The universe is the whole of everything — all that we can see, and even what we cannot. The universe is everything that exists — all of space, time, matter, and energy. It includes:
-
Galaxies (like the Milky Way)
-
Stars (like our Sun)
-
Planets (like Earth)
-
Moons, asteroids, comets, black holes
-
Light, radiation, and even the empty space between things

It began with the Big Bang around 13.8 billion years ago and has been expanding ever since.
Table of Contents
Milky Way
There are groups of millions of stars in space called galaxies. Out of all the stars in the sky, our Sun is just one. It belongs to a galaxy called the Milky Way.
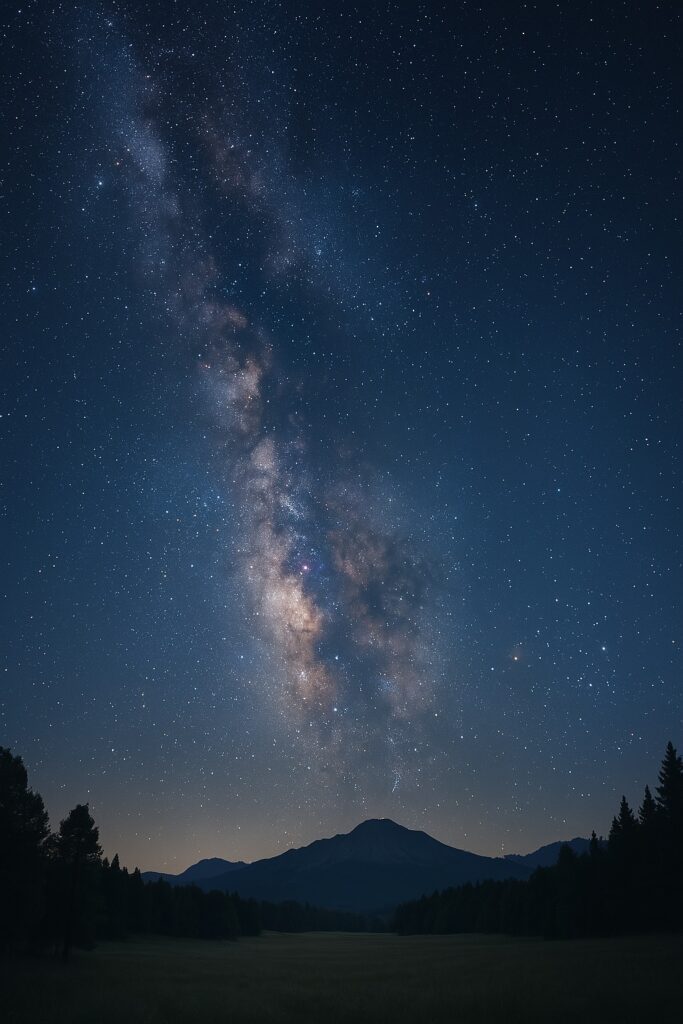

On a clear, dark night, you may see a band of cloudy light across the sky—this is the Milky Way. What we see is only its outer edge. People call it Akashganga, meaning “white river of light.” The Milky Way is shaped like a disc and its center is very far away from us.
"A light year is the distance that light travels in one year at a speed of 300,000 km/second.
The star closest to Earth after the Sun is called Proxima Centauri, and it is about 40 trillion kilometers away. Since this is such a huge number, scientists use a unit called a light year to measure space distances. A light year is the distance light travels in one year. Light moves very fast—about 300,000 kilometers every second—so in one year, light travels almost 95 trillion kilometers.

Our Milky Way galaxy is about 100,000 light years wide, and it’s around 20,000 light years thick at the center. The Sun is located about 30,000 light years from the center of this galaxy.
But the Milky Way isn’t the only galaxy—scientists have found millions of others. About 20 to 25 galaxies are close to ours. Each one contains billions of stars. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is called Andromeda. With a telescope, it looks like a glowing cloud, and you can even see individual stars. Andromeda is about 20 million light years away from Earth.
