Q1. The content of water is greater than fats, the plasma is more than proteins, proteins are more than fats and fats less than plasma. Which constitutes the major Part of the human body ?
(a) Fats
(b) Water
(c) Plasma
(d) Proteins
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (b) Water
Explanation:
The human body is composed mostly of water, which makes up about 60–70% of body weight. It is more abundant than plasma, proteins, or fats, and plays a critical role in physiological processes like temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and cellular function.

Q2. Dialysis is used for a patient suffering from
(a) Kidney trouble
(b) Liver trouble
(c) Lung trouble
(d) Bronchitis
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Kidney trouble
Explanation:
Dialysis is a medical procedure used when the kidneys fail to filter waste products from the blood. It removes toxins, excess salts, and fluids, like the function of healthy kidneys. It is essential for patients with renal failure.

Q3. Pulse reading is done by doctors to find out
(a) Temperature
(b) Heart beat
(c) Blood pressure
(d) Respiration rate
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (b) Heart beat
Explanation:
Pulse reading involves feeling the rhythmic throbbing of arteries, which reflects the heartbeat. It helps assess the rate, rhythm, and strength of the heart, providing vital information about cardiovascular health.
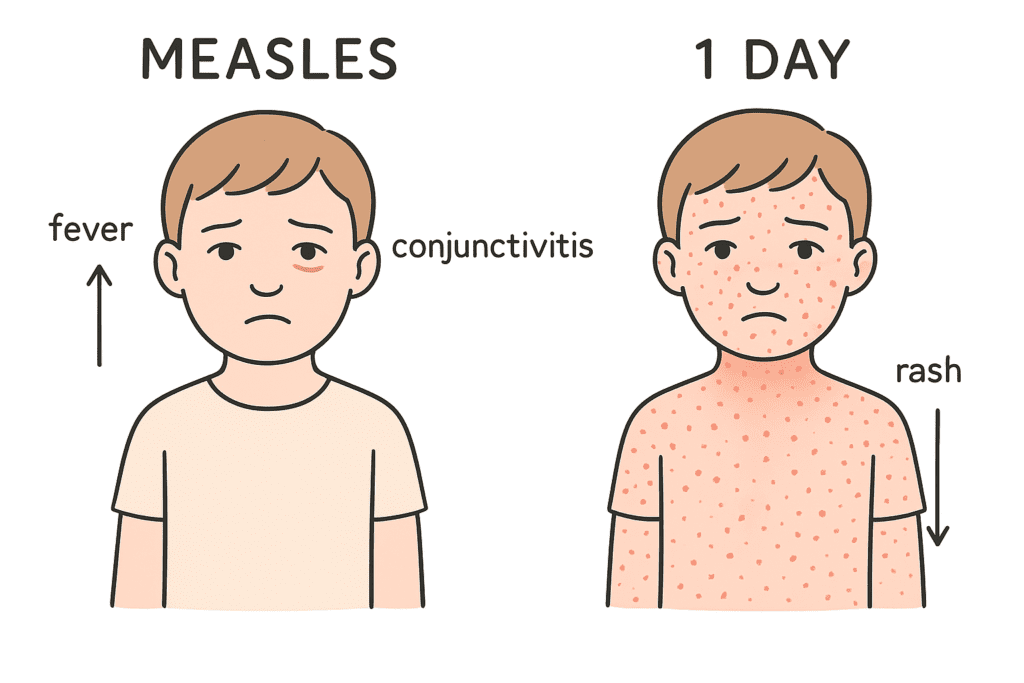
Q4. After how many days rash appears on the body after the attack of Measles ?
(a) One day
(b) Four days
(c) Six days
(d) One week
Answer: (a) One day
Explanation:
In measles, the rash typically appears within one day after the onset of initial symptoms like fever, cough, and conjunctivitis. The rash starts on the face and spreads downward, marking the progression of the viral infection.
Q5. If a large number of people are enclosed in a room, then
(a) Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases
(b) Oxygen increases and carbon dioxide decrease
(c) Both oxygen and carbon dioxide decrease
(d) Both oxygen and carbon dioxide increase
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Oxygen decreases and carbon dioxide increases
Explanation:
In a closed room with many people, oxygen is consumed during respiration and carbon dioxide is released. This leads to a drop in oxygen levels and a rise in carbon dioxide concentration, which can cause discomfort or health issues if ventilation is poor.
