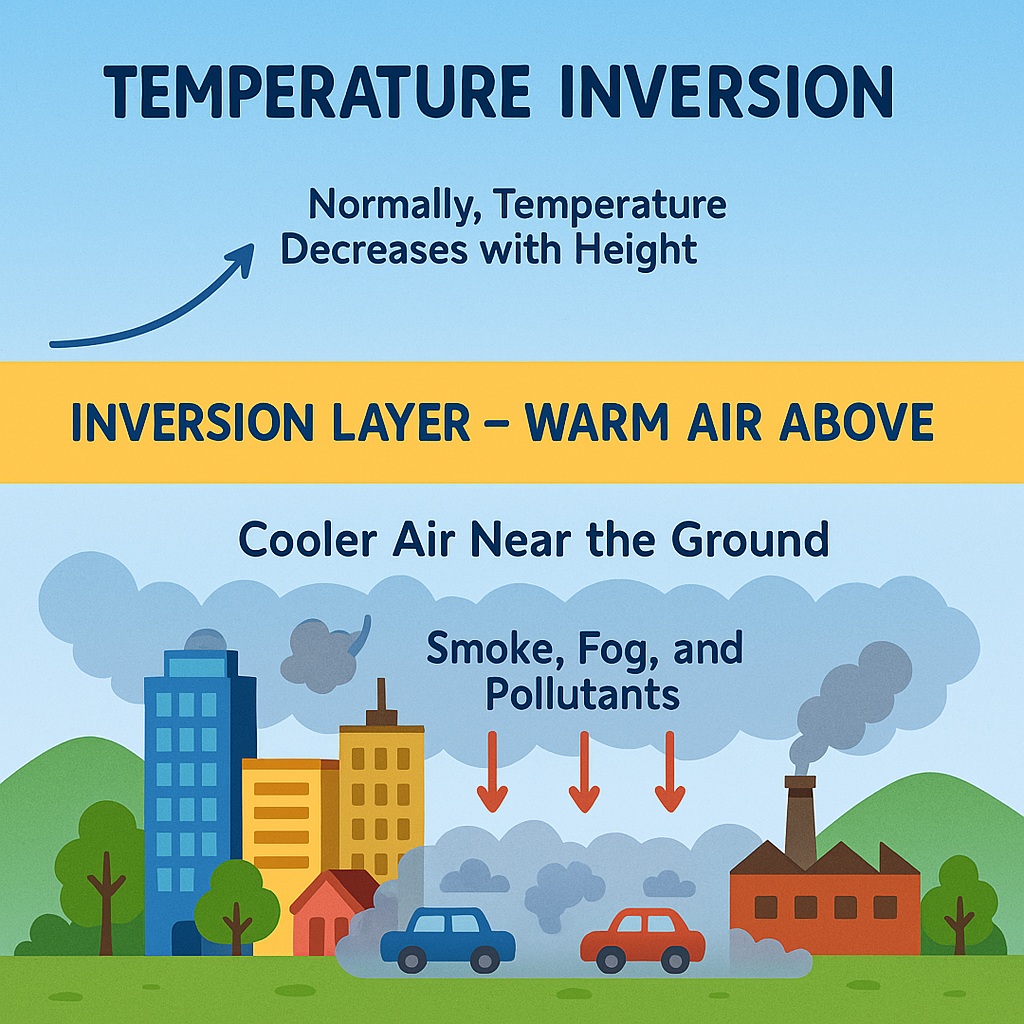
Temperature inversion is a weather phenomenon that occurs when the temperature of the atmosphere increases with height, as opposed to the usual decrease in temperature with height. This can cause a variety of effects, including the trapping of pollutants and the formation of fog.
