The location of any industry is influenced by several geographical and economic factors. For the Iron and Steel Industry, which is both resource-intensive and capital-heavy, location plays a critical role in operational efficiency and cost management. The iron and steel industry is a significant contributor to the Indian economy, providing employment and contributing to the country’s GDP. In India, the distribution of steel plants reflects the influence of various locational determinants.
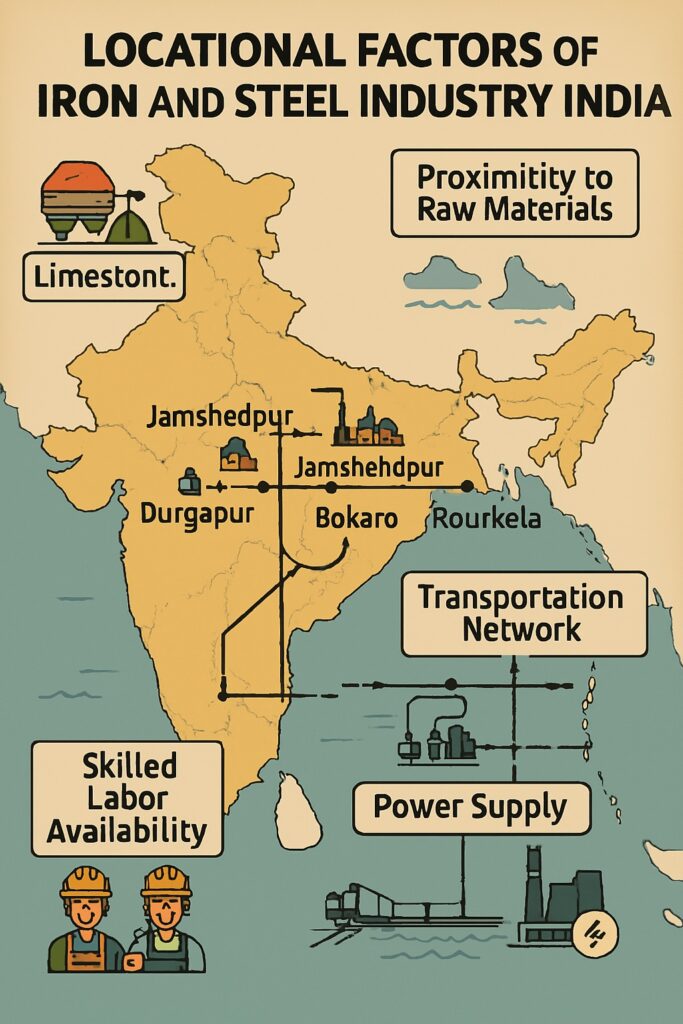
Table of Contents
Availability of Raw Materials
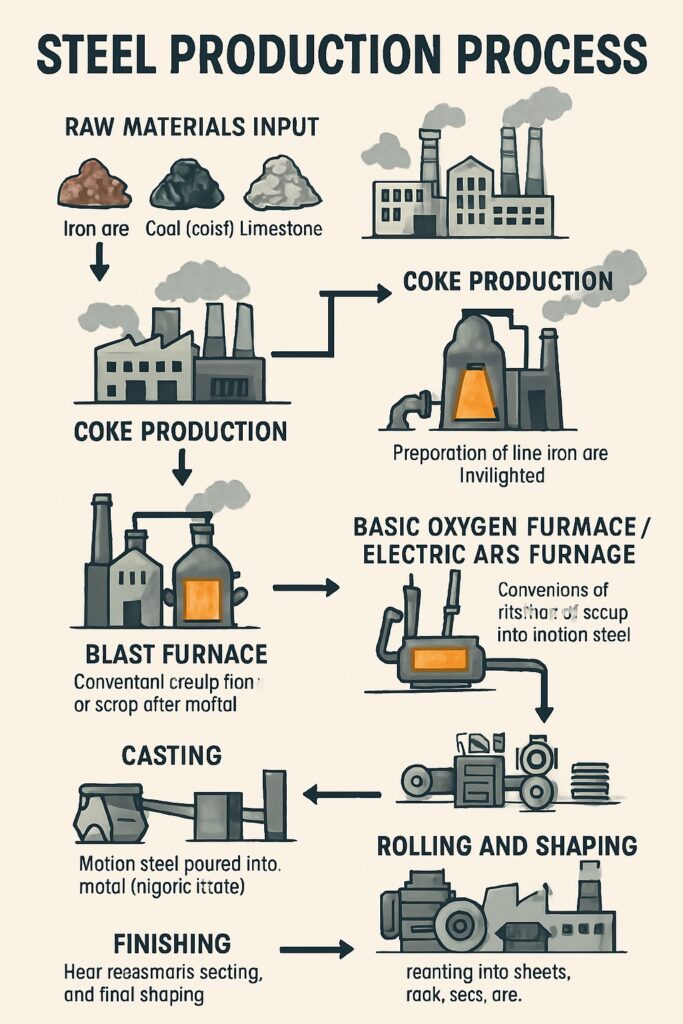
The availability of raw materials such as iron ore, coal, and limestone is a crucial factor in the iron and steel industry. Regions with abundant sources of raw materials are ideal for iron and steel production.
