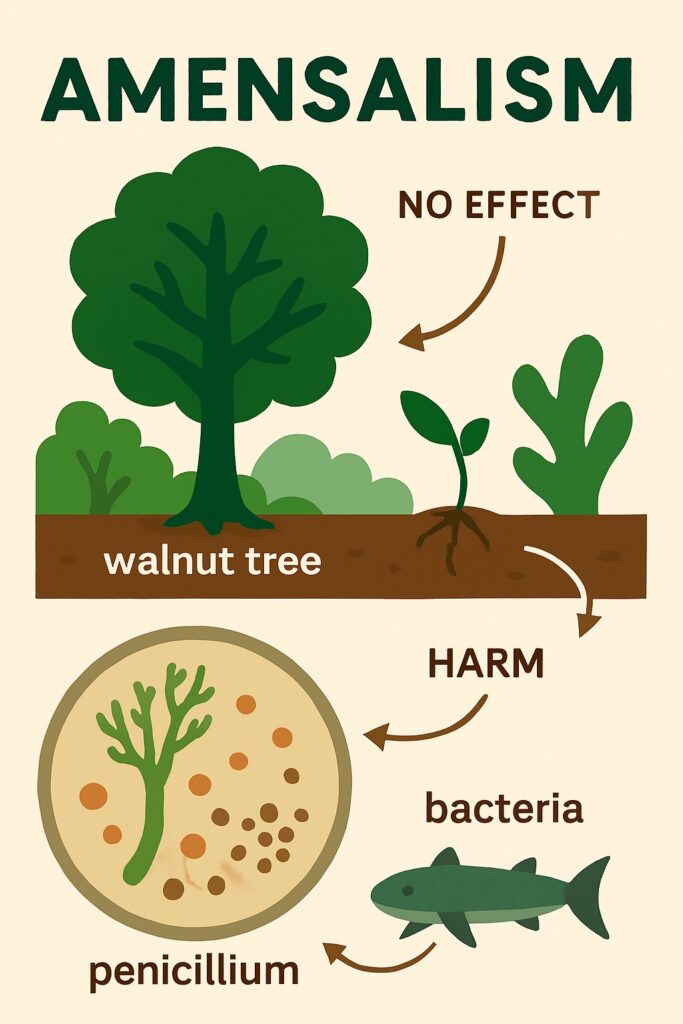
Amensalism
It is a type of relationship between organisms in which one organism is negatively affected, while the other is unaffected. It is important to note that amensalism is less common and less studied compared to other types of ecological relationships. Examples: Walnut tree releases juglone, which suppresses nearby plant growth. Microorganisms produce antibiotics or toxins that kill or inhibit other species.
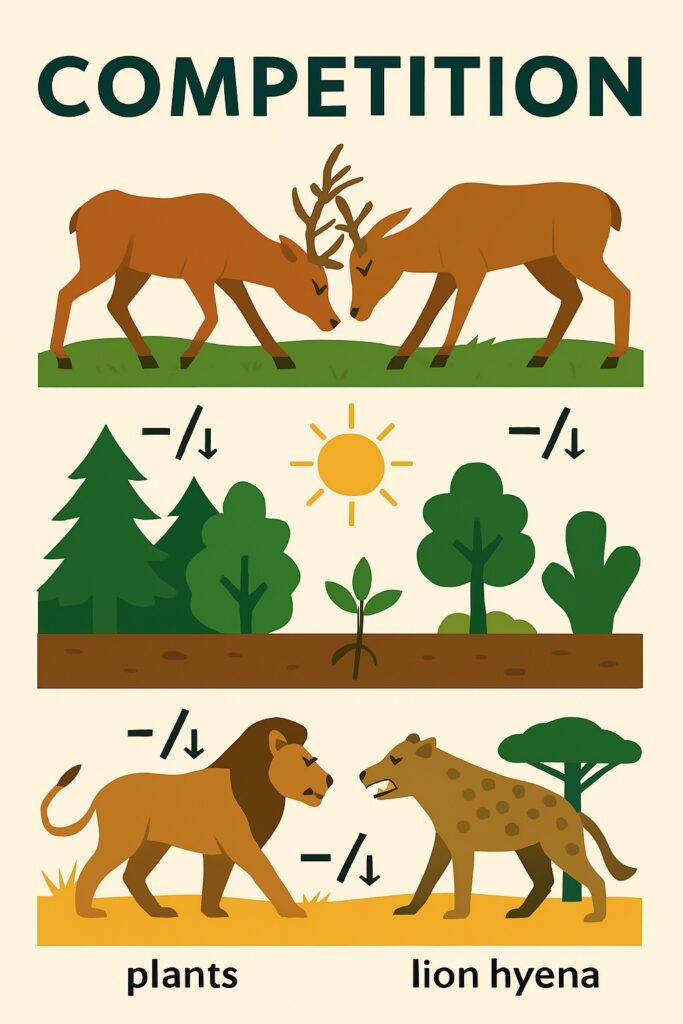
Competition
Competition is a type of biological interaction where two or more organisms or species vie for the same limited resource, such as food, water, shelter, space, sunlight, or mates, in an ecosystem. Because the resource is limited, the presence of one competitor negatively affects the other. Therefore, competition is a (−/−) interaction, meaning both parties are harmed.