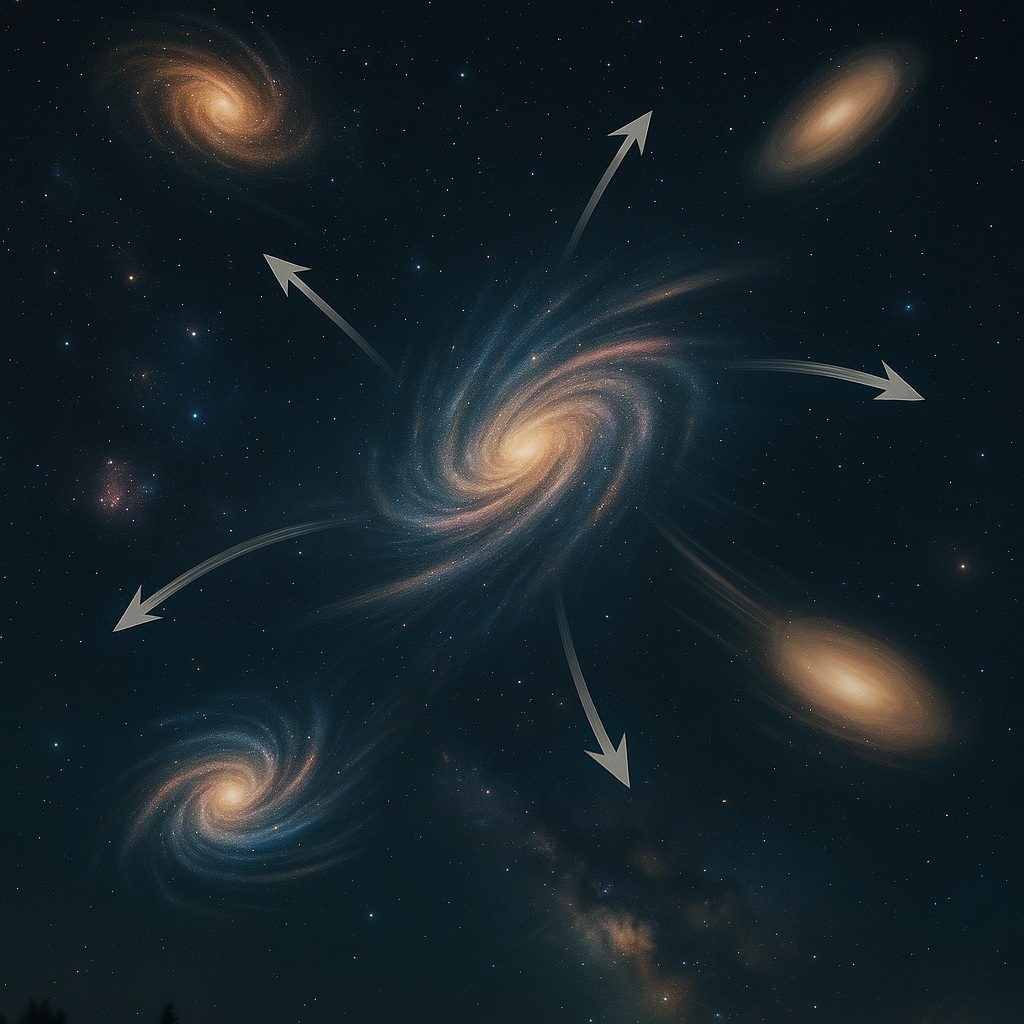

All galaxies are moving away from each other very fast. So, scientists believe the universe is expanding—it keeps getting bigger and changing. Stars have lifespans: they are born, live, grow old, and die. This is why we say that the universe is endless in time and space.
The Sun
The Sun is the center of our solar system. All the planets, their moons, and even objects like meteoroids and comets move around the Sun.
Although the Sun is just one star among many, it’s 1.3 million times bigger than Earth and contains 99% of all the matter in the solar system! Because it’s so big, it has strong gravity that keeps all the planets in their orbits.