-
Iron ore is the basic raw material for steel production. It is bulky and heavy, so proximity to iron ore mines is a major factor.
-
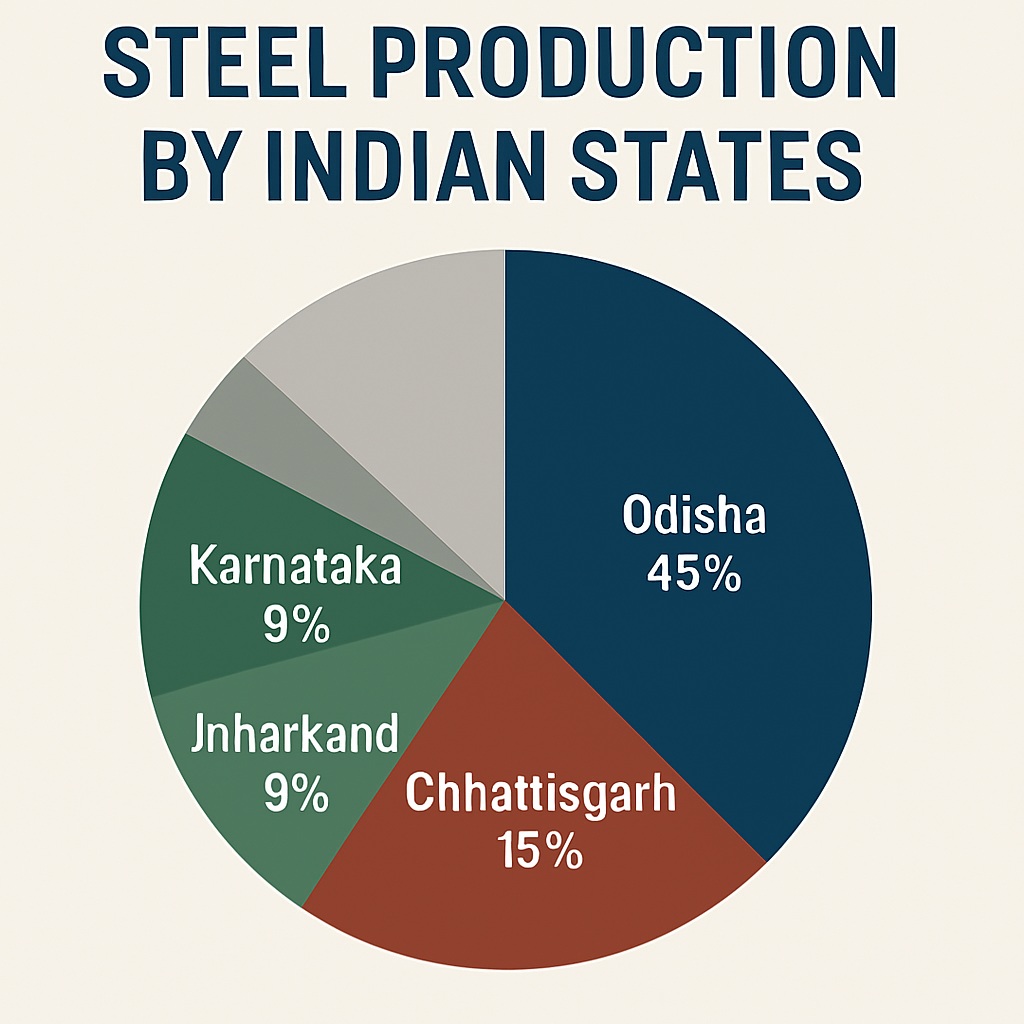
Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Karnataka are rich in high-grade iron ore.
