Q1. The heater element in an electric iron is made of
(a) Nichrome
(b) Tungsten
(c) Copper
(d) Iron
Answer: (a) Nichrome
Explanation: Nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium, is used in heater elements due to its high resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without oxidizing.

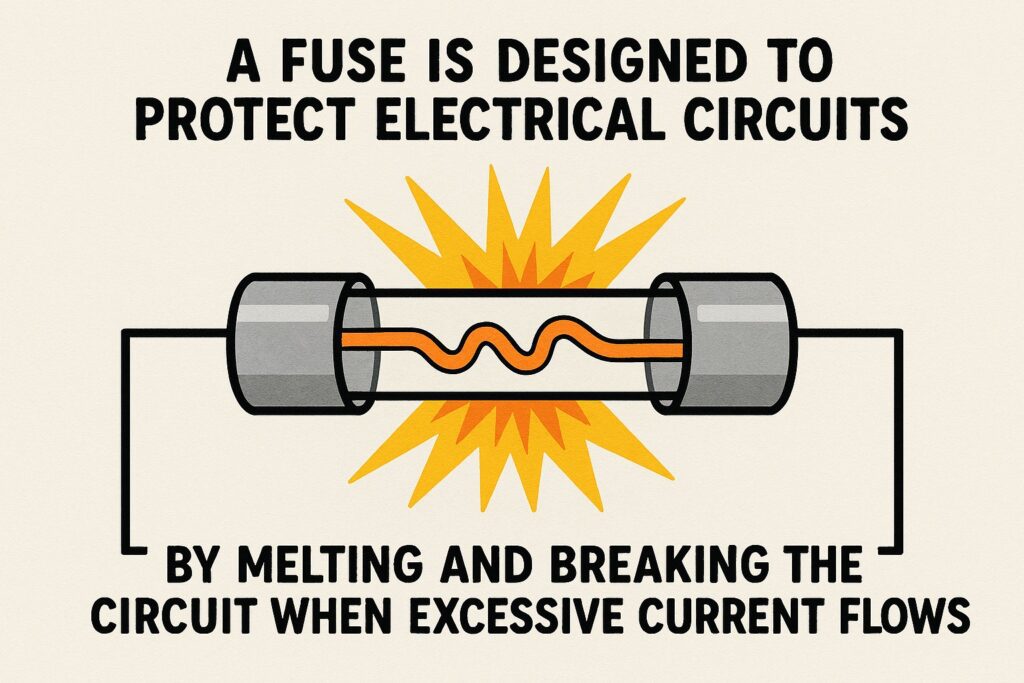
Q2. What is the function of a fuse wire ?
(a) To prevent an unduly high electric current from passing through a circuit
(b) To increase the current supply
(c) To decrease the current supply
(d) To stabilise the voltage
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (a) To prevent an unduly high electric current from passing through a circuit
Explanation: A fuse wire is designed to melt when the current exceeds safe limits, thereby breaking the circuit and preventing damage to appliances or electrical fires. It acts as a safety device in electrical systems.
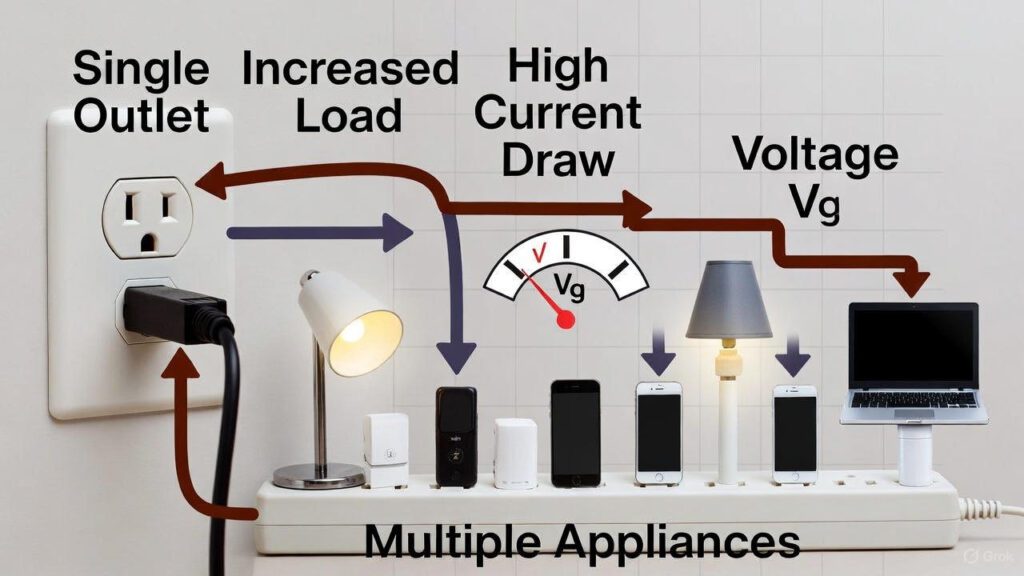
Q3. Why is it advisable not to draw current for many appliances from a single point ?
