Oceanic waves are rhythmic movements of the sea surface, generated by the transfer of energy from the atmosphere to the ocean. They are one of the most visible and dynamic expressions of ocean energy. Waves play a significant role in shaping coastlines, aiding marine navigation, driving coastal erosion, and influencing global ocean circulation. In this article, we will explore the causes, effects, and importance of oceanic waves in depth.
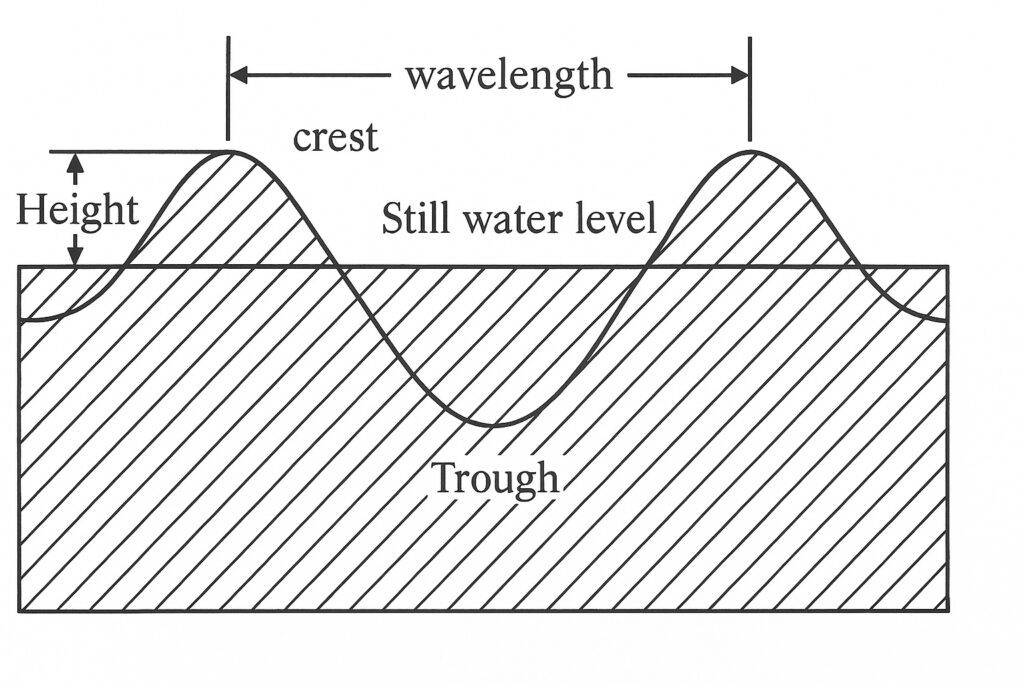
Table of Contents
Causes of Oceanic Waves
Oceanic waves are caused by a variety of factors, including wind, tides, earthquakes, and underwater landslides. Wind is the most common cause of oceanic waves, as it blows across the surface of the ocean, creating ripples that grow into larger waves. Tides are also a significant cause of oceanic waves, as the gravitational pull of the moon and sun creates currents that cause the ocean to rise and fall.

Earthquakes and underwater landslides can also cause oceanic waves, as the seismic energy from these events is transferred to the ocean and creates powerful waves. These waves can travel great distances, causing damage and destruction to coastal communities and ecosystems.
Effects of Oceanic Waves
It has far-reaching effects on the Earth’s climate, coastline, and ecosystems. They play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s coastlines, eroding the land and creating new features such as cliffs, coves, and bays. The energy from oceanic waves can also cause underwater landslides, which can have a significant impact on the ocean’s ecosystems and the distribution of marine life.
It also have a significant impact on the Earth’s climate, as they play a role in transporting heat and energy from one part of the ocean to another. This helps to regulate the planet’s temperature, making the climate more stable and predictable.
Importance of Oceanic Waves
They are an important part of the Earth’s natural systems, and their importance cannot be overstated. They play a crucial role in shaping the planet’s coastlines, regulating its climate, and supporting its ecosystems. Additionally, oceanic waves are a vital source of renewable energy, with the potential to generate electricity through wave energy converters.
Trough and Crest of Ocean Wave
Ocean waves are characterized by a repeating pattern of crests and troughs. A crest is the highest point of a wave, while a trough is the lowest point of a wave. The distance between two adjacent crests or troughs is the wavelength of the wave.
As an ocean wave moves through the water, the water particles move in circular orbits. As the wave approaches, the water particles move upward, away from their resting position. This creates a crest in the water surface. As the wave passes by, the water particles move downward, creating a trough.
The amplitude of a wave is the distance from the resting position of the water surface to the crest or trough. The height of a wave is the distance from the crest to the adjacent trough. The steepness of a wave is the ratio of the wave height to the wavelength.
The behavior of ocean waves is important for a wide range of activities, including shipping, offshore oil drilling, and recreational activities such as surfing. Understanding the characteristics of ocean waves, including their crests and troughs, is crucial for predicting their behavior and their effects on coastal areas.