The Solar System is a vast and complex system of celestial objects that orbit around a central star, the Sun. It is comprised of eight planets, several dwarf planets, numerous moons, asteroids, comets, and other small bodies. The Solar System is located in the Milky Way galaxy and is estimated to be around 4.6 billion years old.
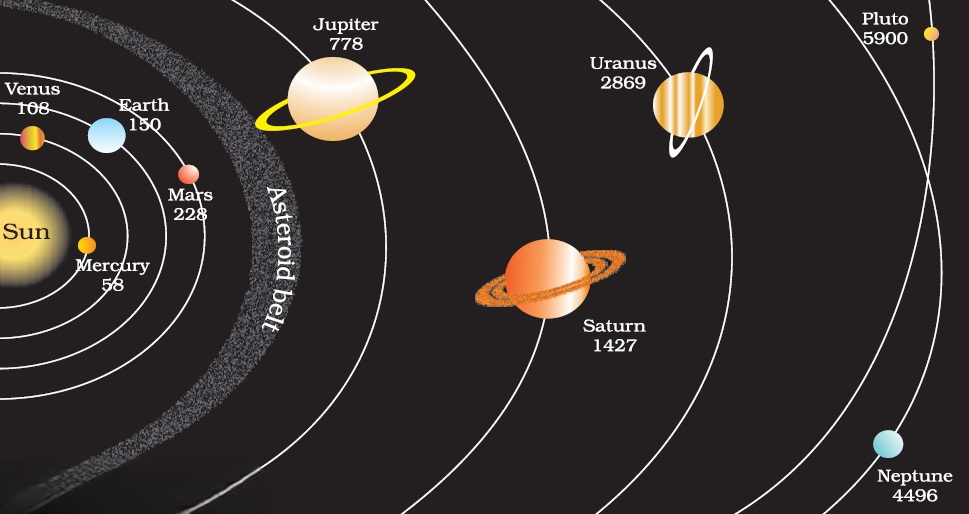
Table of Contents
The Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System and the source of life and energy for all living organisms on Earth. It is an extremely important celestial body that plays a crucial role in maintaining life on our planet.
- The Sun is a massive ball of hot plasma, containing about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System.
- It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium.
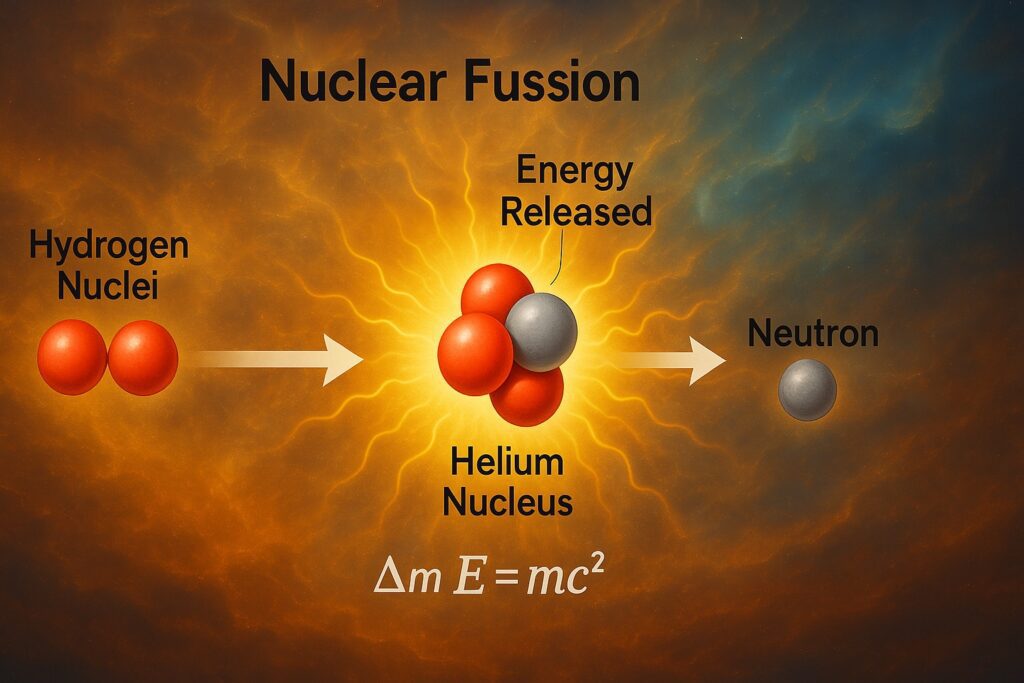
- The Sun is so large that about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside it.