Energy flow
Energy flow is the movement of energy through the various components of an ecosystem. It originates from the sun and is transferred between organisms through food chains and food webs. Unlike nutrients, energy is not recycled—it is constantly inputted, transferred, and eventually lost as heat. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for most ecosystems, as it provides the energy required for photosynthesis to occur.
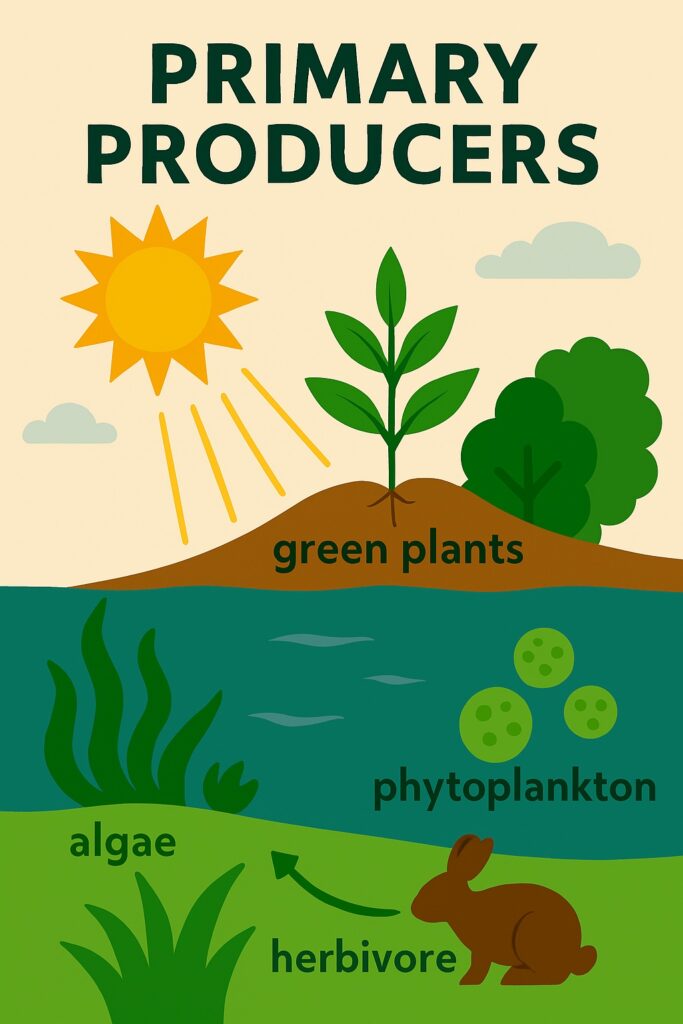
Primary Producers
Primary producers, primarily green plants and some photosynthetic bacteria, convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. They capture sunlight and use it to synthesize organic molecules, such as glucose, from carbon dioxide and water.