Q6. Which of the following is not immunised by ‘Triple Antigen’ ?
(a) Typhoid
(b) Whooping cough
(c) Tetanus
(d) Diphtheria
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Typhoid
Explanation:
The Triple Antigen vaccine protects against Diphtheria, Pertussis (Whooping cough), and Tetanus. Typhoid is caused by a different bacterium and requires a separate vaccine, hence it is not covered by the triple antigen.
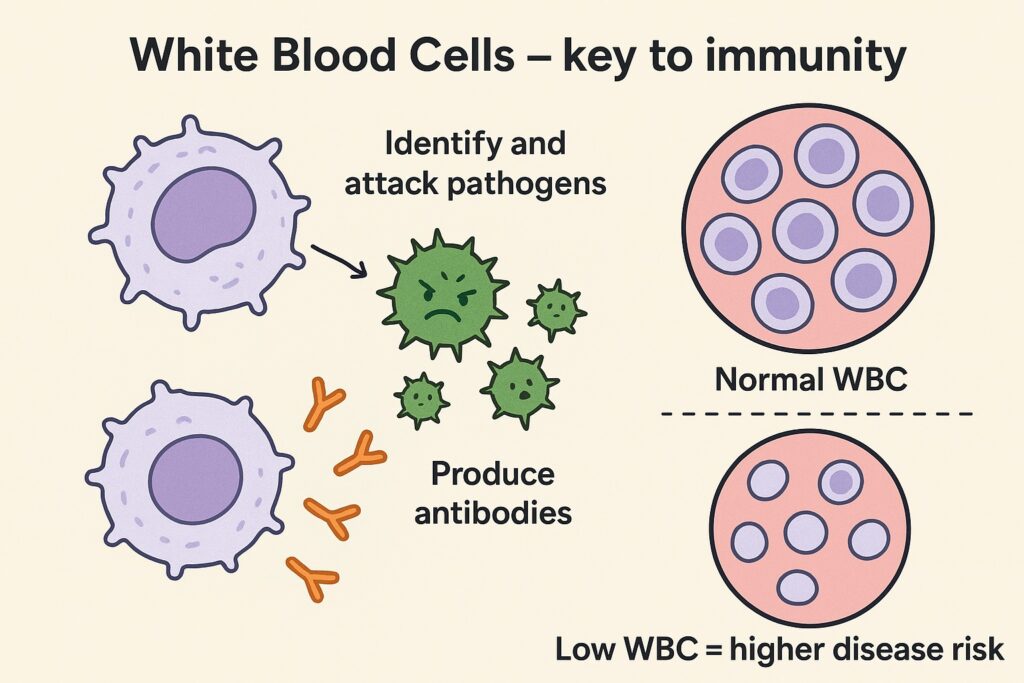
Q7. Decrease in white blood cells results in
(a) Decrease in Antibodies
(b) Increase in Antigens
(c) Increase in Antibodies
(d) No change
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Decrease in Antibodies
Explanation:
White blood cells (WBCs) are crucial for the immune system, especially in producing antibodies that fight infections. A decline in WBC count leads to reduced antibody production, making the body more vulnerable to diseases.
