Q1. Two capacitors C and 2C charged to V and 2V respectively are connected in parallel with opposite polarity. The common potential is:
(A) V
(B) V/2
(C) V/3
(D) 3V
Ans: (A) V
Solution: Given:
Capacitor 1: Capacitance = \( C \), Potential = \( V \)
Capacitor 2: Capacitance = \( 2C \), Potential = \( 2V \)
Charge on first capacitor:
\[
Q_1 = C \times V = CV
\]
Charge on second capacitor:
\[
Q_2 = 2C \times 2V = 4CV
\]
Since the capacitors are connected in parallel with opposite polarity, the net charge is:
\[
Q_{\text{net}} = Q_2 – Q_1 = 4CV – CV = 3CV
\]
Total capacitance in parallel:
\[
C_{\text{total}} = C + 2C = 3C
\]
Common potential:
\[
V_{\text{common}} = \frac{Q_{\text{net}}}{C_{\text{total}}}
= \frac{3CV}{3C} = V
\]
Q2. Ratio of de Broglie wavelengths of a proton and an alpha particle accelerated through the same potential difference is:
(A) \( 1 : 2 \)
(B) \( 2\sqrt{2} : 1 \)
(C) \( 2 : 1 \)
(D) \( \sqrt{6} : 1 \)
Correct Answer: (B) \( 2\sqrt{2} : 1 \)
Explanation:
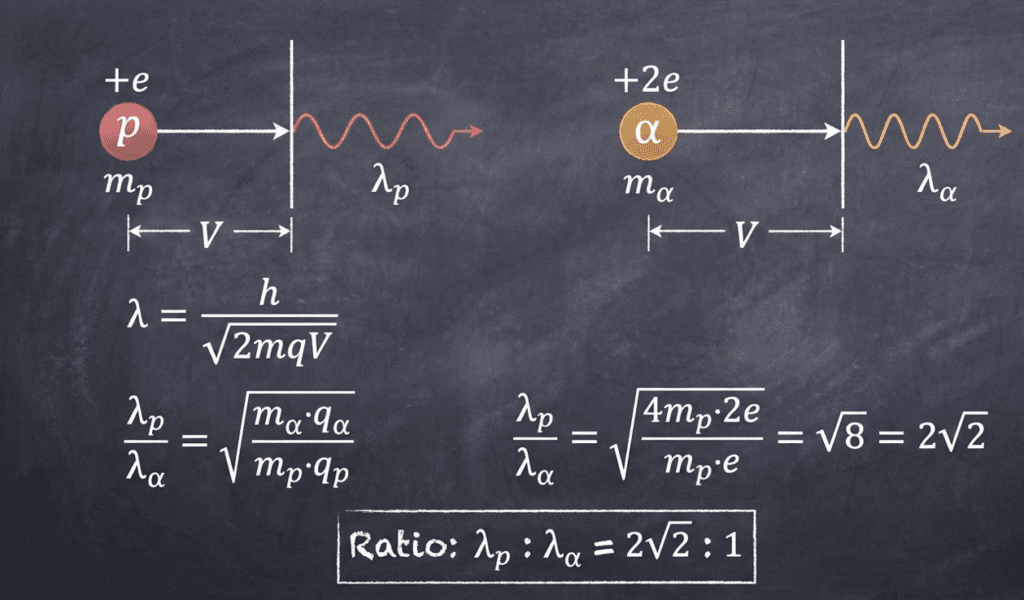
The de Broglie wavelength is given by:
\[
\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{\sqrt{2mK}}
\]
When a particle is accelerated through a potential difference \( V \), its kinetic energy is:
\[
K = qV
\]
Substituting this in the wavelength expression:
\[
\lambda \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{mq}}
\]
For a proton:
- Mass \( = m \)
- Charge \( = e \)
For an alpha particle:
- Mass \( = 4m \)
- Charge \( = 2e \)
Ratio of their wavelengths:
\[
\frac{\lambda_p}{\lambda_\alpha} =
\sqrt{\frac{m_\alpha q_\alpha}{m_p q_p}} =
\sqrt{\frac{4m \cdot 2e}{m \cdot e}} =
\sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2}
\]
Q3. From a ring of area \(1\,\text{m}^2\) and resistance \(100\,\Omega\), a magnetic field \[ B = \sin(100t)\ \text{T} \]
is passing perpendicular to the ring. Find the heat produced in one time period (in joule):
(1) \(4\pi\)
(2) \(3\pi\)
(3) \(2\pi\)
(4) \(\pi\)
Ans: (4) \(\pi\)
Given:
- Area of the ring, \( A = 1\,\text{m}^2 \)
- Resistance, \( R = 100\,\Omega \)
- Magnetic field, \( B = \sin(100t)\,\text{tesla} \)
- The magnetic field is perpendicular to the ring