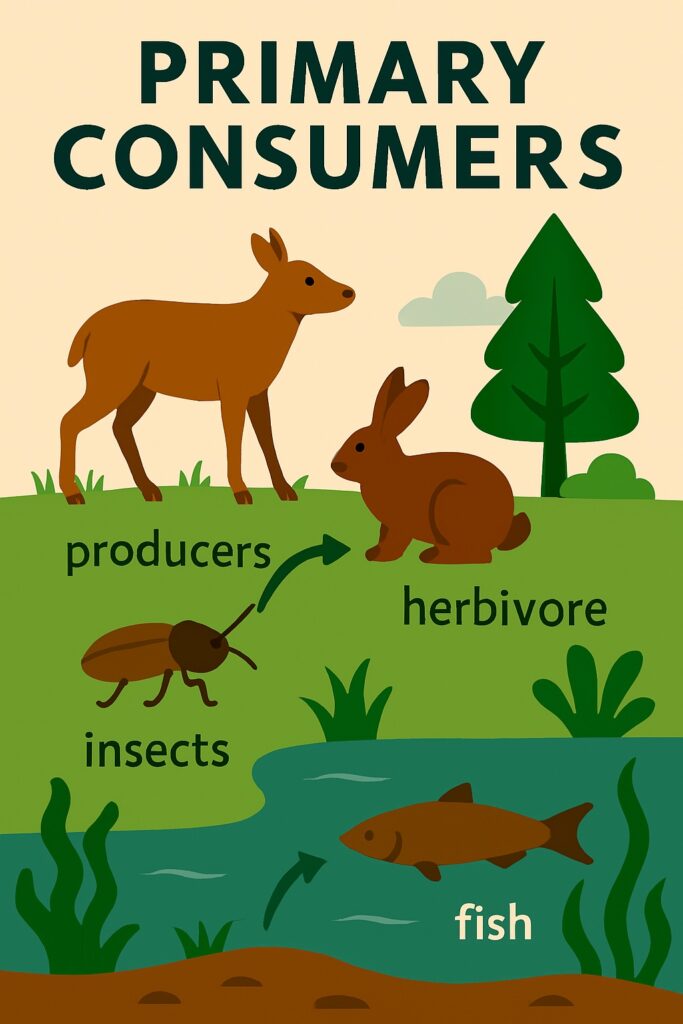
Primary Consumers
Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, are organisms that consume the primary producers. They obtain energy by feeding on plants or algae, thereby transferring the energy stored in the organic molecules of the plants into their own bodies.
Secondary Consumers
Secondary consumers are carnivores that feed on primary consumers. They obtain energy by consuming herbivores or other primary consumers. Energy continues to flow through the ecosystem as organisms are consumed by higher trophic levels, such as tertiary consumers (carnivores that feed on other carnivores) and top predators.
Decomposers
Decomposers, including bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in energy flow by breaking down dead organisms and organic waste material. They release energy stored in organic matter back into the ecosystem as they decompose it. This energy can be used by other organisms, including primary producers, to continue the cycle.
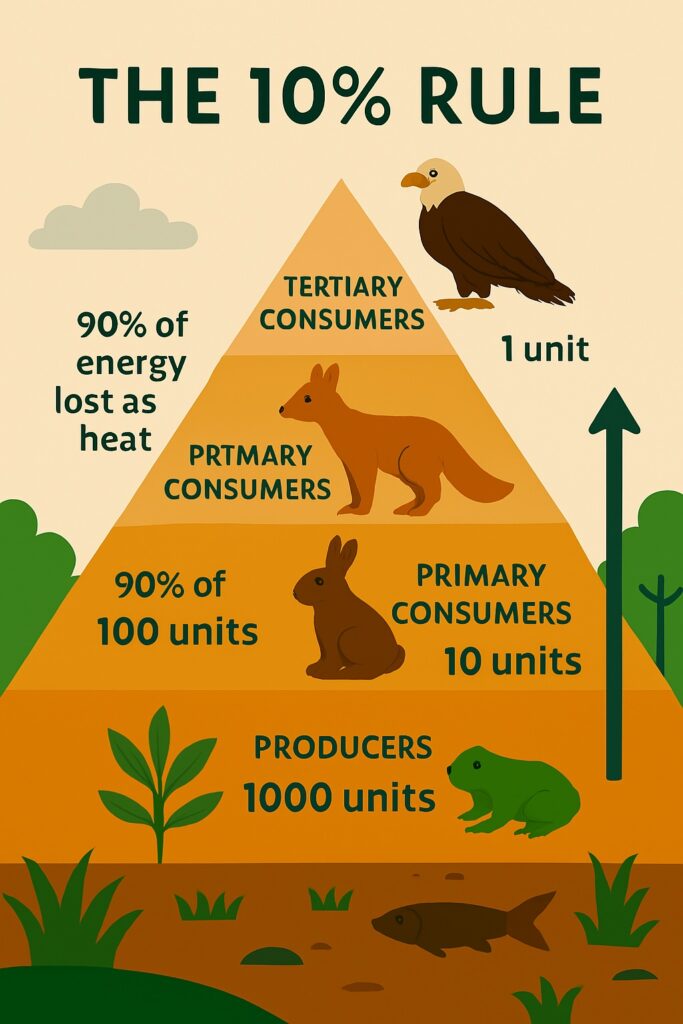
The 10% Rule in Ecology
The flow of energy through an ecosystem follows the 10% rule, also known as the ecological pyramid. According to this rule, only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next level. The remaining energy is used by organisms for their own metabolic processes or lost as heat.