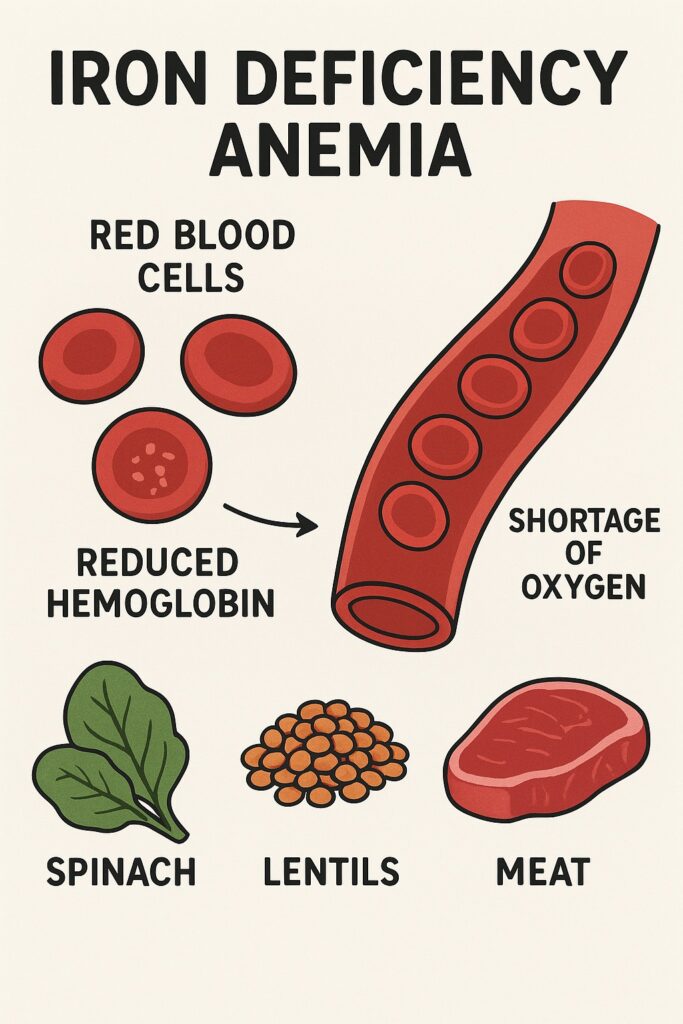
Q8. In India people suffer from Anaemia due to lack of
(a) Iron
(b) Iodine
(c) Calcium
(d) Potassium
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Iron
Explanation:
Anaemia is commonly caused by iron deficiency, which leads to reduced hemoglobin levels in the blood. In India, nutritional deficiencies, especially among women and children, contribute significantly to the prevalence of anaemia.
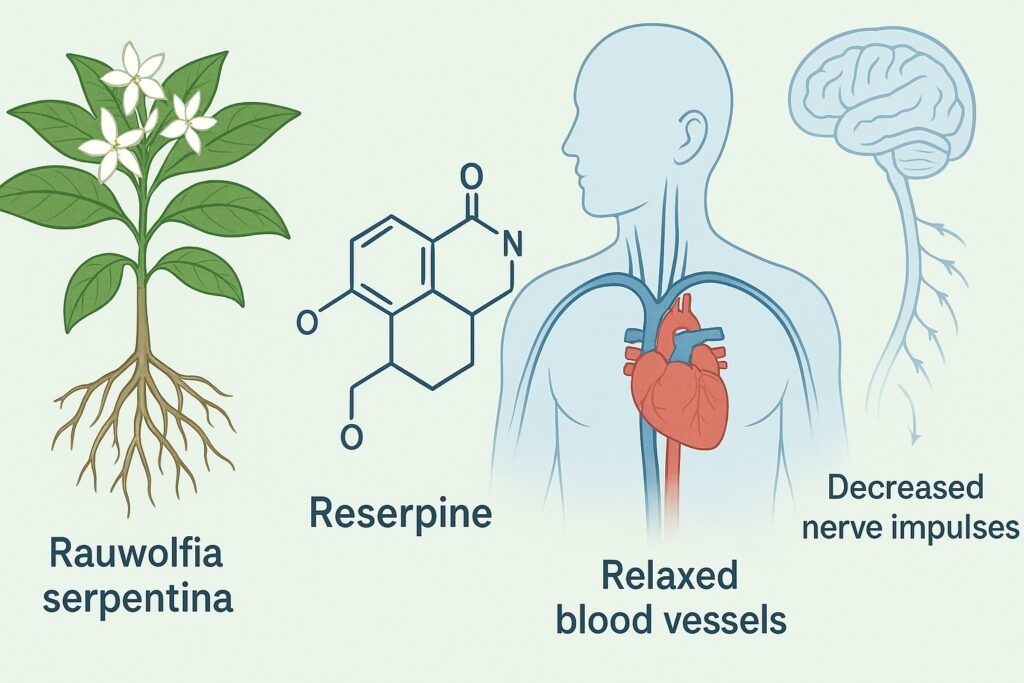
Q9. Reserprine derived from the plant ‘Serpentina’ is used to
(a) Alleviate pains
(b) Alleviate high blood pressure
(c) Alleviate low blood pressure
(d) Cure rickets
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (b) Alleviate high blood pressure
Explanation:
Reserpine, extracted from Rauwolfia serpentina, is a natural alkaloid used to treat hypertension. It works by reducing nerve impulses, thereby lowering blood pressure and calming the nervous system.
