Rural settlements are small communities in non-urban areas where people primarily engage in agriculture and related activities. Their form, structure, and distribution depend on several natural and cultural factors. Studying these settlements helps in understanding rural life, planning infrastructure, and supporting regional development.

Table of Contents
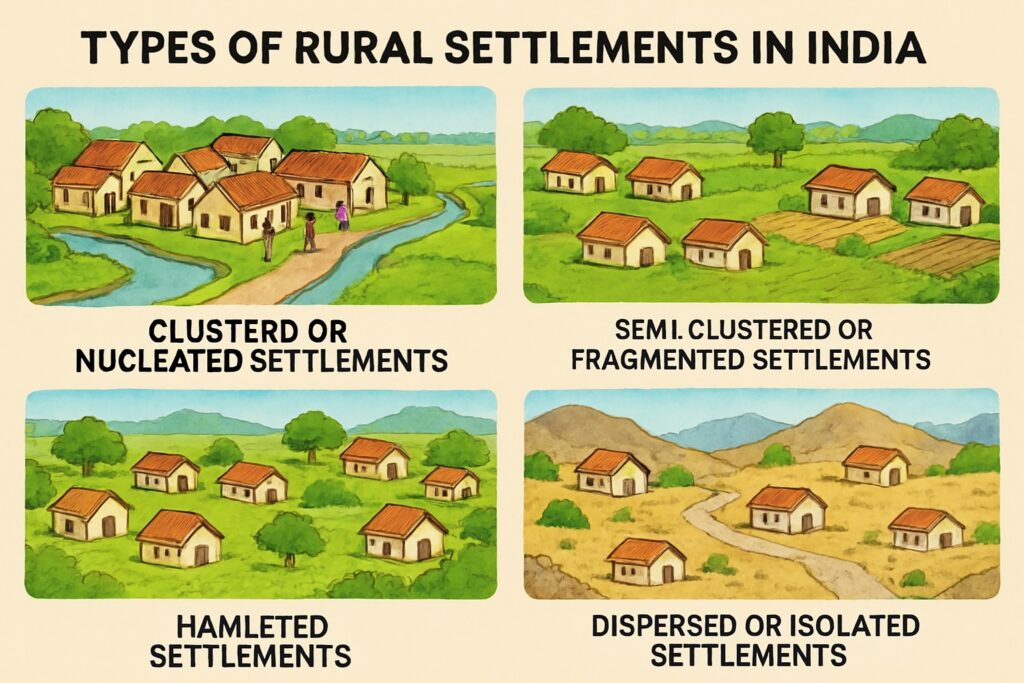
Types of Rural Settlements
Clustered or Nucleated Settlements
These are compact settlements where houses are grouped together. Such settlements are found in fertile plains with good water supply. They allow for better social interaction, safety, and sharing of resources. Examples include villages in Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar.
Semi-clustered or Fragmented Settlements
In these settlements, homes are partly grouped but may also be separated. This type often results from land division, social divisions, or migration of families. They can be found in areas experiencing agricultural expansion or social shifts.
Hamleted Settlements
The main village is broken into several small hamlets or tolas. Each hamlet may be inhabited by a particular caste or community. This type is common in tribal areas and hilly regions like Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
Dispersed or Isolated Settlements
Here, houses are scattered over large areas. This type is found in areas with rough terrain, poor soil, or limited water. People live near their farmland rather than in a central village. Such patterns are seen in parts of Rajasthan and the Himalayan region.
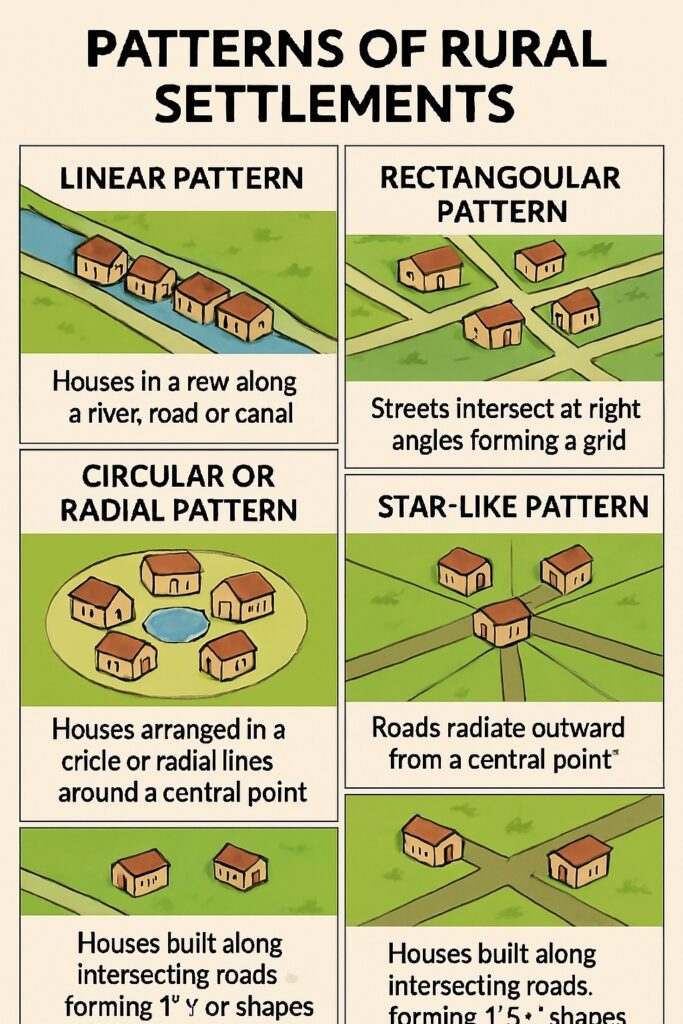
Patterns of Rural Settlements
Linear Pattern
Houses are built along roads, rivers, or canals. This pattern is common in river valleys and coastal areas, where transportation and water access are important.
Rectangular Pattern
Settlements are laid out with streets crossing at right angles. This type is usually found in flat areas with planned agricultural fields, such as parts of Haryana and Punjab.
Circular or Radial Pattern
Houses are arranged around a central point like a temple, pond, or marketplace. This helps ensure easy access to water or common resources and is common in dry regions.
Star-like Pattern
Roads spread out from a central point like a star, and houses are built along these routes. This form is often seen in developing rural areas with expanding road networks.
T-shaped, Y-shaped, or Cross-shaped Pattern
These patterns emerge where roads meet or cross each other, forming specific shapes. They are found in plain regions with good transportation links.
Factors Influencing Rural Settlements
- Topography: Hilly and mountainous areas usually have dispersed settlements, while plains support clustered ones.
- Climate and Water Availability: Regions with adequate rainfall or irrigation favor compact settlements.
- Soil Fertility: Fertile regions encourage dense population and nucleated settlements.
- Social and Cultural Practices: Caste, religion, and land ownership influence how people organize their villages.
- Historical and Security Reasons: In earlier times, threats from animals or invaders encouraged people to live close together.
Conclusion
Rural settlements reflect how people adapt to their environment and organize their lives around natural resources and cultural traditions. Understanding the types and patterns of these settlements is essential for planning rural development, improving infrastructure, and promoting sustainable growth.
Read: Geography Notes