Insolation is the amount of energy in terms of solar radiation that the Earth receives from the sun. It plays a crucial role in driving the planet’s climate and weather patterns, and has important implications for everything from agriculture to renewable energy.
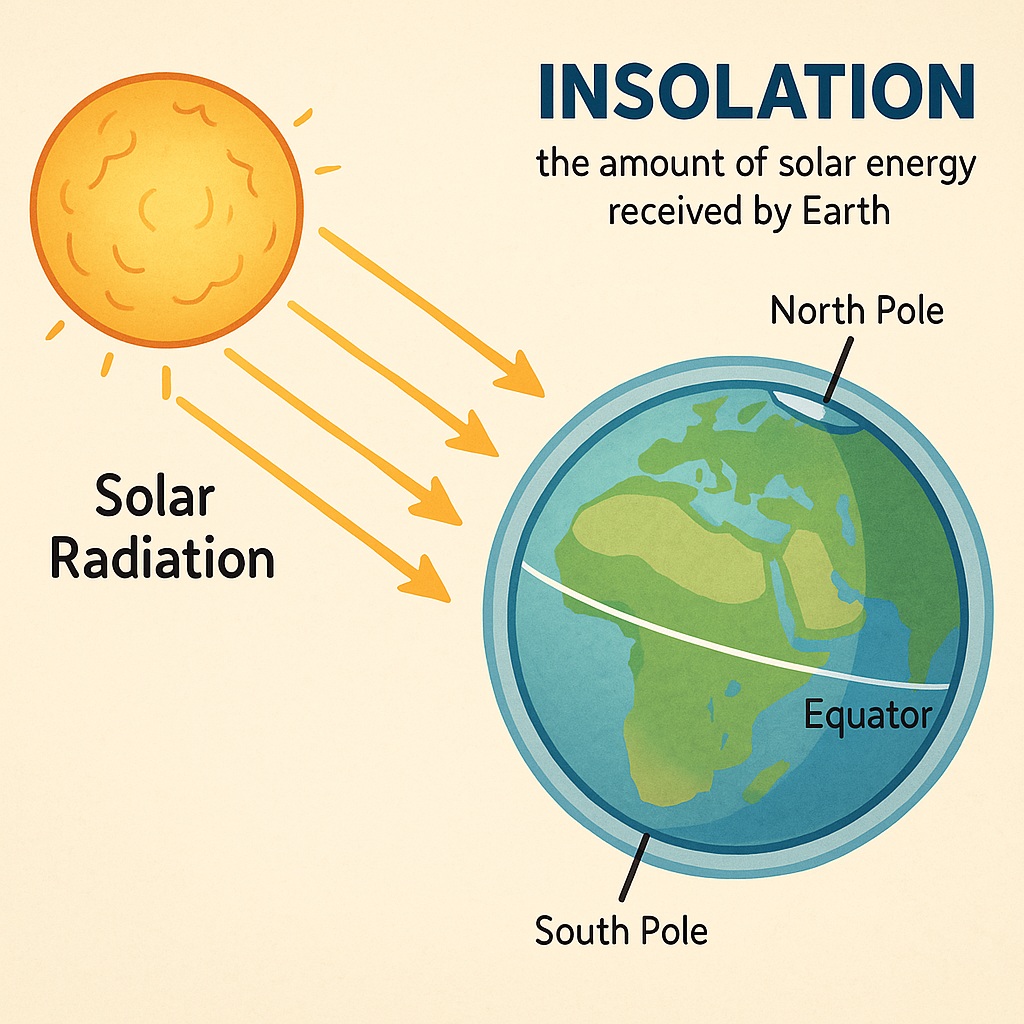
Table of Contents
What is Insolation?
Insolation refers to the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface. This energy comes from the sun, which emits a wide range of wavelengths of light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Most of this radiation is absorbed or scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere, but a portion of it reaches the surface, where it can be used for a variety of purposes.
Factors affecting Insolation
Not every place on Earth gets the same amount of insolation. It changes by location and season. Tropical areas (near the equator) get the most insolation. Polar areas get the least.