Q10. In summer, man with excess perspiration feels weak, because of the
(a) Loss of more water through evaporation
(b) Loss of salts through evaporation
(c) Loss of carbohydrates through evaporation
(d) All factors mentioned above
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Loss of more water through evaporation
Explanation: Excessive sweating in summer leads to loss of body fluids, primarily water, causing dehydration. This results in fatigue, dizziness, and a feeling of weakness. Though some salts are lost, the major contributor to weakness is water loss.

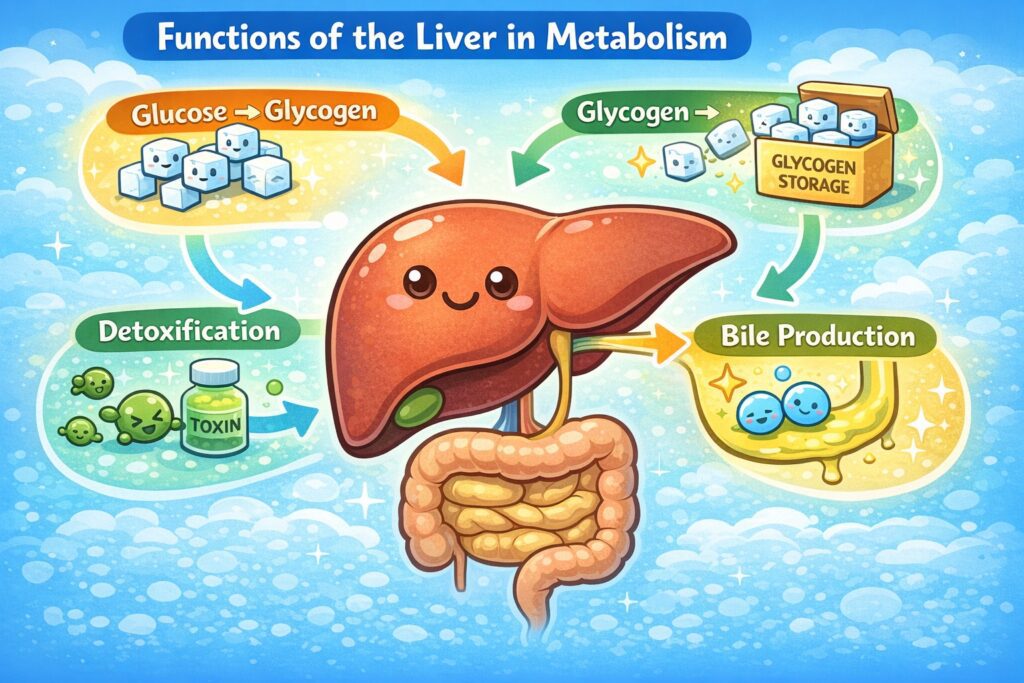
Q11. The function of the liver is to
(a) Promote digestion of food
(b) Promote respiration
(c) Store glucose as glucogen
(d) None of these
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (c) Store glucose as glucogen
Explanation: The liver plays a central role in metabolism, including converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This glycogen can be converted back into glucose when needed, helping regulate blood sugar levels. It also aids in detoxification and bile production.
