Oceanic Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea levels that occur along coastlines across the globe. They are one of the most observable and predictable movements in the ocean. Tides are primarily caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on Earth’s oceans, combined with the Earth’s rotation. It occurs roughly every 12 hours and 25 minutes.
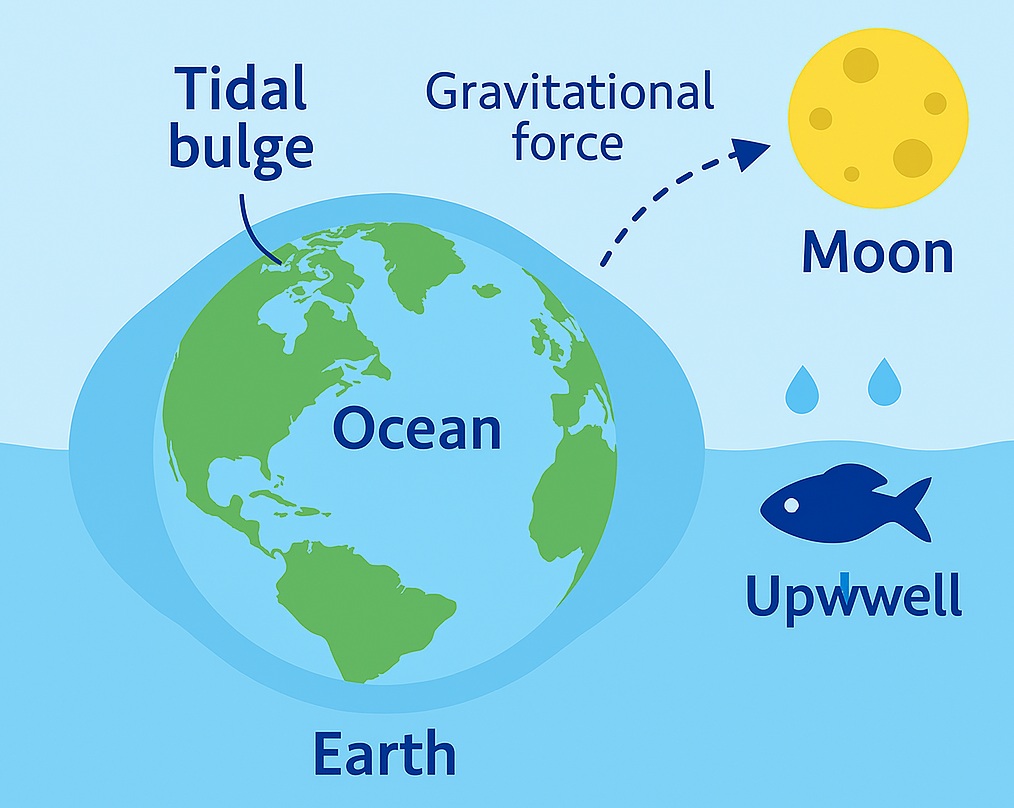
Table of Contents
What are Oceanic Tides?
Oceanic tides are the periodic rise and fall of sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the Earth’s water. Tides are created by the friction between the ocean and the ocean floor, causing water to move towards the shore in a slow, rhythmic cycle. The result of this cycle is a predictable pattern of high and low tides that occur every 12 hours and 25 minutes.