- It is approximately 4.6 billion years old and is expected to shine for another 5 billion years.
- The Sun is the primary source of energy for all living organisms on Earth.
- Solar energy is produced by the Sun and is used by plants during photosynthesis to make food.
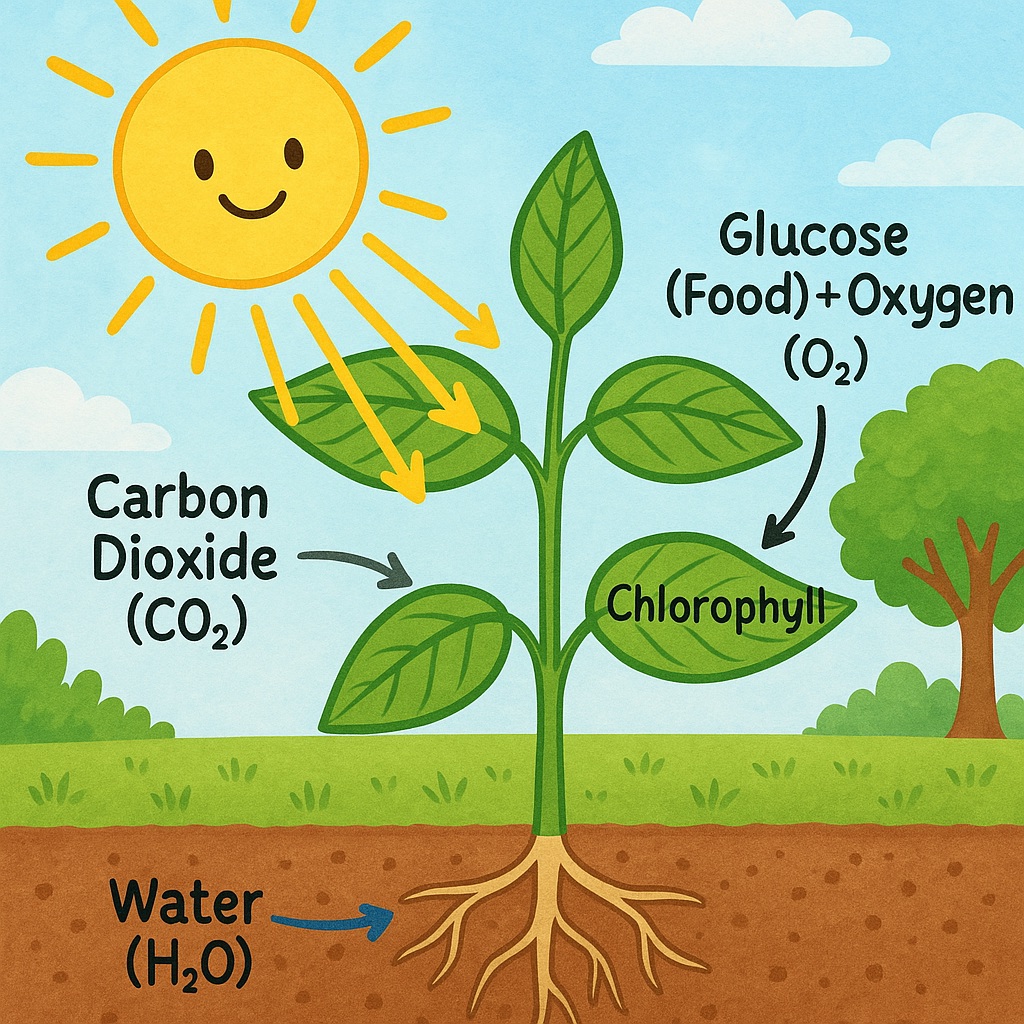
- Humans also harness solar energy through solar panels, which convert sunlight into electricity.
- The Sun regulates Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
- Its heat and light drive atmospheric circulation, influencing wind patterns, ocean currents, and rainfall.
- The Sun’s energy is crucial for the water cycle, which supports life on Earth.