-
Coking coal is another essential raw material, used as a reducing agent. It is not found in sufficient quantity in India, so it is often imported, but domestic supplies from Jharkhand and West Bengal are still significant.
-
Other materials like limestone, dolomite, and manganese are also critical and are available in central and eastern India.
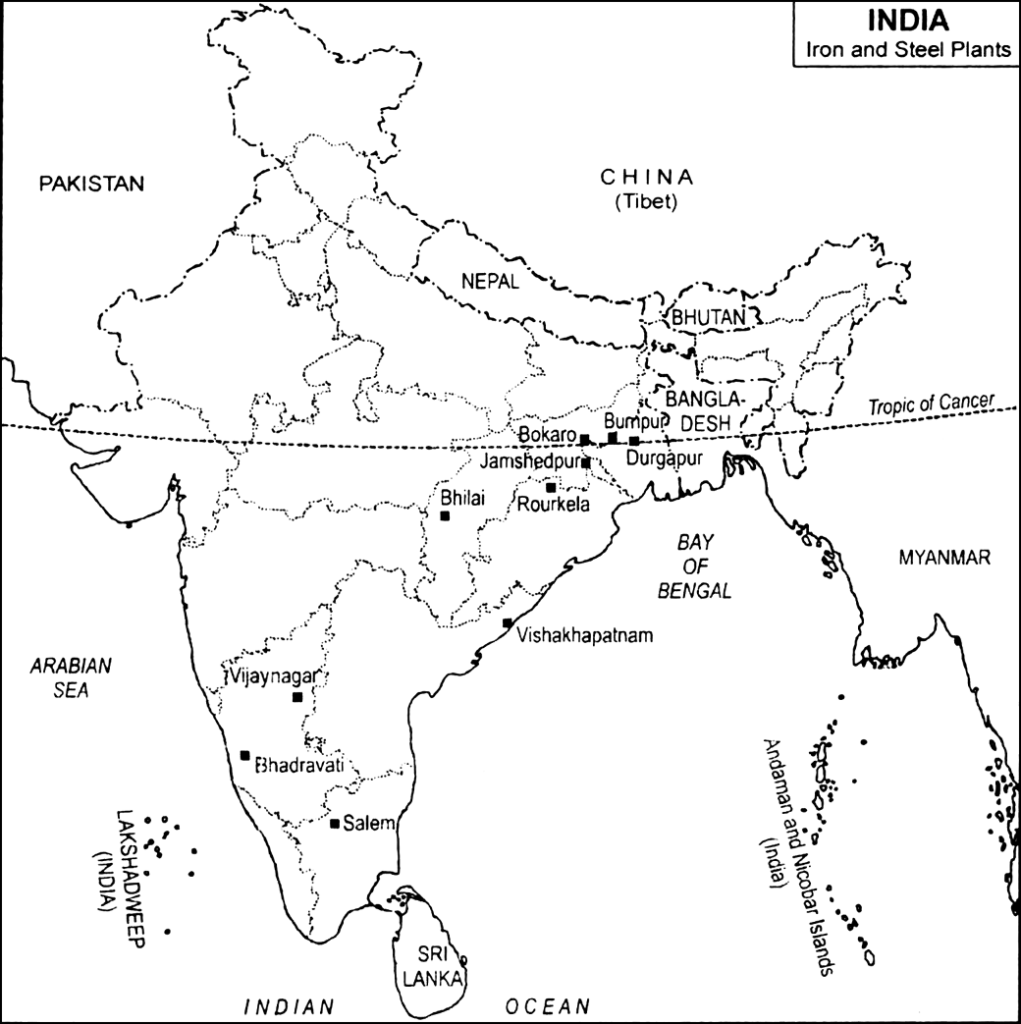
Example: The Bhilai Steel Plant is located in Chhattisgarh, close to iron ore (Dalli-Rajhara mines) and coal (Korba and Jharia).