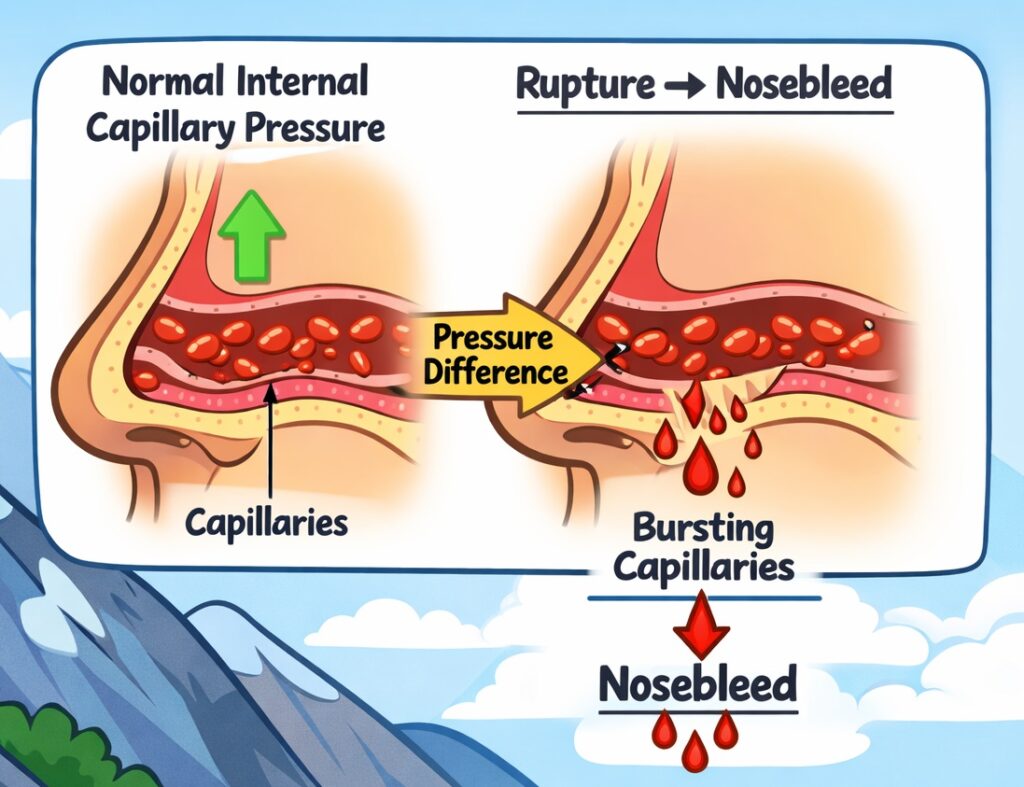
Q12. In high mountain regions bleeding through nose occurs because
(a) The pressure of the blood capillaries is higher than the outside pressure
(b) The pressure at high altitudes is greater than that in the plains
(c) The blood pressure increases at high altitudes
(d) The blood pressure decreases at high altitudes
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) The pressure of the blood capillaries is higher than the outside pressure
Explanation:
At high altitudes, the atmospheric pressure drops significantly, but the internal pressure in blood capillaries remains unchanged. This pressure difference causes capillaries in the nose to rupture, leading to nosebleeds, a common symptom of altitude sickness.
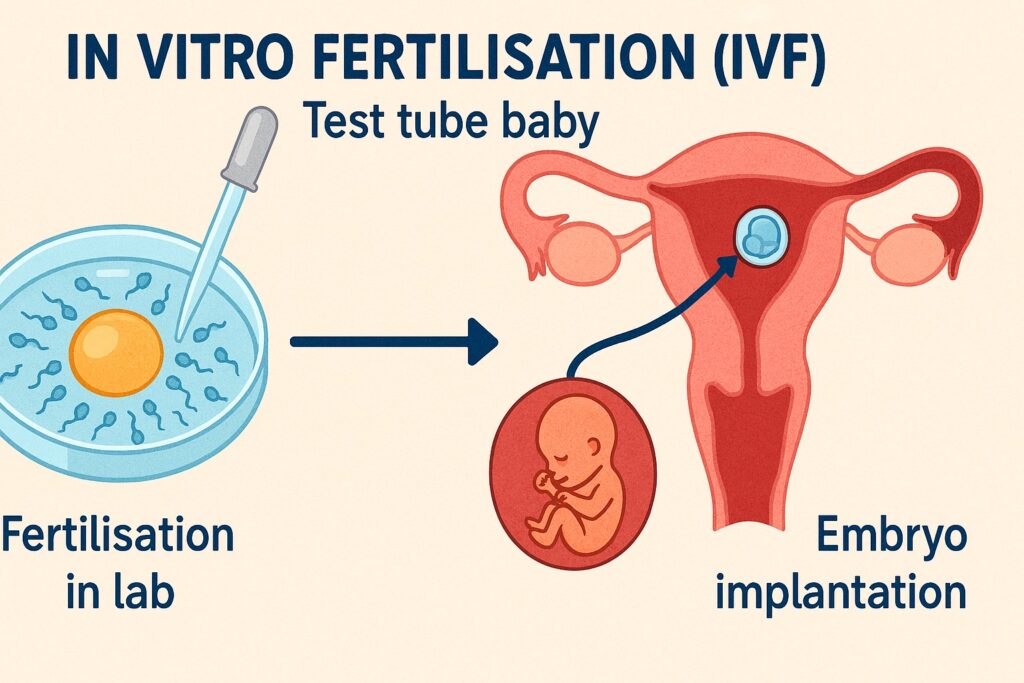
Q12. The term ‘Test Tube Baby’ implies
(a) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube but it develops in uterus
(b) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube and develops in the test tube itself
(c) Fertilisation of the ovum takes place in the uterus but develops in the test tube
(d) Fertilisation takes place in uterus and embryo develops in uterus
(UPSC Prelims, 1979)
Answer: (a) Fertilisation of ovum takes place in the test tube but it develops in uterus
Explanation: A test tube baby refers to a child conceived through in vitro fertilisation (IVF), where the egg and sperm are fertilised outside the body, typically in a laboratory dish. The resulting embryo is then implanted into the uterus, where it develops naturally.
