Q1. Identical twins are born when
(a) Two sperms fertilise one ovum
(b) Two sperms fertilise two ovums simultaneously
(c) One sperm fertilises the ovum and zygote divides into two separate cells developing independently
(d) One sperm fertilises two ovums
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (c) One sperm fertilises the ovum and zygote divides into two separate cells developing independently
Explanation: Identical twins result from a single fertilised egg (zygote) that splits into two embryos, sharing the same genetic material. This leads to twins that are genetically identical and usually of the same sex.
Q2. Conception generally takes place at the time of
(a) Menses
(b) Before menses
(c) Immediately after menses
(d) Two weeks after menses
Answer: (d) Two weeks after menses
Explanation: Ovulation typically occurs about 14 days after menstruation, which is the most fertile period. If sperm fertilises the ovum during this time, conception occurs. This timing aligns with the menstrual cycle’s reproductive phase.
Q3. Hybridisation is useful in developing improved crops by
(a) Creating new and better genes
(b) Eliminating undesirable genes
(c) Producing favourable combination of gases
(d) By encouraging favourable genes and removing unfavourable ones
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (d) By encouraging favourable genes and removing unfavourable ones
Explanation: Hybridisation combines desirable traits from different parent plants, promoting favourable genes like disease resistance, high yield, and drought tolerance, while suppressing undesirable traits, leading to improved crop varieties.
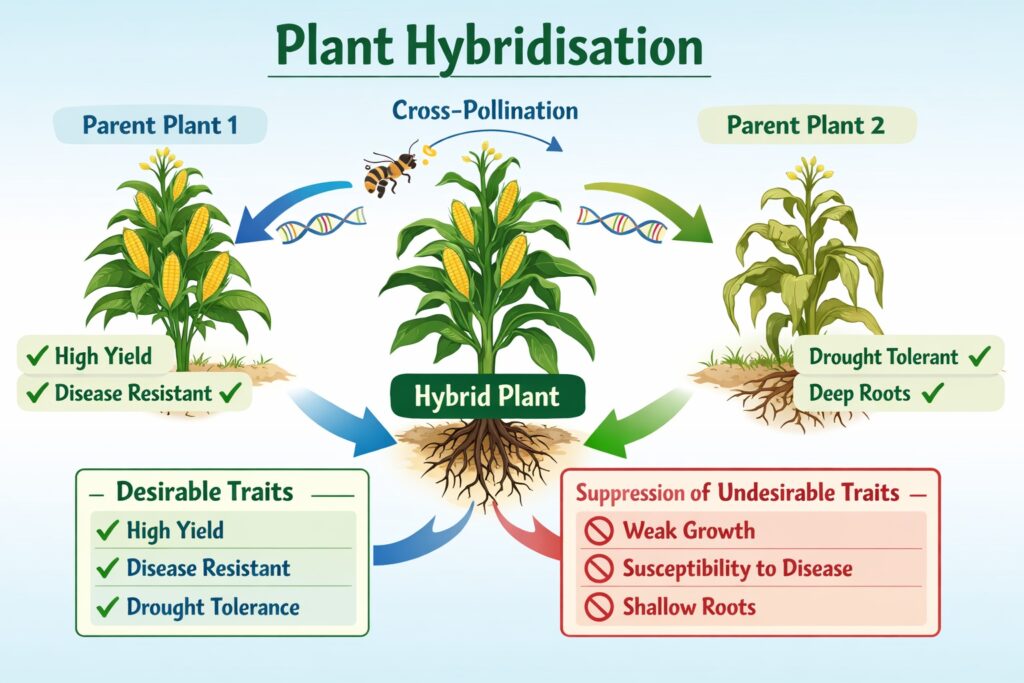
Q4. The varieties of corn can be improved by which of the following methods ?
(a) Dihybrid cross
(b) Back cross
(c) Double cross
(d) Natural selection
(UPSC Prelims 1981)
Answer: (c) Double cross
Explanation: Double cross hybridisation involves crossing two hybrid lines, enhancing genetic diversity and yield potential. It’s widely used in corn breeding to combine favourable traits from multiple parent lines.
Q5. The genetic code can be translated through an intermediate, adaptor molecule by
(a) tRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) ATP
(d) ADP
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) tRNA
Explanation: tRNA (transfer RNA) acts as an adaptor molecule that translates the genetic code from mRNA into amino acids during protein synthesis. It carries specific amino acids and matches them to the corresponding codons on the mRNA strand through its anticodon region, enabling accurate translation.
Q6. What is the tissue culture ?
(a) Preparation of fragments of the cells of organism for biochemical examination
(b) Japanese culture
(c) Name given to a special type of surgery
(d) None of the above
(UPSC Prelims 1985)
Answer: (a) Preparation of fragments of the cells of organism for biochemical examination
Explanation: Tissue culture involves growing cells or tissues in a controlled environment, often for biochemical analysis, genetic studies, or plant propagation. It is widely used in biotechnology.
Q7. Influence of genes in controlling the activity of living organisms is through
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Protein synthesis
(c) Vitamins
(d) Hormones
(UPSC Prelims 1986)
Answer: (b) Protein synthesis
Explanation: Genes carry instructions for protein synthesis, which regulates cellular functions, growth, and metabolism. Proteins are the functional products of gene expression, making this the correct biological mechanism.
Q8. The hybrids of which of the following plants are available for commercial production ?
(1) Rice
(2) Wheat
(3) Jute
(4) Pulses
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2 and 4
Explanation:
Hybrid varieties of rice, wheat, and pulses have been developed and are used in commercial agriculture to improve yield and disease resistance. Jute hybrids are not widely available for commercial use, making option (a) correct.
Q9. Which of the following is necessary for improvement of the quality of crops ?
(1) Introduction
(2) Hybridisation
(3) Selection
(4) Segregation
(a) 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2 and 3
(UPSC Prelims 1987)
Answer: (c) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Introduction of new varieties, hybridisation to combine traits, and selection of superior plants are key steps in crop improvement. Segregation is a genetic process but not directly used in crop quality enhancement, making option (c) accurate.
Q10. UP-308 is a variety of
(a) Millet
(b) Rice
(c) Cotton
(d) Wheat
Answer: (d) Wheat
Explanation: UP-308 is a recognized high-yielding wheat variety, developed for agricultural use in India, especially suited to northern regions.