(a) Current will decrease
(b) Current will increase
(c) Current and voltage both will increase
(d) Voltage will decrease whereas current will increase
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (d) Voltage will decrease whereas current will increase
Explanation: Drawing current for many appliances from a single outlet causes voltage drop due to increased load, while current demand rises, risking overheating, short circuits, or fuse failure. This can lead to electrical hazards.
Q4. Kilowatt is the unit of
(a) Voltage
(b) Power
(c) Resistance
(d) Current
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (b)
Explanation: A kilowatt (kW) is a unit of power, representing 1000 watts. It measures the rate of energy consumption or generation, commonly used in electricity billing and appliances.
Q5. Metals used in voltaic cell are
(a) Zinc and lead
(b) Carbon and zinc
(c) Zinc and copper
(d) Carbon and nickel
(UPSC Prelims 1982)
Answer: (c)
Explanation: A typical voltaic cell uses zinc as the anode and copper as the cathode. The electrochemical reaction between these metals generates electric current, forming the basis of battery technology.
Q6. Chips used in integrated circuits in computers are made of
(a) Mica
(b) Manganese
(c) Silicon
(d) Zinc
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (c) Silicon
Explanation: Silicon is the primary material used in manufacturing semiconductor chips for integrated circuits. It has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability, making it ideal for electronic devices. Silicon wafers are the foundation of modern computing.
Q7. Mica is abundantly used in which of the following industries ?
(a) Cement
(b) Electrical
(c) Plastic
(d) Fire resistance bricks
(UPSC Prelims 1984)
Answer: (b) Electrical
Explanation: Mica is a non-conductive, heat-resistant mineral widely used in the electrical industry for insulation in capacitors, transformers, and other devices. Its thermal and dielectric properties make it ideal for electrical applications.
Q8. Which of the following is most suitable for the remote hilly villages of about 100 families where streams are tiny and slow ?
(a) Construction of big dams
(b) Installation of solar panels
(c) Building of hydel projects
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (b) Installation of solar panels
Explanation: In remote hilly villages with small streams, solar panels are the most practical solution for electricity generation. They require minimal infrastructure, are environmentally friendly, and work well in sunlit terrains.
Q9. Which of the following is the correct sequence in order of increasing power consumption ?
(a) Television, Fan, Electric Kettle, Electric Iron
(b) Television, Fan, Electric Iron, Electric Kettle
(c) Fan, Television, Electric Kettle, Electric Iron
(d) Fan, Television, Electric Iron, Electric Kettle
Answer: (c) Fan, Television, Electric Kettle, Electric Iron
Explanation: In terms of power consumption:
- Fan uses the least
- Followed by Television
- Then Electric Kettle
- Electric Iron consumes the most
Thus, the correct ascending order is Fan < Television < Electric Kettle < Electric Iron
Q10. To increase the voltage of alternative current, we can use
(a) Capacitor
(b) Transformer
(c) Inverter
(d) Rectifier
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (b) Transformer
Explanation: A transformer is an electrical device used to increase or decrease the voltage of alternating current (AC). It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, making it the correct choice for voltage amplification.
Q11. Which of the following is a conventional source of energy ?
(a) Geothermal
(b) Hydropower
(c) Solar
(d) Wind
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (b) Hydropower
Explanation: Hydropower is a conventional energy source, used for centuries to generate electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing water. The others—geothermal, solar, and wind—are considered non-conventional or renewable sources.
Q12. Resistance of a 100 watt bulb is R₁ and that of a 60 watt bulb is R₂. Which of the following is correct ?
(a) R₁/R₂ > 1
(b) R₁/R₂ < 1
(c) R₁/R₂ = 1
(d) Data is inadequate
Answer: (b) R₁/R₂ < 1
Explanation: Resistance R = V² / P. For same voltage, higher wattage means lower resistance.
So, 100W bulb has lower resistance than 60W bulb, hence R₁ < R₂, making R₁/R₂ < 1.
Q13. Distribution of electric power from one place to another is done at high A.C. voltage because
(a) Wastage of electricity is minimised
(b) Stealing of electric wires is prevented
(c) Electricity spreads in very short time
(d) It adds brightness
Answer: (a) Wastage of electricity is minimised
Explanation: High A.C. voltage transmission reduces power loss due to resistance in wires. It allows efficient long-distance transmission, minimizing energy wastage and improving economic viability.