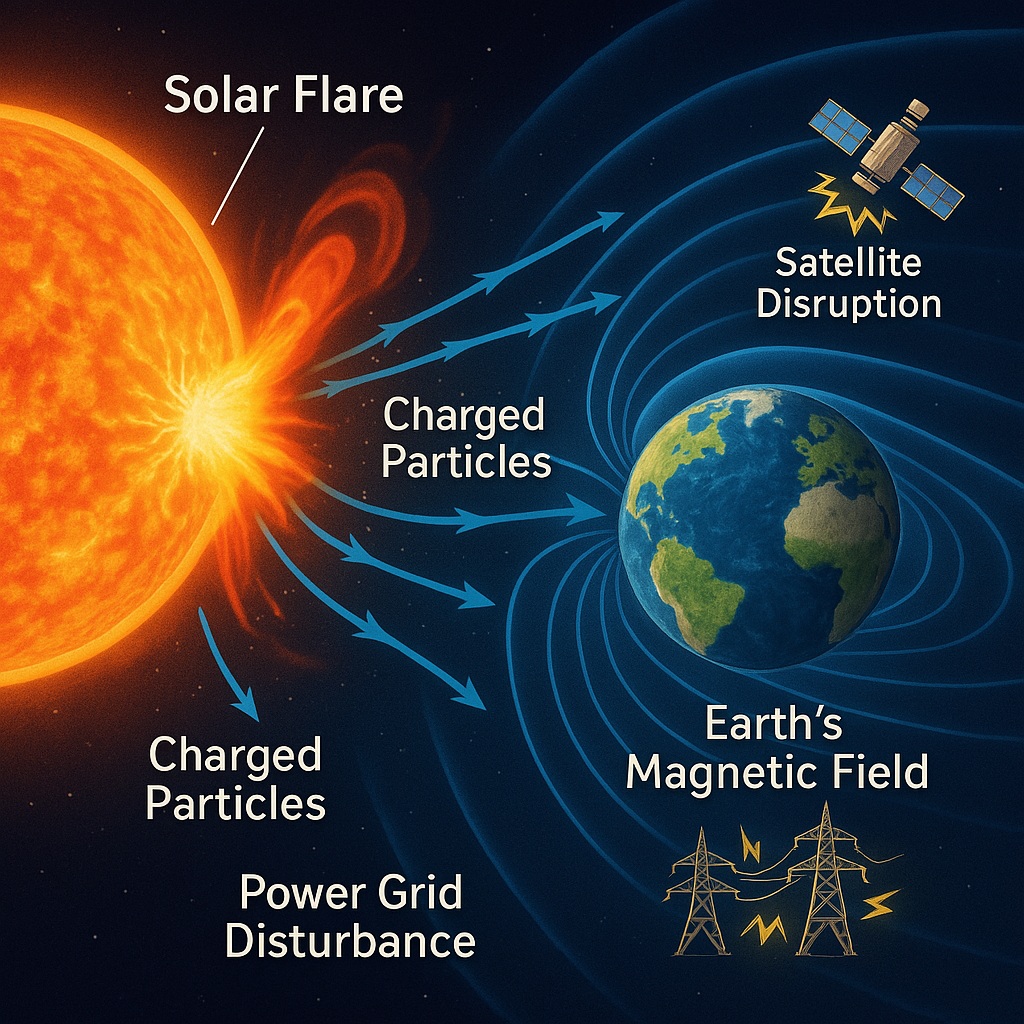
- The Sun can also pose threats to life on Earth.
- Solar flares can release high-energy particles that affect Earth’s magnetic field, disrupting communication and navigation systems.