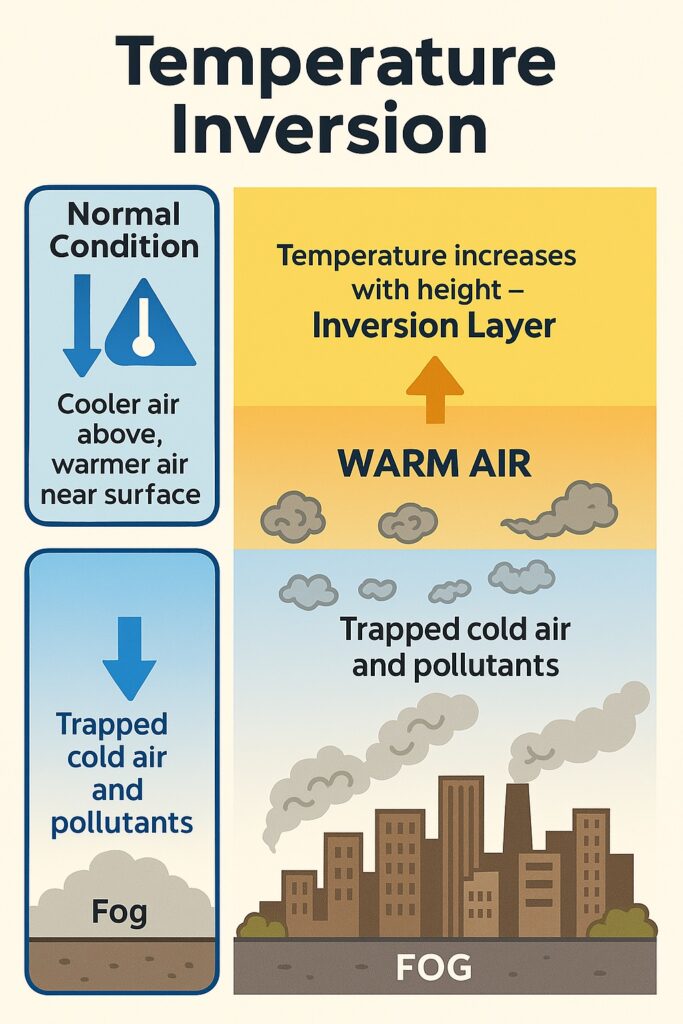

Table of Contents
Causes
Temperature inversion occurs when the air close to the surface of the earth is cooler than the air above it. This can happen due to a variety of factors, including:
Radiative cooling: The surface of the earth cools off at night, causing the air close to the surface to become cooler than the air above it.
Advection: Cold air from a nearby region can flow into an area, causing a localized temperature inversion.
Subsidence: Air sinking from higher altitudes can cause compression and warming, leading to a temperature inversion.
Effects
Temperature inversion can have a variety of effects on the environment, including:
Trapping of pollutants: When there is a temperature inversion, pollutants emitted at ground level are trapped below the inversion layer. This can cause poor air quality and health problems for people who are exposed to the pollutants.
Formation of fog: Temperature inversion can cause the air near the surface to become saturated with moisture, leading to the formation of fog.
Inversion lid: Temperature inversion can create a “lid” on the atmosphere, preventing vertical mixing of air. This can lead to the accumulation of pollutants and cause health problems for people in the area.
Types of Temperature Inversion
There are several types of temperature inversion, including:
Radiation inversion: This occurs when the ground cools at night, causing the air close to the surface to become cooler than the air above it.
Advection inversion: This occurs when cold air from a nearby region flows into an area, causing a localized temperature inversion.
Frontal inversion: This occurs when warm air moves over cold air, creating a temperature inversion.
Subsidence inversion: This occurs when air sinks from higher altitudes, causing compression and warming, leading to a temperature inversion.
Preventing the Effects of Temperature Inversion
To prevent the harmful effects of temperature inversion, several measures can be taken, including:
Reducing emissions: Reducing emissions from factories, vehicles, and other sources can reduce the amount of pollution trapped below the inversion layer.
Using alternative modes of transportation: Using public transportation, carpooling, or biking can reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to reduced emissions.
Supporting renewable energy: Supporting renewable energy sources like wind and solar power can reduce the emissions from power plants, leading to cleaner air.
Monitoring air quality: Regular monitoring of air quality can help identify areas where pollution is concentrated and take steps to reduce it.
Conclusion
Temperature inversion is a weather phenomenon that can have a variety of effects on the environment and human health. It occurs when the air close to the surface of the earth is cooler than the air above it. The main effects of temperature inversion include trapping of pollutants and the formation of fog. There are several types of temperature inversion, including radiation, advection, frontal, and subsidence inversion. To prevent the harmful effects of temperature inversion, reducing emissions, using alternative modes of transportation, supporting renewable energy, and monitoring air quality are some of the measures that can be taken.
Read: Geography Notes