Direction of Energy Flow
It is important to note that energy flow is a unidirectional process within an ecosystem. Once energy is used by an organism, it is no longer available to be recycled or reused by other organisms. Consequently, ecosystems rely on a continuous influx of solar energy to sustain the flow of energy and support the functioning of the various organisms within the system.
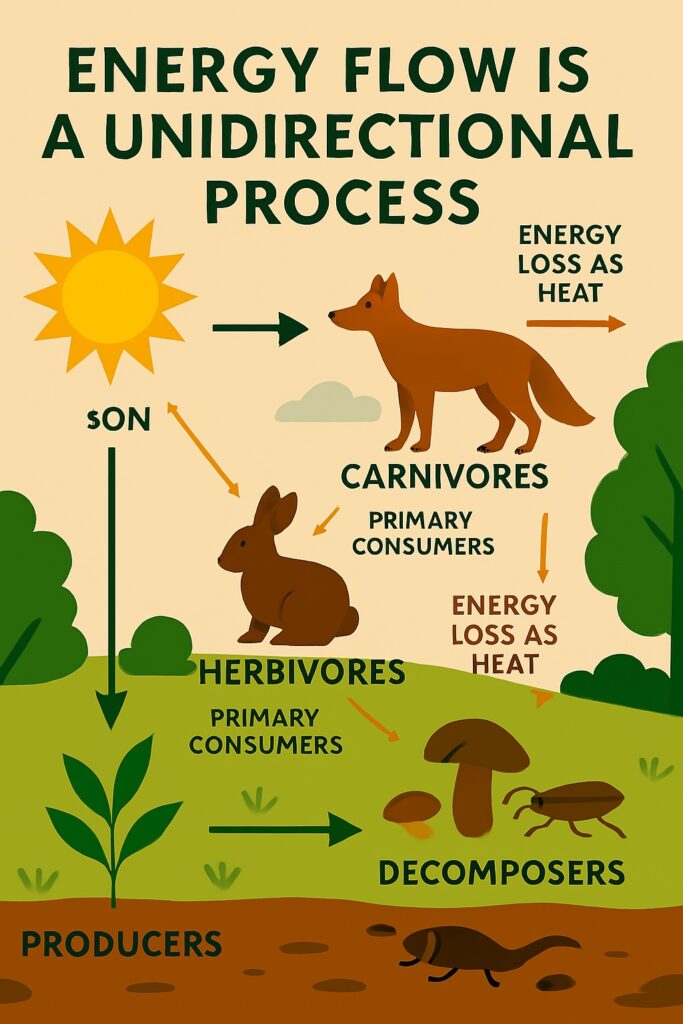
Energy flows through ecosystems, from the sun to primary producers (plants), to consumers (herbivores), and finally to top predators (carnivores). This flow of energy is the basis for all life on Earth.
Applications of Principles of Ecology
- Nutrient cycling: Nutrients are cycled within ecosystems, from the soil to plants to animals and back to the soil. The cycling of nutrients is essential for the health and functioning of ecosystems.
- Diversity and stability: Ecosystems with a high level of biodiversity are more stable and resilient than those with low biodiversity. This is because a diverse range of species can respond to changes in the environment in different ways, reducing the risk of ecological collapse.
- Adaptation and evolution: Organisms adapt to their environment over time through evolution. This allows them to better cope with changes in their environment and increases their chances of survival.
- Human impact: Human activities, such as deforestation, overfishing, pollution, and climate change, have significant impacts on ecosystems and the species that depend on them. It is important to understand these impacts and develop sustainable practices that reduce their negative effects.
In conclusion, the principles of ecology provide a framework for understanding the complex relationships between organisms and their environment. By understanding these relationships, we can better protect ecosystems and the species that depend on them. Implementing sustainable land-use practices and reducing human impacts on the environment are essential for ensuring the long-term health and stability of ecosystems.
Read: Geography Notes