In India, the major sources of iron ore are located in the states of Odisha, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh. The coal reserves in Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal provide a stable source of energy for iron and steel production. Limestone is also found in abundance in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
" Indian coal reserves primarily consist of low-grade and high-ash content coal, which is not suitable for producing high-quality steel."
Proximity to Markets
Proximity to markets is a critical factor in the iron and steel industry, as steel products are heavy and costly to transport. Regions with easy access to markets are ideal for iron and steel production, as they ensure that the products can be transported quickly and efficiently to the markets. The major iron and steel producing regions of India, such as Jamshedpur, Rourkela, Bhilai, and Bokaro, are located near major cities and towns, which act as significant steel markets.
-
While raw materials are the dominant factor, access to major steel-consuming markets is also crucial.
-
Proximity to construction hubs, automobile manufacturing centers, and ports boosts profitability.
Example: JSW Steel’s plant in Vijayanagar (Karnataka) benefits from being close to the southern market and export ports like Goa and Mangalore.
Access to Water and Power
The iron and steel industry requires a significant amount of water and power for production. Regions with access to a regular supply of water and power are ideal for iron and steel production. The major iron and steel producing regions of India are located near rivers, which provide a steady source of water for industrial use. The availability of power is also an essential factor in the industry, and regions with easy access to thermal or hydroelectric power are preferred for iron and steel production.
-
Steel production is highly energy-intensive.
-
Thermal power (coal-based) plants near coalfields help meet energy demands.
-
The use of captive power plants by companies like Tata Steel ensures reliable energy supply.