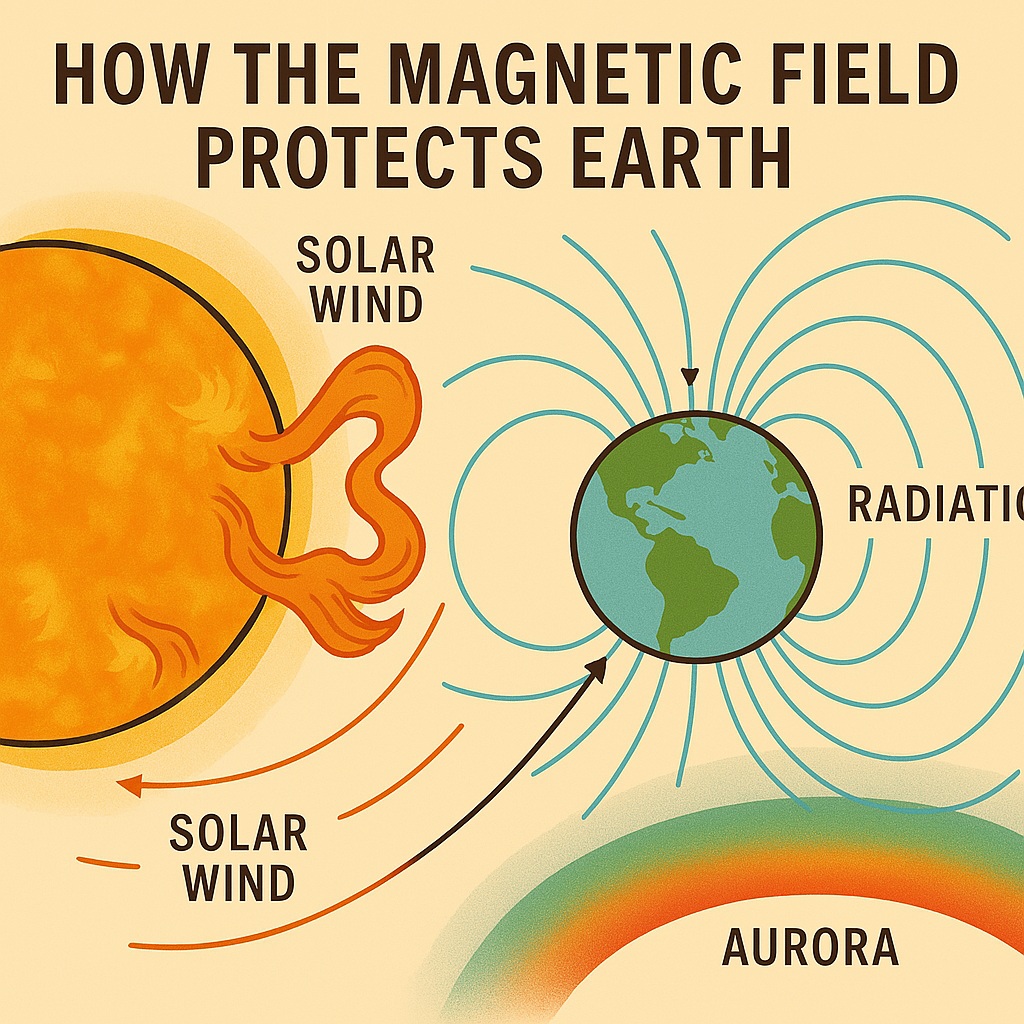
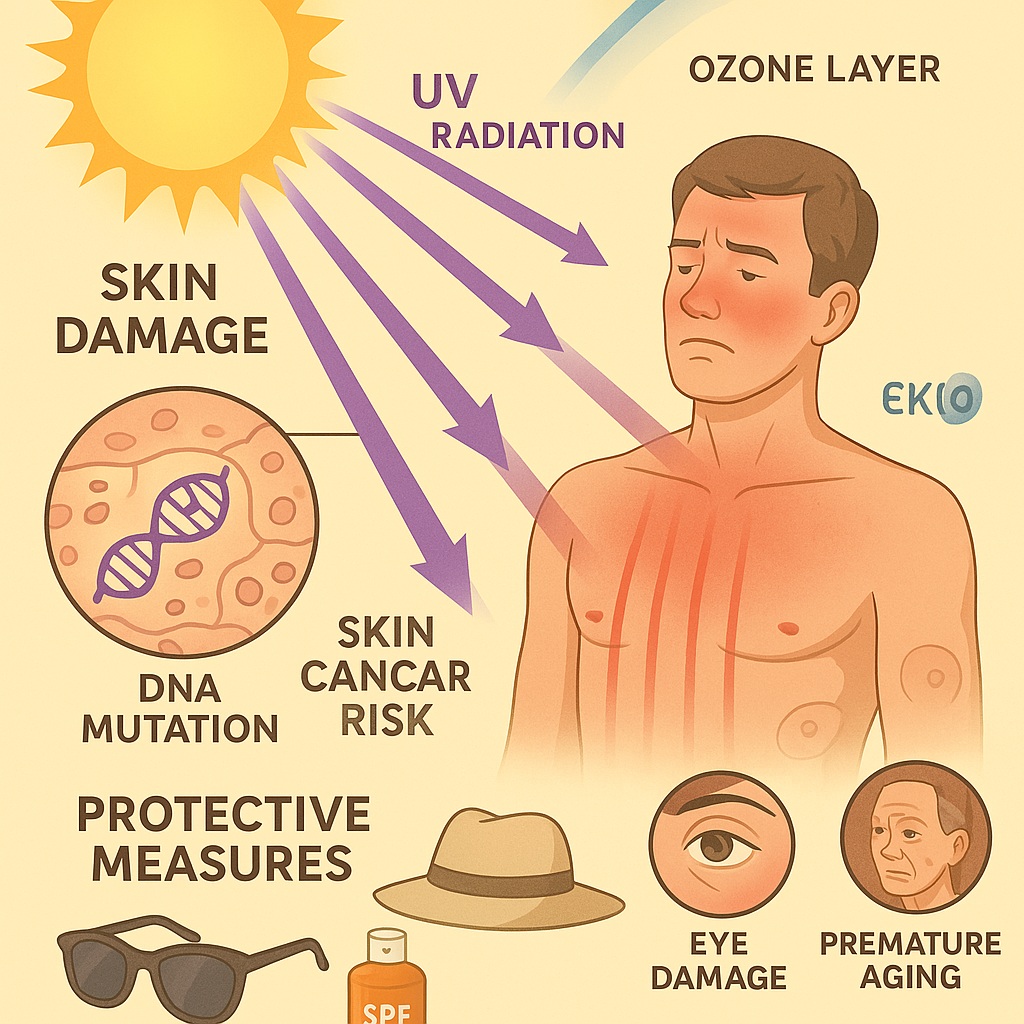
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun can cause skin cancer and other health issues.
Planets of Solar System
There are eight planets in the Solar System, and they are divided into two groups: the inner planets and the outer planets. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. They are also called the terrestrial planets because they are made of rock and have a solid surface. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. They are also called the gas giants because they are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium and have no solid surface.
Mercury
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System, and it is also the closest planet to the Sun. It has a rocky surface, and it has no atmosphere. Mercury is also known for its extreme temperature variations, with temperatures reaching as high as 800 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and dropping to minus 290 degrees Fahrenheit at night.
- Mercury completes one orbit around sun in 88 days.
- Mercury completes One spin on axis in 59 days.

Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, and it is similar in size and composition to Earth. It has a thick atmosphere that is primarily composed of carbon dioxide, and it is also the hottest planet in the Solar System, with temperatures that can reach up to 900 degrees Fahrenheit. In fact it is the hottest planet of the solar system due to green house effect.
- One orbit around the Sun: 225 days
- One spin on axis: 243 days

Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and it is the only planet in the Solar System that has life. It has a solid surface and a thin atmosphere that is rich in oxygen and nitrogen. Earth also has a strong magnetic field that protects it from harmful solar radiation.

- One orbit around the Sun: 365 days
- One spin on axis: 1 day
- Number of moons: 1
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and it is also known as the “Red Planet” because of its reddish appearance. It has a rocky surface, and it is also the planet in the Solar System that is most similar to Earth. Mars also has a thin atmosphere that is primarily composed of carbon dioxide.
"Mars is called the 'Red Planet' due to the presence of iron oxide on its surface"

- One orbit around the Sun: 687 days
- One spin on axis: 1 day
- Number of moons: 2
Jupiter
Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar System, and it is also one of the gas giants. It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, and it also has the most extensive planetary system in the Solar System, with 79 known moons.

