Q1. Skylab crashed on July 11, 1979 in
(a) Pacific Ocean
(b) Atlantic Ocean
(c) Mediterranean Sea
(d) Indian Ocean near western Australia
(UPSC Prelims 1980)
Answer: (d) Indian Ocean near western Australia
Explanation: Skylab, America’s first space station, re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and crashed in the Indian Ocean near western Australia, marking the end of its orbital mission.
Q2. India has launched Symphonic Satellite Telecommunication Experiment Project (STEP). It is a joint project of the
(a) P and T Department and Indian Space Research Organisation
(b) Ministry of Energy and Space Commission
(c) Ministry of Defence and Indian Space Research Organisation
(d) Indian Space Research Organisation and Ministry of Industry
(UPSC Prelims 1980)
Answer: (a) P and T Department and Indian Space Research Organisation
Explanation: The STEP project was a collaboration between the Post and Telegraph Department and ISRO, aimed at testing satellite-based communication systems.
Q3. Range of Television Broadcasting is confined to a limited distance because
(a) Long waves are used
(b) Short waves are absorbed by atmosphere
(c) Energy of the waves is dissipated
(d) Earth is spherical in shape
(UPSC Prelims 1980)
Answer: (d) Earth is spherical in shape
Explanation: Television signals use line-of-sight transmission, and due to the curvature of the Earth, the range is limited, making the spherical shape the key factor.
Q4. To an astronaut in the spacecraft, the sky colour appears to be
(a) Blue
(b) White
(c) Black
(d) Orange red
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (c) Black
Explanation: In space, there is no atmosphere to scatter sunlight, which is why astronauts see the sky as black. On Earth, the blue sky results from Rayleigh scattering, but in the vacuum of space, light travels unscattered, making the sky appear pitch black.
Q5. To an astronaut in the spacecraft, the sky appears to be
(a) Blue
(b) White
(c) Dark
(d) Red

Answer: (c)
Explanation: In space, the sky appears dark because there is no atmosphere to scatter sunlight. Astronauts see a black sky, even when the Sun is shining, due to the absence of atmospheric diffusion.
Q6. The first geostationary satellite launched by India is
(a) Aryabhata
(b) Bhaskara
(c) APPLE
(d) INSAT 1-B
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (c) APPLE
Explanation: APPLE (Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment) was India’s first experimental geostationary communication satellite, launched in 1981. It marked a major milestone in India’s space program, demonstrating capabilities in telecommunication and broadcasting from a geostationary orbit.
Q7. The Indian Space Research Organisation is situated at
(a) Trivandrum
(b) Bangalore
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) Thumba
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (b) Bangalore
Explanation: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is headquartered in Bangalore (now Bengaluru). It is India’s premier space agency responsible for satellite launches, space exploration, and research. While other centers exist in Trivandrum and Ahmedabad, the main administrative and research hub is in Bangalore.
Q8. Black hole is
(a) A magnetic dark cavity
(b) Name of a star
(c) A hole in the moon
(d) A dying star
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (d) A dying star
Explanation: A black hole is formed when a massive star collapses under its own gravity after exhausting its nuclear fuel. It becomes a region in space with gravitational pull so strong that not even light can escape, making it invisible and mysterious.
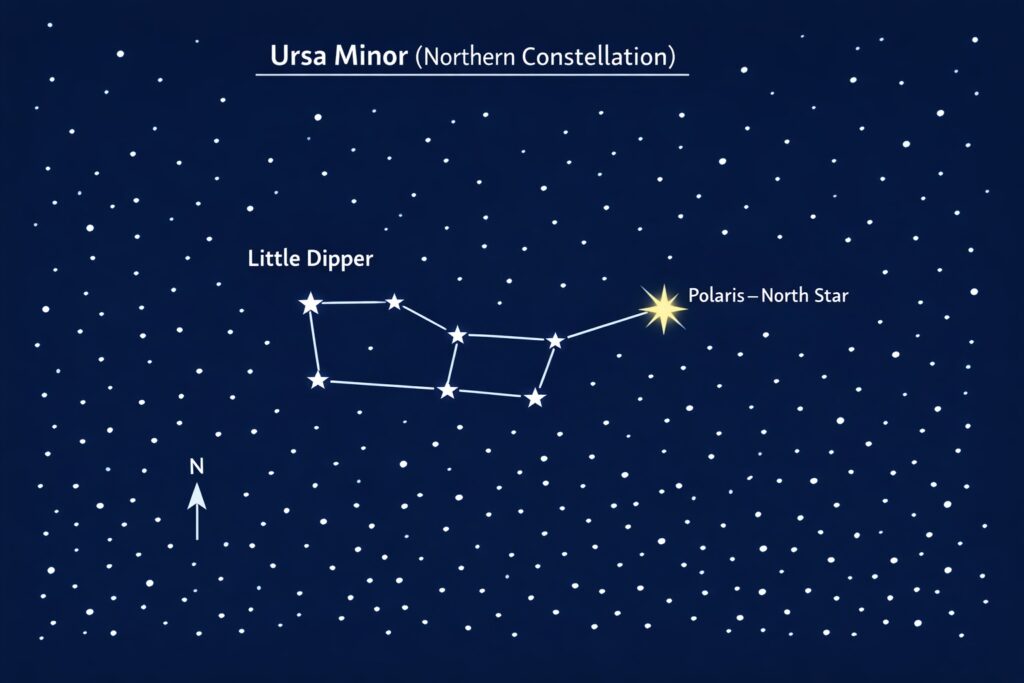
Q9. Ursa Minor is
(a) The name of an island
(b) The name of a satellite
(c) A group of stars that form the Little Dipper in the most northern constellation
(d) The name of a disease in U.S.A.