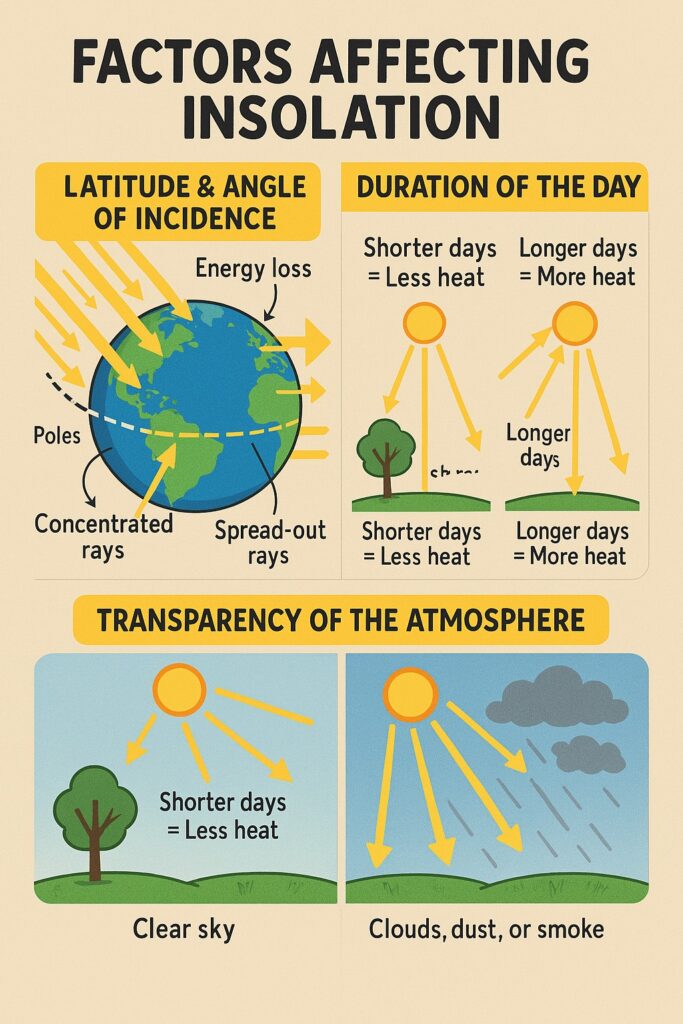
Latitude & Angle of Incidence
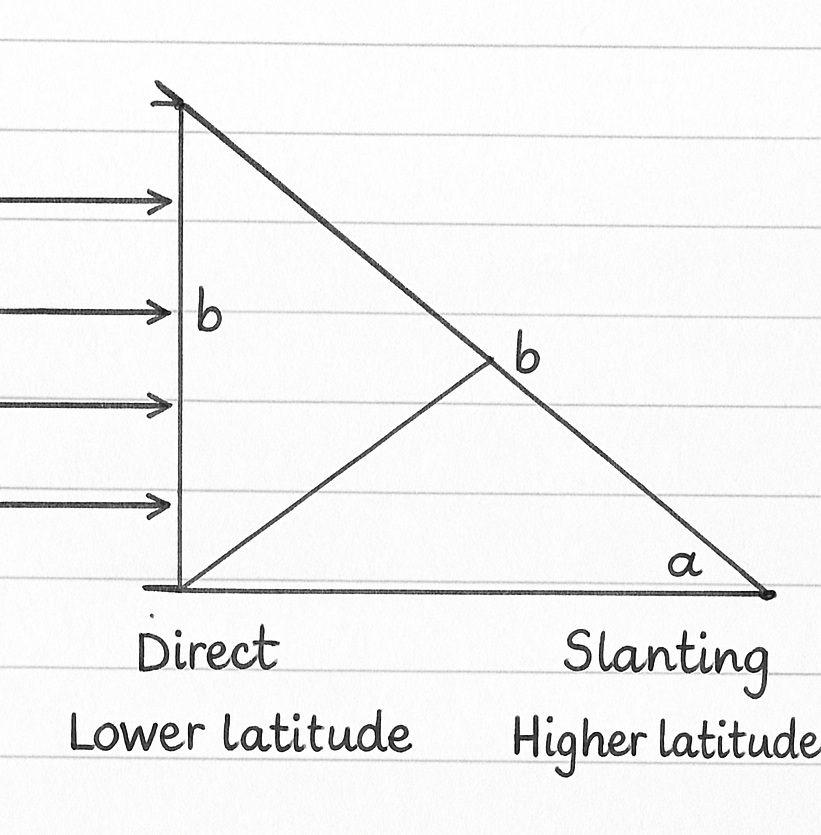
The amount of insolation decreases as you move away from the equator and move towards the poles.
- This means the angle at which sunlight hits Earth
- When the Sun is directly overhead, its rays are concentrated in a small area = more heat
- When the Sun is at a slant, its rays spread out over a larger area = less heat
- Also, slanting rays pass through more of the atmosphere, so they lose more energy
Duration of the Day
- The longer the day, the more time sunlight has to heat the Earth
- That’s why summer days are warmer—they’re longer!
Transparency of the Atmosphere
- If the air is clean and clear, more sunlight reaches the ground
- If the air is full of dust, smoke, or clouds, less sunlight gets through
- Thick clouds, dust, or water vapour block sunlight
- Water vapour absorbs sunlight, so less reaches the surface
How Insolation affects climate and weather?
Insolation is one of the primary drivers of the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. It provides the energy that powers the planet’s water cycle, driving evaporation, precipitation, and other forms of weather. It also plays a key role in determining the Earth’s temperature and climate, as areas with more insolation tend to be warmer than those with less.
One important way that insolation affects climate is through the creation of temperature gradients. As the sun heats different parts of the Earth’s surface unevenly, it creates differences in temperature between different regions. These temperature gradients drive the movement of air and water around the planet, leading to the formation of weather patterns such as winds, storms, and ocean currents.
Insolation and Renewable Energy
Insolation is also an important factor in the production of renewable energy, particularly solar energy. Solar panels are designed to convert the energy in sunlight into electrical energy, and the amount of energy they can produce depends on the amount of insolation that they receive. In areas with high levels of insolation, such as deserts and other sunny regions, solar energy can be a particularly effective source of renewable energy.
Insolation and Agriculture
Insolation also plays an important role in agriculture. Plants rely on sunlight for photosynthesis, which is the process by which they produce energy from sunlight. As such, the amount of insolation that a particular region receives can have a significant impact on crop yields and the types of crops that can be grown.
Insolation and Human Health
Finally, insolation can also have important implications for human health. Exposure to sunlight is necessary for the body to produce vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and immune function. However, excessive exposure to sunlight can also increase the risk of skin cancer, so it is important to balance the benefits of sunlight with the need to protect against harmful UV radiation.
Conclusion
Insolation is a crucial factor in the Earth’s climate, weather patterns, and energy systems. By understanding the factors that affect insolation and its many applications, we can better appreciate the importance of this fundamental aspect of our world. From renewable energy to agriculture to human health, insolation touches
Read: Geography Notes