- One orbit around the Sun: 11 years, 11 months (about 12 years)
- One spin on axis: 9 hours, 56 minutes
- Number of moons: 16
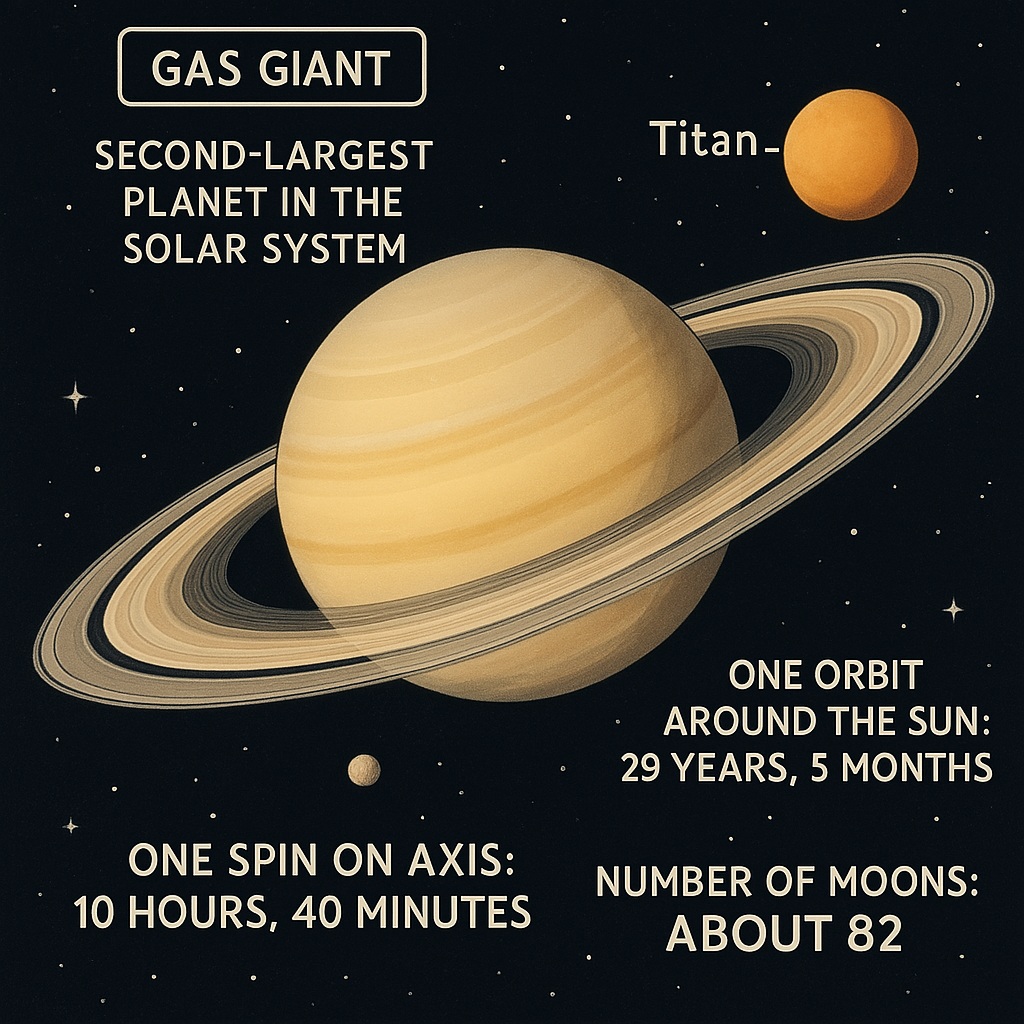
Saturn
Saturn is the second-largest planet in the Solar System, and it is also a gas giant. It is known for its beautiful rings, which are made of ice particles and rock fragments. Saturn also has 82 known moons, including Titan, which is the largest moon in the Solar System.
-
One orbit around the Sun: 29 years, 5 months
-
One spin on axis: 10 hours, 40 minutes
-
Number of moons: about 18
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun, and it is also a gas giant. It has a unique feature of being tilted at an angle of almost 98 degrees, which gives it its unusual appearance. Uranus also has 27 known moons.
-
One orbit around the Sun: 84 years
-
One spin on axis: 17 hours, 14 minutes
-
Number of moons: about 17
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun, and it is also a gas giant. It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, and it has 14 known moons. Neptune is also known for its strong winds, which can reach up to 1,500 miles per hour.
