Soil erosion, degradation, and conservation are critical issues in modern agriculture and land management. Soil erosion is the removal of topsoil by natural forces such as wind and water, while soil degradation refers to the decline in soil quality due to human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and overuse of chemicals.
Conservation of soil involves protecting and preserving soil resources for future generations. In this article, we will discuss soil erosion, degradation, and conservation in detail.
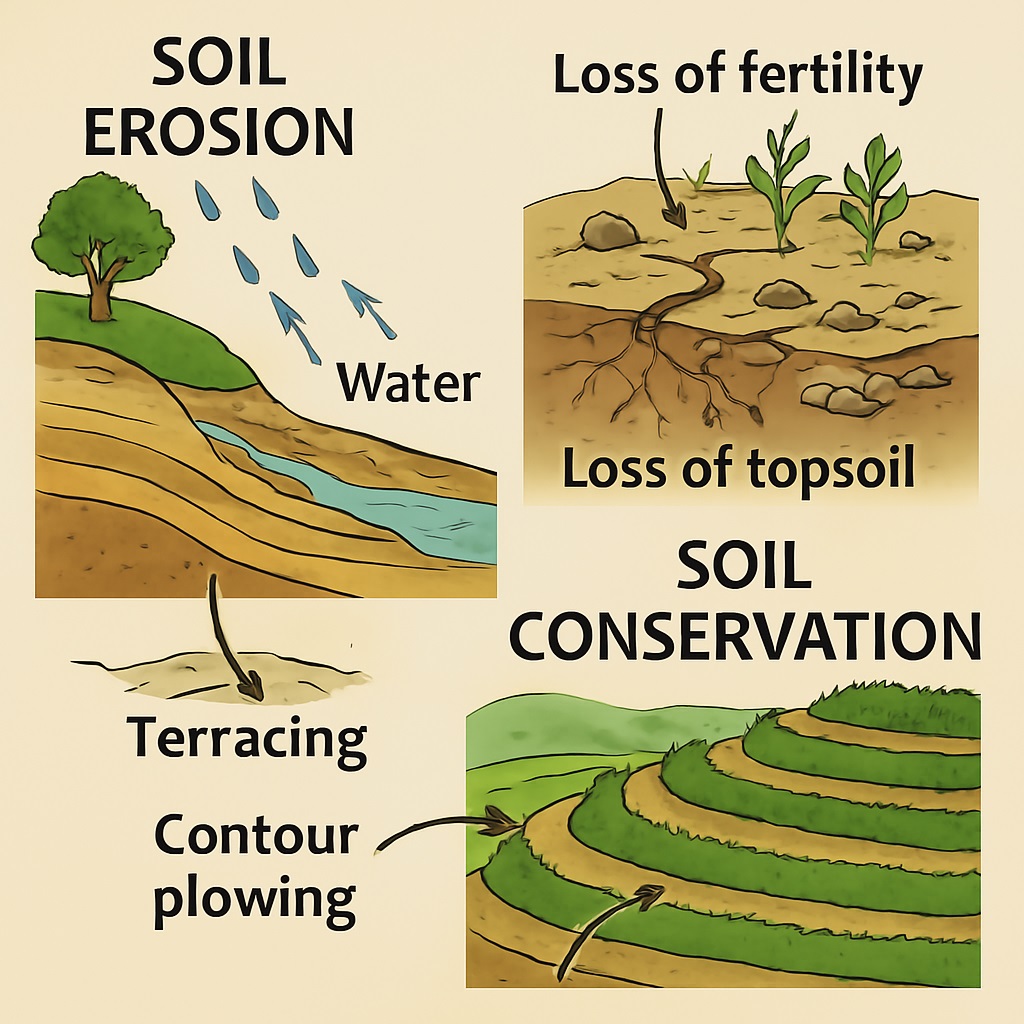
Table of Contents
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion means the removal or wearing away of the topsoil, which is the most fertile part. It happens naturally due to rain, wind, frost, and human activities, but when it becomes too fast or extreme, it leads to damage and loss of soil fertility.
