The Marxian Model in human geography provides a critical perspective on the social and economic inequalities shaped by capitalism. It emphasizes how the control of the factor of production (land, labor, and resources) leads to social stratification, uneven development, and exploitation.
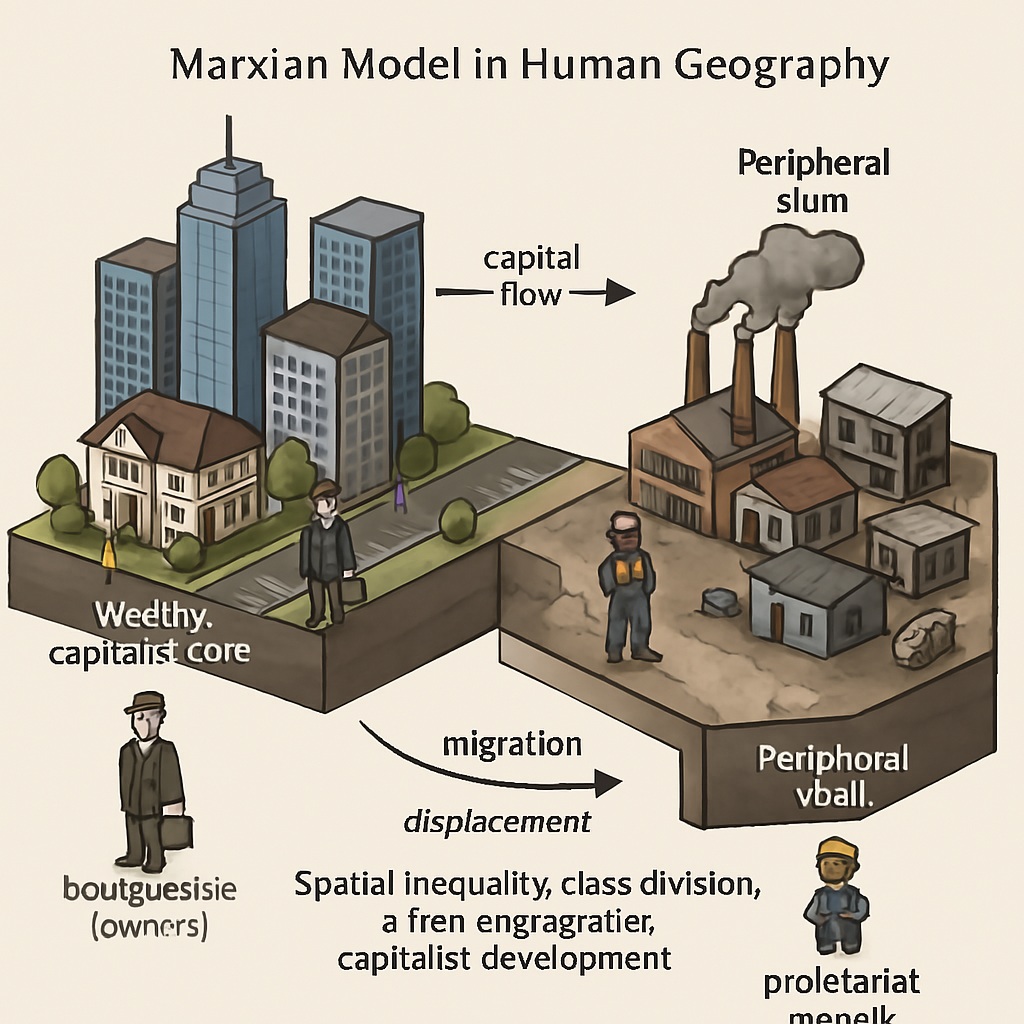
The Marxian Model, based on the ideas of Karl Marx, offers a critical framework to understand how economic structures, especially capitalism, shape spatial organization, urban development, and social inequality. By analyzing urbanization, labor distribution, and environmental degradation, the Marxian approach helps in understanding the structural forces behind spatial inequalities worldwide.
Table of Contents
Capitalism and Exploitation in Marxian Model
At the heart of the Marxian model is the concept of capitalism and the exploitation of the working class by the capitalist class. According to Marx, the accumulation of capital by the capitalist class is the main driving force of economic growth. However, this growth comes at the expense of the working class, who are paid low wages and work in poor conditions.
In human geography, this exploitation is evident in the uneven development of different regions and countries. Capitalist countries often exploit the resources and labor of developing countries, leading to economic and social inequalities. This can result in the concentration of wealth in certain regions, while others are left in poverty.

Zero-Sum Game of Development
The Marxian model views development as a zero-sum game where one class benefits at the expense of the other. In order to achieve true development, Marx believed that the working class must overthrow the capitalist class and establish a socialist system.
This perspective is important in human geography as it highlights the inequalities that can arise in capitalist societies. The Marxian model also emphasizes the importance of political action and social movements in achieving economic and social justice.
Overthrowing the Capitalist Class for True Development
It emphasizes the importance of collective action and political mobilization in achieving true development. In order to overthrow the capitalist class, the working class must unite and organize to challenge the existing power structures.

The Marxian model is an important framework for understanding social and economic development in human geography. This model emphasizes the role of capitalism and exploitation in shaping economic and social conditions and highlights the importance of political action and social movements in achieving true development. By understanding the power dynamics and inequalities that arise in capitalist societies, human geographers can work to promote economic and social justice and support sustainable development.
Read: Geography Notes