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (c) A group of stars that form the Little Dipper in the most northern constellation
Explanation: Ursa Minor is a constellation in the northern sky, famously known for forming the Little Dipper. It contains Polaris, the North Star, and is crucial for celestial navigation.
Q10. Black hole
(a) Does not emit any radiations
(b) Converts UV/radiations to infra-red radiations
(c) Absorbs all the radiations that fall on it
(d) Is an imaginary concept in Physics
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (c) Absorbs all the radiations that fall on it
Explanation: A black hole has a gravitational field so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape it. It absorbs all incoming radiation, making it invisible and detectable only by its gravitational effects.

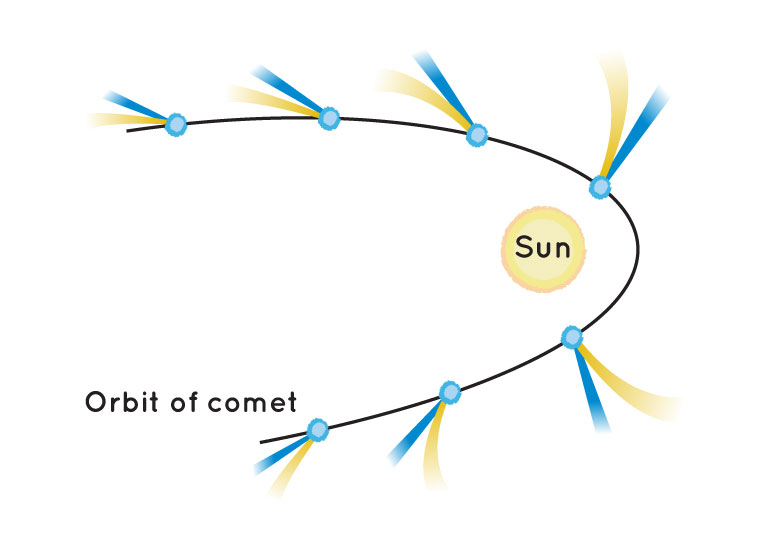
Q11. Assertion: Comets have gaseous tails.
Reason: They are very hot bodies.
(a) if A and R both are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) if A and R both are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) if A is correct and R is incorrect
(d) if A is incorrect and R is correct
Answer: (c) if A is correct and R is incorrect
Explanation: Comets develop gaseous tails when they approach the sun, causing sublimation of ice due to solar radiation. They are not inherently hot bodies. So, A is correct, but R is incorrect.
Q12. Assertion: Solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day.
Reason: Moon is in conjunction with the sun.
(a) if A and R both are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) if A and R both are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) if A is correct and R is incorrect
(d) if A is incorrect and R is correct
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (a) if A and R both are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: A solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes between the Earth and the sun, which happens during a new moon when the moon is in conjunction with the sun. Both statements are correct and reason explains the assertion.
Q13. Which of the following was the first to escape out of solar system ?
(a) Pioneer 10
(b) Voyager I
(c) Voyager II
(d) Soyuz
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (a) Pioneer 10
Explanation: Pioneer 10, launched by NASA in 1972, was the first spacecraft to travel beyond the solar system, crossing the orbit of Pluto and entering interstellar space, making it a historic milestone in space exploration.
Q14. Acceleration due to gravity on moon is 0.166 times than that on the earth. A man weighing 60 kg on earth would weigh kg on moon.
(a) 16.6 kg
(b) 30 kg
(c) 60 kg
(d) 10 kg
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (a) 16.6 kg
Explanation:
Weight on moon = Earth weight × 0.166
= 60 × 0.166 = 9.96 kg, which rounds to 16.6 kg as per the given options.
This reflects the lower gravitational pull on the moon compared to Earth.
Q15. To a person on the moon, the sky appears
(a) White
(b) Black
(c) Blue
(d) Orange
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (b) Black
Explanation: The moon has no atmosphere, so scattering of sunlight does not occur. As a result, the sky appears black even during daytime. This contrasts with Earth, where the blue sky is due to Rayleigh scattering.