There are three major types of soil erosion:
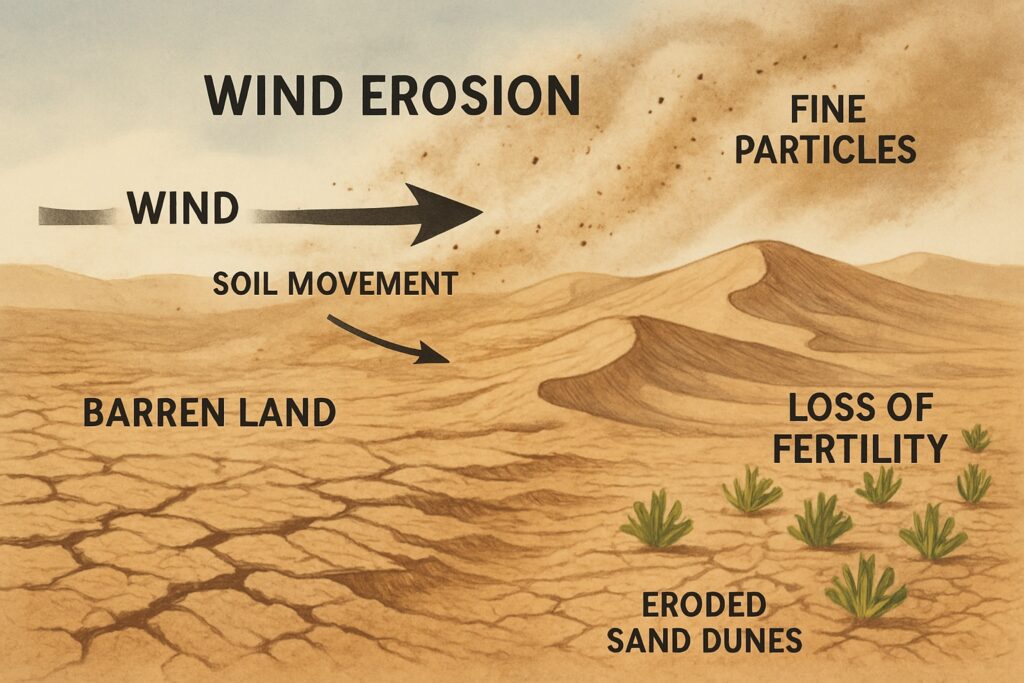
Wind Erosion
- Happens in deserts and dry areas.
- Strong winds blow away the fine soil particles, especially where there is no vegetation.
- This makes nearby farms and land less fertile.
- Example: The Thar Desert in India spreads into Gujarat, Rajasthan, Punjab, and Haryana.
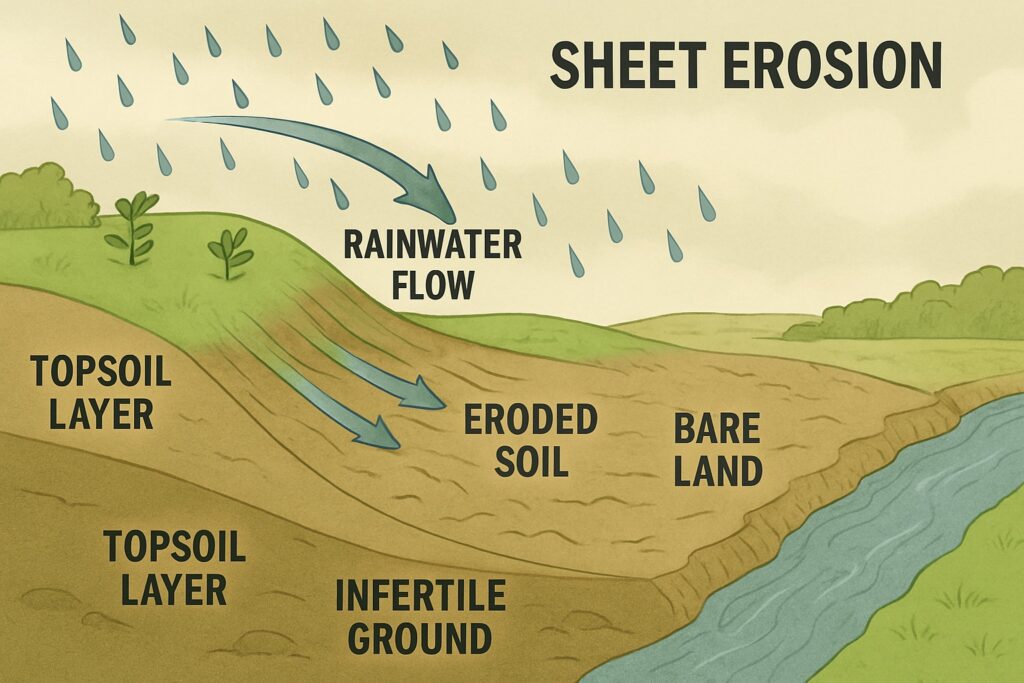
Sheet Erosion
- Happens when rainwater flows over land like a sheet and washes away thin layers of soil.
- Common along riverbanks and flood-prone areas.
- Over time, this causes the topsoil to disappear, leading to infertile land.