Transportation Infrastructure
The transportation infrastructure plays a crucial role in the iron and steel industry. Regions with well-developed transportation networks, such as railways, roads, and ports, are ideal for iron and steel production. The major iron and steel producing regions of India have access to major transportation hubs, such as Kolkata port, Paradeep port, and various national highways, which ensure easy transport of raw materials and finished products.
Labour Availability
-
Both skilled and unskilled labour is required.
-
Industrial areas in eastern India have developed a steady workforce through training institutions and nearby rural populations.
Government Policies
Government policies, such as incentives and subsidies, play a key role in the growth and success of the iron and steel industry. The government policies related to taxation, labor laws, and infrastructure development have a significant impact on the industry. In India, the government has taken various steps to promote the growth of the iron and steel industry, such as the National Steel Policy, which aims to increase domestic production and exports of steel.
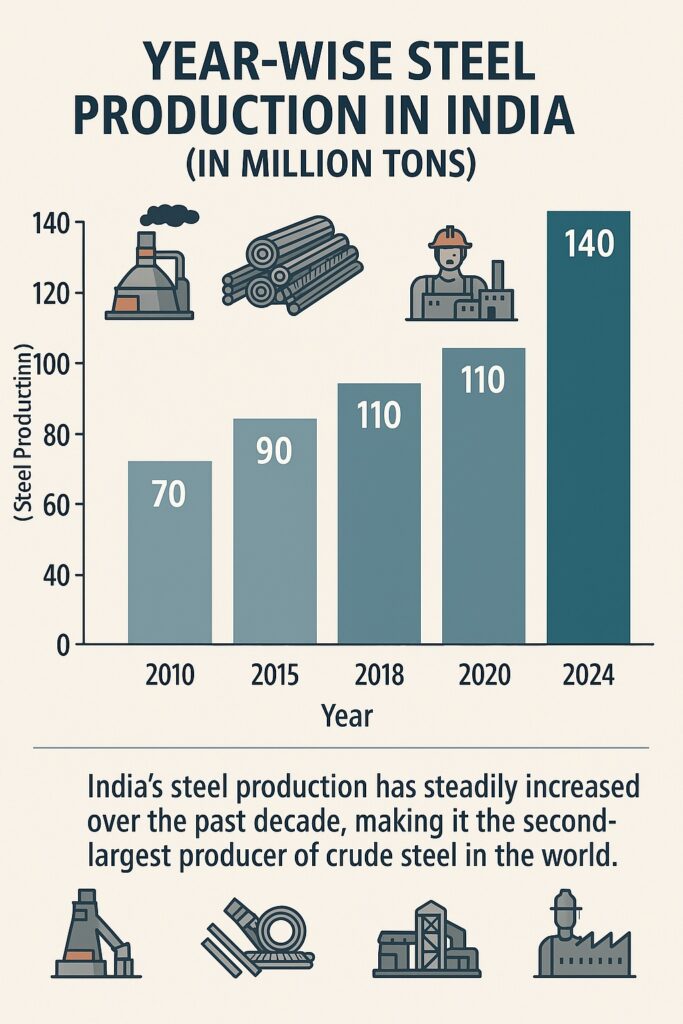
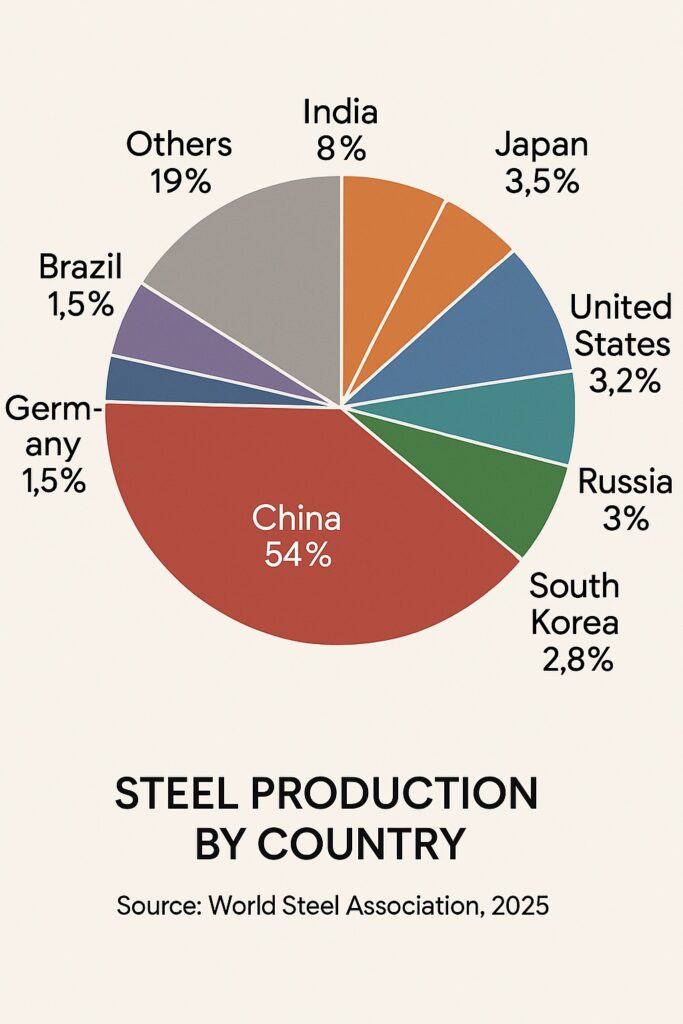
" India produced 125.3 million tons of crude steel in FY 2022-23"
Shifts in Location Trends
Earlier, industries were strictly raw material-oriented. However, with modern transportation, power generation, and port infrastructure:
-
New plants are being set up near coastal regions (e.g., Hazira in Gujarat, Vizag in Andhra Pradesh).
-
Focus is also shifting towards market-oriented and port-based locations for ease of export.
In conclusion, the iron and steel industry in India is influenced by several locational factors, including availability of raw materials, proximity to markets, access to water and power, transportation infrastructure, and government policies. Understanding these factors is essential for the success and growth of iron and steel production and trade in India.
Read: Geography Notes