Magnetic Flux:
\[
\Phi = BA = \sin(100t) \times 1 = \sin(100t)
\]
Induced EMF:
Using Faraday’s law,
\[
\mathcal{E} = -\frac{d\Phi}{dt}
\]
\[
\mathcal{E} = -\frac{d}{dt}[\sin(100t)] = -100\cos(100t)
\]
Induced Current:
\[
i = \frac{\mathcal{E}}{R} = \frac{-100\cos(100t)}{100}
\]
\[
i = -\cos(100t)
\]
(The negative sign indicates direction and is ignored for heating calculations.)
Power Dissipated as Heat:
\[
P = i^2 R
\]
\[
P = \cos^2(100t) \times 100
\]
Heat Produced in One Time Period:
Time period of the magnetic field:
\[
T = \frac{2\pi}{100}
\]
Heat produced:
\[
H = \int_0^T P\,dt = 100 \int_0^T \cos^2(100t)\,dt
\]
Average value of \( \cos^2 \) over one period is \( \frac{1}{2} \).
\[
H = 100 \times \frac{1}{2} \times T
\]
\[
H = 50 \times \frac{2\pi}{100}
\]
\[
H = \pi \,\text{joule}
\]
Q4. In a double slit experiment, the distance between the slits is $0.1 \text{ cm}$ and the screen is placed at $50 \text{ cm}$ from the slit plane. When one slit is covered with a transparent sheet having thickness $t$ and refractive index $n = 1.5$, the central fringe shifts by $0.2 \text{ cm}$. The value of $t$ is:
$t = 8 \mu\text{m}$
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Identify the Given Parameters:
- Shift in central fringe ($\Delta y$) = $0.2 \text{ cm} = 2 \times 10^{-3} \text{ m}$
- Distance between slits ($d$) = $0.1 \text{ cm} = 10^{-3} \text{ m}$
- Distance to screen ($D$) = $50 \text{ cm} = 0.5 \text{ m}$
- Refractive index ($n$) = $1.5$
- Apply the Fringe Shift Formula:The shift $\Delta y$ produced by introducing a transparent sheet of thickness $t$ in front of one slit is given by:
$$\Delta y = \frac{D}{d} (n – 1)t$$ - Solve for Thickness ($t$):Rearranging the formula to find $t$:
$$t = \frac{\Delta y \cdot d}{D(n – 1)}$$
Substitute the values:
$$t = \frac{(2 \times 10^{-3} \text{ m}) \cdot (10^{-3} \text{ m})}{0.5 \text{ m} \cdot (1.5 – 1)}$$
$$t = \frac{2 \times 10^{-6}}{0.5 \cdot 0.5}$$
$$t = \frac{2 \times 10^{-6}}{0.25}$$
$$t = 8 \times 10^{-6} \text{ m}$$ - Convert to Micrometers:Since $1 \mu\text{m} = 10^{-6} \text{ m}$, the thickness is: $t = 8 \mu\text{m}$