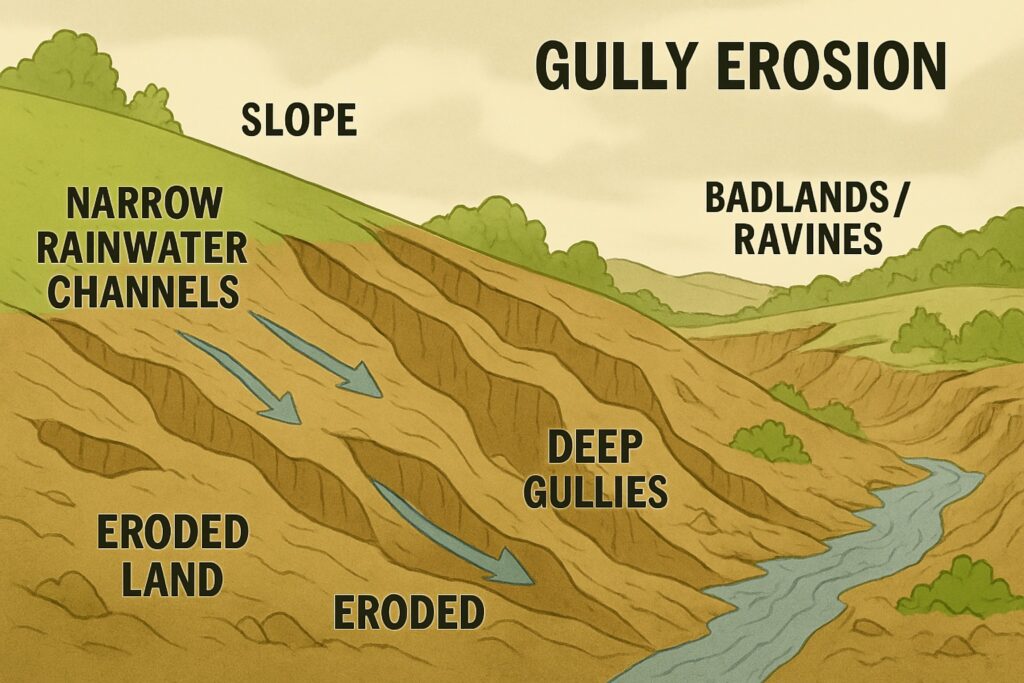
Gully Erosion
- Caused when rainwater flows down slopes in narrow channels.
- These channels cut deep gullies into the soil.
- Over time, many gullies can form, turning the land into badlands or ravines.
- Example: Ravines along the Chambal and Yamuna Rivers in Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
Other causes of erosion are:
- Seawaves, which erode coastlines.
- Melting snow and changing river paths, especially in hilly regions.
- Human actions like cutting forests, overgrazing, bad farming methods, and mining speed up erosion.
Important point: What takes nature thousands of years to form can be washed away in just a few years if erosion is not controlled.
Soil Degradation
Soil degradation refers to the decline in soil quality due to human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and the overuse of chemicals. Soil degradation results in the loss of fertile soil, reduced crop yields, and increased soil erosion. Additionally, soil degradation can lead to the contamination of water resources and the loss of biodiversity.
Soil Conservation
Soil conservation is the protection and preservation of soil resources for future generations. This involves the use of sustainable land management practices such as the use of cover crops, terracing, and the reduction of tillage. Soil conservation also involves the use of soil conservation technologies such as the use of conservation tillage practices and the use of soil-conserving crops.
Soil conservation means using methods to prevent the loss of soil and protect its fertility. This is important because soil takes thousands of years to form, but erosion can destroy it very quickly. Erosion also causes problems like floods, damaged roads and bridges, and clogged rivers due to sediment buildup.
Here are some main ways to conserve soil:
Protection of Forests
- Trees hold soil together with their roots and help prevent erosion.
- Cutting down forests (deforestation) increases erosion.
- Protecting forests by declaring them reserved areas is a key conservation method.
Afforestation (Planting Trees)
- Planting new trees in barren or empty areas helps prevent soil from being blown or washed away.
- This is very effective in desert and hilly areas.
Flood Control
- Building dams helps stop floods that cause soil erosion.
- Water from rivers can also be diverted to dry areas through canals.
Planned Grazing
- Too much grazing by animals removes plant cover and loosens the soil.
- Limiting grazing helps keep vegetation healthy, which protects the soil.
Bunding
- This means building walls or ridges across land to stop water from flowing too fast.
- It helps save water, reduce erosion, and keep soil fertile.
Terracing
- On mountain slopes, land is shaped into flat steps or terraces.
- This slows down water, prevents soil loss, and makes farming possible in hilly regions.
Contour Ploughing
- Instead of ploughing up and down slopes, farmers plough along the curves or contours.
- This method slows water flow and reduces erosion.
Strip Farming
- Farmers divide land into strips. They plant crops in one strip while leaving the other strip covered with grass to protect soil.
- Next year, they switch the strips. This keeps the land fertile and prevents erosion.
Crop Rotation
- Growing different crops each year helps prevent nutrient loss and protect soil fertility.
- It also gives the soil a chance to recover naturally.
Reclamation of Land
- Areas damaged by erosion, like gullies or ravines, can be leveled and improved.
- This method is used in places like the Chambal and Yamuna valleys in India.
Conclusion
Soil erosion, degradation, and conservation are critical issues in modern agriculture and land management. Soil erosion results in the loss of fertile soil, while soil degradation results in the decline in soil quality. Conservation of soil involves protecting and preserving soil resources for future generations. By using sustainable land management practices and soil conservation technologies, we can ensure the health and productivity of our soil resources for future generations.
Read: Geography Notes