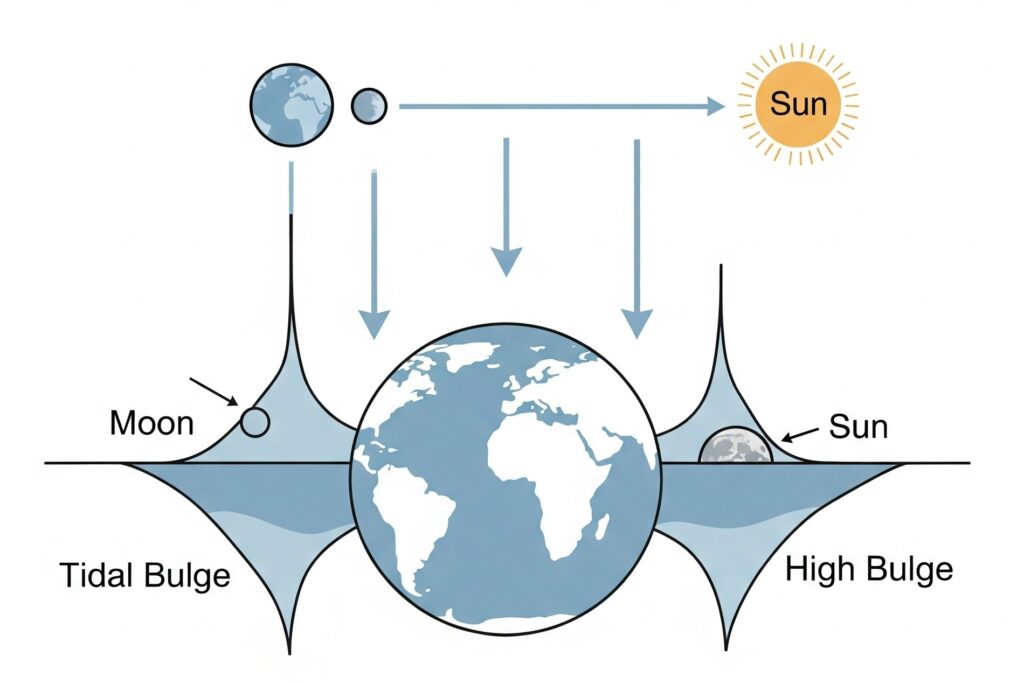
There are two main types of oceanic tides: spring tides and neap tides. Spring tides occur when the moon and the sun are in alignment, causing the gravitational pull of these two celestial bodies to combine and create a larger tidal bulge.
Neap tides occur when the moon and the sun are at right angles to one another, reducing the gravitational pull and creating a smaller tidal bulge.
What Causes Oceanic Tides?
Oceanic tides are caused mainly by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the Earth’s water. The gravitational pull of these two celestial bodies creates a tidal bulge in the ocean, causing the water to move towards the shore in a slow, rhythmic cycle.
"The Moon causes two high tides and two low tides roughly every 24 hours and 50 minutes."
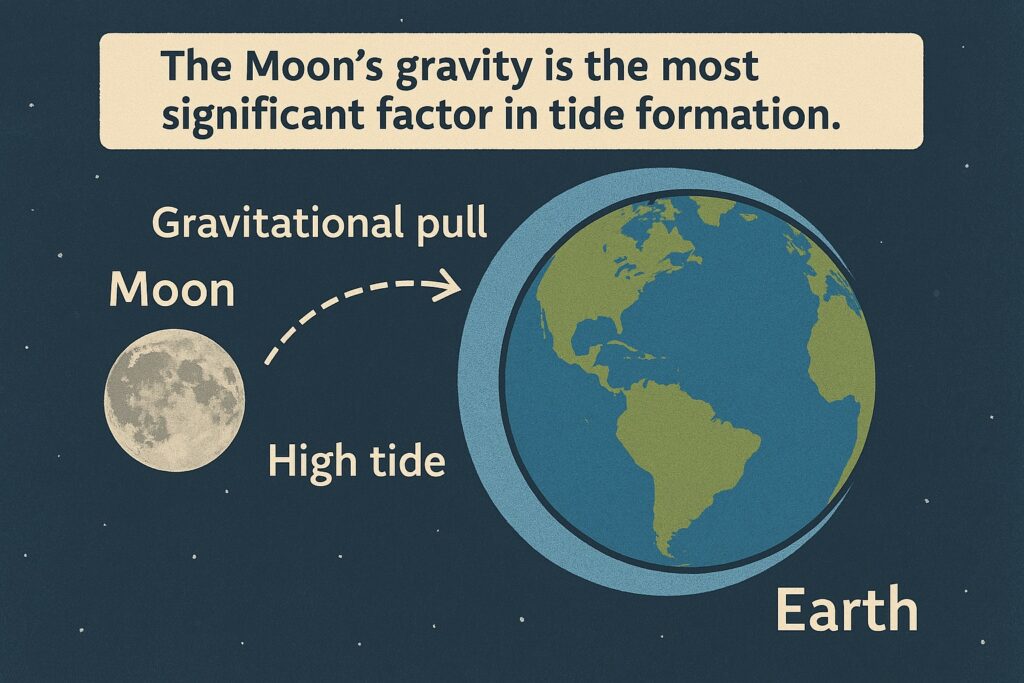
1. Gravitational Pull of the Moon
-
The Moon’s gravity is the most significant factor in tide formation.