Q13. Dialysis is used for a patient suffering from
(a) Kidney trouble
(b) Liver trouble
(c) Lung trouble
(d) Heart trouble
(UPSC Prelims 1980)
Answer: (a) Kidney trouble
Explanation: Dialysis is a medical process that removes waste and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys fail to function properly.
Q14. What happens when alcohol is taken in excess?
(a) It destroys the liver
(b) It produces inflammation of the stomach
(c) It causes the heart to become weak
(d) All of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage (e.g., cirrhosis), gastric inflammation, and cardiovascular issues. It affects multiple organs and systems, making it a major cause of chronic health problems.
Q15. A fan makes a hot noon to feel cool by
(a) Blowing out hot air
(b) Increasing the rate of evaporation
(c) Letting in cool air
(d) Regulating the air flow
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (b)
Explanation: A fan increases the rate of evaporation of sweat from the skin, which absorbs body heat and creates a cooling effect. This is a physical process that helps regulate body temperature during hot conditions.
Q16. During cardiac failure, which of the following is advised as a first aid?
(a) Mouth to mouth resuscitation
(b) Giving external cardiac massage
(c) Giving cool water to drink
(d) Giving complete body massage
Answer: (a)
Explanation: In the event of cardiac failure, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation is a critical first aid technique to restore breathing and oxygen supply. It helps maintain vital functions until professional medical help arrives.
Q17. Dehydration in the human body results due to loss of
(a) Salts
(b) Water
(c) Vitamins
(d) Hormones
Answer: (b)
Explanation: Dehydration occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in, affecting cellular functions, blood pressure, and temperature regulation. It can lead to fatigue, dizziness, and organ stress.
Q18. Hormones which are necessary for the development of the human body are secreted by
(a) Thyroid gland
(b) Pituitary gland
(c) Parathyroid gland
(d) Exocrine gland
Answer: (b) Pituitary gland
Explanation: The pituitary gland is known as the master gland because it regulates the secretion of various hormones essential for growth, metabolism, and reproduction. It influences other endocrine glands as well.

Q19. The ductless and secretory glands in the human body are known as
(a) Endocrine glands
(b) Exocrine glands
(c) Salivary glands
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (a) Endocrine glands
Explanation:
Endocrine glands are ductless glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate body functions such as growth, metabolism, and mood.

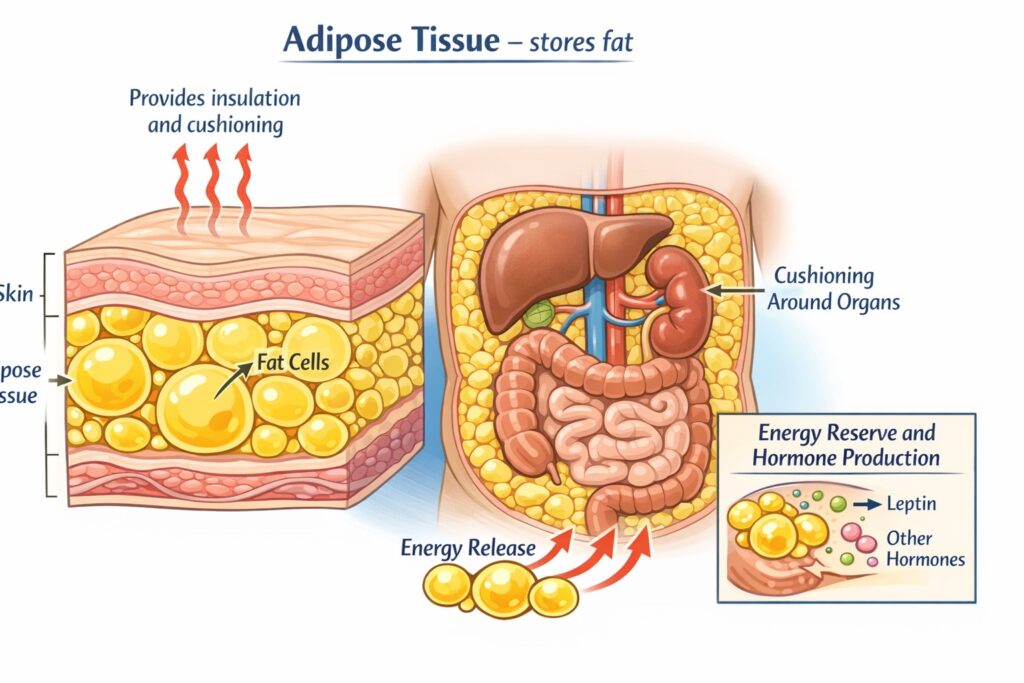
Q20. Fat is stored in the human body in
(a) Muscular tissue
(b) Connective tissue
(c) Adipose tissue
(d) Epithelial tissue
(UPSC Prelims 1983)
Answer: (c) Adipose tissue
Explanation: Adipose tissue is specialized for fat storage, serving as an energy reserve and providing insulation and cushioning. It plays a key role in metabolic regulation and hormone production.
Q21. Which of the following groups represents the correct order of four types of teeth in human beings ?
(a) Incisors, premolars, molars, canines
(b) Incisors, canines, premolars, molars
(c) Molars, canines, incisors, premolars
(d) Canines, incisors, molars, premolars