-
One orbit around the Sun: 164 years
-
One spin on axis: 16 hours, 7 minutes
-
Number of moons: 8
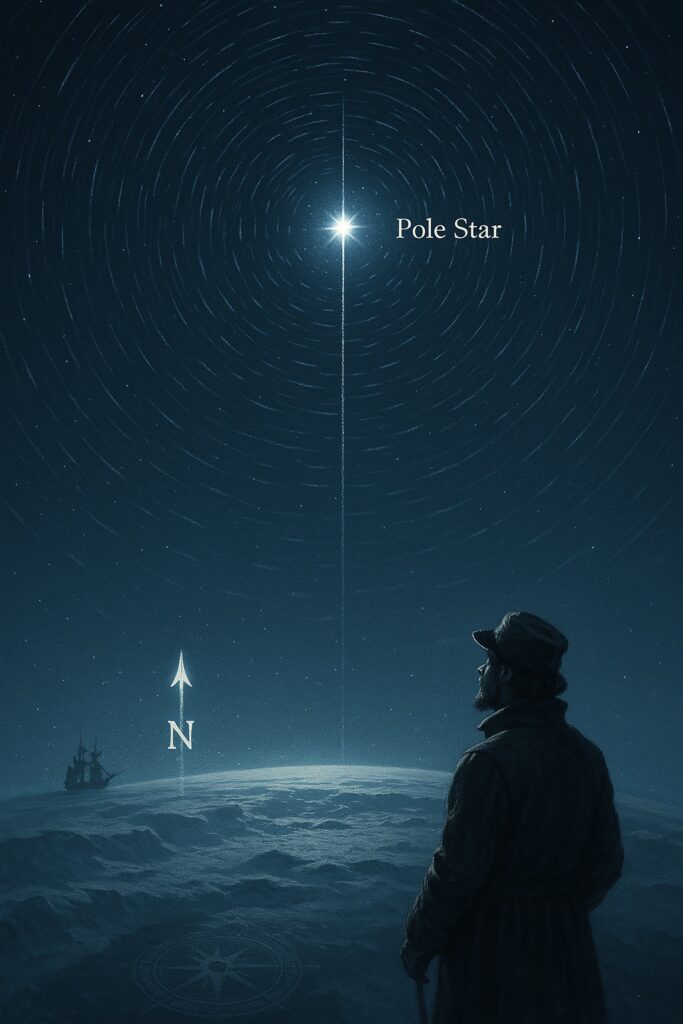
What is Pole Star?
Pole Star, also known as the North Star or Polaris, is a bright star that lies nearly in a direct line with the Earth’s rotational axis above the North Pole. This means:
- It appears fixed in the sky while all other stars seem to rotate around it.
- It always points toward true north, making it an important navigational reference for centuries.
- Used by sailors and travelers to find direction at night.
- Pole Star stays nearly stationary in the night sky.

Moons in Solar System
In addition to the planets, the Solar System is also home to numerous moons. Most of the moons in the Solar System are located in orbit around the gas giants, and they come in a wide range of sizes and compositions. Some of the most well-known moons in the Solar System include Titan, which is the largest moon of Saturn, and Ganymede, which is the largest moon of Jupiter.
Asteroids
Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun, and they are often called minor planets. Most of the asteroids in the Solar System are located in the asteroid belt, which is located between Mars and Jupiter.
"Scientists believe asteroids are fragments of a planet that exploded long ago."
- The largest asteroid is Ceres.
Comets
Comets are icy bodies that orbit the Sun, and they often have a tail that is visible from Earth. Comets are thought to be remnants from the early Solar System and are made up of ice, dust, and rock. Some of the most well-known comets in the Solar System include Halley’s Comet and Comet Hale-Bopp.
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper Belt is a region of the Solar System located beyond Neptune’s orbit that is home to numerous small, icy objects, including dwarf planets and comets. Pluto was once considered the ninth planet in the Solar System but was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 and is now considered a member of the Kuiper Belt.
Exoplanets
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars outside of our Solar System. Since the first exoplanet was discovered in 1995, astronomers have discovered thousands of exoplanets using a variety of detection methods. Exoplanets come in a wide range of sizes and compositions, and some may even be habitable.
Formation of the Solar System
The System formed around 4.6 billion years ago from a giant cloud of gas and dust called a nebula. As the nebula collapsed, it formed a disk-like structure, with the Sun forming at the center and the planets forming from the leftover gas and dust in the disk. The process of planet formation is complex and involves gravity, collisions, and other forces.
Role of Gravity in Solar System
Gravity is a fundamental force in the Solar System and is responsible for keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun. Gravity also plays a role in the formation of the Solar System, as it causes the gas and dust in the disk to clump together and form larger objects.
Read: Geography Notes