Even though the Sun is 150 million kilometers away, it’s much closer to us than any other star, which is why it looks so bright. In fact, it only takes about 8 minutes for sunlight to reach Earth.
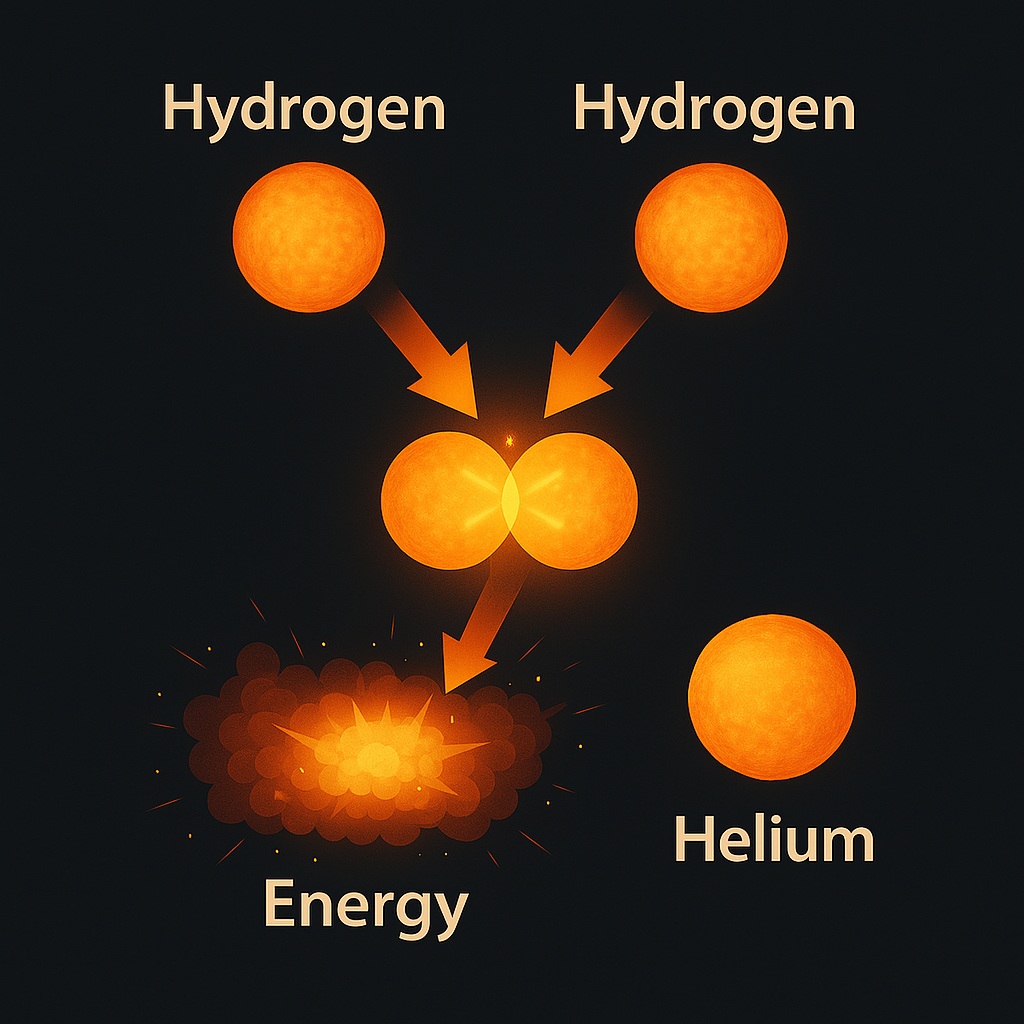
Source of Energy of the Sun
The Sun is the main source of energy on Earth. Things like coal, oil, and hydroelectricity are all indirect forms of solar energy.
The Sun works like a huge nuclear furnace. It is mostly made of hydrogen and helium gases. The center of the Sun is extremely hot around 15 million degrees Celsius! Due to this intense heat, hydrogen atoms collide and combine to form helium, releasing a huge amount of energy in the process.
Read: Geography Notes