-
As the Moon orbits Earth, its gravitational force pulls the ocean water toward it.
-
This causes a bulge of water (high tide) on the side of Earth facing the Moon.
-
Simultaneously, a second bulge forms on the opposite side of the Earth. This is due to inertia — the tendency of the water to continue moving outward as Earth and Moon revolve around a common center of mass located inside Earth.
-
These two bulges cause two high tides on most coastlines in a day.
2. Gravitational Pull of the Sun
-
The Sun’s gravity also affects tides, though it is less influential than the Moon’s because it is much farther away.
-
When the Sun and Moon align (during New Moon and Full Moon), their combined gravitational pull enhances the tides, leading to Spring Tides.
-
When the Sun and Moon form a right angle (during First and Third Quarters), their opposing forces reduce tidal range, resulting in Neap Tides.
"Effect of the Sun: Even though it's 27 million times more massive than the Moon, its influence on tides is about 46% of the Moon’s."
3. Centrifugal Force (Inertia)
-
As Earth and the Moon revolve around their shared center of mass, centrifugal force is generated.
-
This force acts away from the Moon, causing water on the far side of Earth to form another high tide bulge.
-
Thus, one high tide is caused directly by the Moon’s pull, and the second high tide is caused by centrifugal force.
4. Earth’s Rotation
-
Earth rotates on its axis, moving under the tidal bulges.
-
As a result, any given coastal location typically experiences two high tides and two low tides in a 24-hour and 50-minute period.
-
This rotation causes the timing of tides to shift by about 50 minutes each day.
5. Shape and Depth of Ocean Basins
-
The topography of the ocean floor, shape of the coastline, and depth of water bodies also influence tidal patterns.
-
Narrow bays, inlets, and estuaries can amplify tides, sometimes leading to extreme tidal ranges like in the Bay of Fundy (Canada).
6. Alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun
- The relative position of these three celestial bodies determines the type of tide:
- Spring Tides: Occur during New Moon and Full Moon, when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are in a straight line. The gravitational pull is strongest, resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides.
- Neap Tides: Occur during the First Quarter and Last Quarter of the Moon, when the Sun and Moon are at right angles. Their gravitational pulls partly cancel out, leading to lower high tides and higher low tides.
Types of Tides
- Spring Tides: These are extra high and extra low tides. They occur during New Moon and Full Moon when the sun, moon, and Earth are in a straight line. The sun and moon pull the water together, making the tides stronger.
- Neap Tides: These are weaker tides. They happen during the first and third quarter of the moon when the sun and moon pull the water in different directions, canceling each other out.
Impact of Oceanic Tides on the Ocean and Coastline
Oceanic tides play a crucial role in shaping the world’s oceans and coastlines. The constant rise and fall of sea level creates ocean currents and waves that transport sediment and nutrients along the shore, helping to build and reshape coastlines over time.
Tides also play a crucial role in the mixing of ocean water, as the rise and fall of sea level creates currents that mix water from the surface with water from the depths. This mixing helps to distribute heat, nutrients, and dissolved gases throughout the ocean, helping to regulate the Earth’s climate and support a diverse range of marine life.
In addition to these environmental benefits, oceanic tides also have practical applications for human societies. Tidal energy, for example, is a renewable source of energy that can be harnessed from the rise and fall of sea level. Tides can also be used to predict weather patterns and to navigate the open ocean.
Conclusion
Tides are caused by a complex interplay of gravitational forces, centrifugal force, Earth’s rotation, and local geography. While the Moon has the greatest influence, the Sun and the dynamic motion of Earth also play crucial roles. These combined forces give rise to the rhythmic and predictable nature of tides that influence life and activity in coastal regions.
The moon has the largest effect on oceanic tides, as it is much closer to the Earth than the sun and its gravitational pull is therefore stronger. However, the sun also has an impact on tides, as its gravitational pull combines with that of the moon to create spring tides.
In addition to the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun, oceanic tides are also influenced by other factors such as wind patterns, water density, and the shape of the ocean floor. These factors can cause variations in the height and timing of tides, creating unique tidal patterns in different regions of the world.