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (b) Incisors, canines, premolars, molars
Explanation: Human teeth are arranged in a specific sequence: incisors (for cutting), canines (for tearing), premolars (for crushing), and molars (for grinding). This order reflects their functional roles in digestion and is anatomically consistent across individuals.
Q22. Triple Antigen does not immunise against
(a) Diphtheria
(b) Tetanus
(c) Typhoid
(d) Whooping cough
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (c) Typhoid
Explanation: The Triple Antigen vaccine (DPT) provides protection against Diphtheria, Pertussis (Whooping cough), and Tetanus. It does not cover Typhoid, which requires a separate vaccine. This makes Typhoid the exception in the given list.
Q23. Bile is secreted by
(a) Liver
(b) Gall bladder
(c) Kidney
(d) Pancreas
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) Liver
Explanation: Bile is a digestive fluid secreted by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. It plays a crucial role in the emulsification of fats, aiding in their digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
Q24. Wisdom teeth normally grow during the age of
(a) 34-40 years
(b) 12-15 years
(c) 17-30 years
(d) 40-45 years
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (c) 17-30 years
Explanation: Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, typically emerge between the ages of 17 and 30. Their growth can cause discomfort or require extraction, depending on jaw space and alignment.
Q25. ‘Acupuncture’ is a medical system of treatment prominently used in China in which
(a) Herbs are used for the pain relief
(b) Drugs are used for the pain relief
(c) Special needles are inserted into particular parts of the body for the relief
(d) Electric shocks are applied for the relief of pain
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (c) Special needles are inserted into particular parts of the body for the relief
Explanation: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medical practice where fine needles are inserted into specific pressure points on the body to relieve pain and restore energy balance. It is widely used for chronic pain and stress-related conditions.
Q26. Snake bite first affects the
(a) Nervous system
(b) Blood circulation
(c) Brain
(d) Lungs
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (b) Blood circulation
Explanation: Most snake venoms, especially from vipers, primarily affect the blood circulation, causing internal bleeding, clotting disorders, and tissue damage. Some neurotoxic venoms affect the nervous system, but blood is the first target in many cases.
Q27. Ultrafiltering units of kidney are known as
(a) Nephron
(b) Glomerulus
(c) Vena Cava
(d) Tubule
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (a) Nephron
Explanation: The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for ultrafiltration of blood and formation of urine. It includes structures like the glomerulus and tubules, but the entire nephron performs the filtration process.
Q28. Foetus development in women’s womb can be ascertained by
(a) CAT scanning
(b) Ultrasound
(c) PTT scanning
(d) Co-27 experiment
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (b) Ultrasound
Explanation: Ultrasound imaging is a safe and non-invasive method to monitor foetal development, assess growth, position, and health, and detect abnormalities during pregnancy.