Q.1 A man walks down the backside of his house straight 25 metres, then turns to the right and walks 50 metres again; then he turns towards left and again walks 25 metres. If his house faces to the East, what is his direction from the starting point?
(a) South-East
(b) South-West
(c) North-East
(d) North-West
Answer: (d)
Refer the above picture, it clearly indicates that the man is finally standing in the North-West Direction.

Q.2 Two Statements are given followed by two Conclusions:
Statements:
All numbers are divisible by 2.
All numbers are divisible by 3.
Conclusion-I:
All numbers are divisible by 6.
Conclusion-II:
All numbers are divisible by 4.
Which of the above Conclusions logically follows/follow from the two given Statements?
(a) Only Conclusion-I
(b) Only Conclusion-II
(c) Neither Conclusion–I Conclusion-II
(d) Both Conclusion–I and Conclusion-II
Answer: A
The numbers divisible by both 2 and 3 will be divisible by the product of the two numbers i.e. 6.
Example: 18 is divisible by 6 but not by 4. Hence, only conclusion I follow.
Q.3 Two Statements are given followed by two Conclusions:
Statements:
All cats are dogs.
All cats are black.
Conclusion-I:
All dogs are black.
Conclusion-II:
Some dogs are not black.
Which of the above Conclusions
logically follows / follow from the two
given Statements, disregarding
commonly known facts?
(a) Only Conclusion-I
(b) Only Conclusion-II
(c) Neither Conclusion-I nor Conclusion-II
(d) Both Conclusion-I and Conclusion-II
Answer: C
Refer the above Venn Diagram, all dogs are not black.
Note: Since both the statements are universal (Universal statements are statements with word like All, None), the conclusion will always be universal. Hence, Some word can not be the part of the conclusion.
Q.4 Consider the following sequence of numbers:
5 1 4 7 3 9 8 5 7 2 6 3 1 5
8 6 3 8 5 2 2 4 3 4 9 6
How many odd numbers are followed by the odd number in the above sequence?
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer: b
5 1 4 7 3 9 8 5 7 2 6 3 1 5
8 6 3 8 5 2 2 4 3 4 9 6
Here, there are five pairs of odd number followed by the Odd Number. (51), (7,3), (3,9), (5,7), (3,1), (1,5)
Q.5 A is 16th from the left end in a row of boys and Vis 18th from the right end. G is 11th from A towards the right and 3rd from V towards the right end. How many boys are there in the row?
(a) 40
(b) 41
(c) 42
(d) Cannot be determined due to insufficient data
Answer: (b)
Q.6 Three Statements SI, S2 and S3 are given below followed by a Question:
S1 : C is younger than D, but older than A and B.
S2 : D is the oldest.
S3 : A is older than B.
Question:
Who among A, B, C and D is the youngest?
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above Statements and the Question?
(a) SI alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(b) S1 and S2 together are sufficient to answer the Question.
(c) S2 and S3 together are sufficient to answer the Question.
(d) S1 and S3 together are sufficient to answer the Question.
Answer: D
S1: D>C>(A,B)
S2: D is the oldest
S3: A>B
To get the complete order, you must club S1 and S3, this will conclude D>C>A>B. B is the youngest.
S2 is redundant as S1 already says the same thing.
Q.7 How many integers are there between 1 and 100 which have 4 as a digit but are not divisible by 4?
(a) 5
(b) 11
(c) 12
(d) 13
Answer: C
Here, the numbers must be between 1 and 100, Now the numbers can be either in single digits or in double digits.
Double Digit: (40), (41), (42), (43), (44), (45), (46), (47), (48), (49)
or, (04), (14), (24), (34), (44), (54), (64), (74), (84), (94)
Total Numbers: 20
Divisible by 4: 8
Hence, Numbers not divisible by 4 are (20-8=12)
Q.8 Let x, y be the volumes; m, n be the masses of two metallic cubes P and Q respectively. Each side of Q is two times that of P and mass of Q is two times that of P. Let u = m / x and v = n / y. Which one of the following is correct?
(a) u = 4v
(b) u = 2v
(c) v = u
(d) v = 4u
Answer: A
Step1
x, y: Volume P, Q
m, n: Masses of P, Q
Side of Q=2*Side of P, hence, Volume of Q will be 8 times the volume of P. Hence, y=8x
Mass of Q=2*Mass of P, hence, n=2m
Step2
Now, u=m/x , v=n/y
So, u/v= (m/x)/(n/y)
= my/nx
=(m*8x)/(2m*x)
=4/1
Hence, u=4v
Q.9 The average age of a teacher and three students is 20 years. If all the three students are of same age and the difference between the age of the teacher and each student is 20 years, then what is the age of the teacher?
(a) 25 years
(b) 30 years
(c) 35 years
(d) 45 years
Answer: C
Let, age of teacher is t
Let age of three students is s.
Now, Average age of teacher and three three students will be (t+3s)/4
Hence, (t+3s)/4= 20
or, (s+20+3s)/4=20
or, 4s+20= 80
or, 4s=60
or, s=15
Hence, t=15+20=35
Q.10 A person bought a car and sold it for Rs 3,00,000. If he incurred a loss of 20%, then how much did he spend to buy the car?
(a) Rs 3,60,000
(b) Rs 3,65,000
(c) Rs 3,70,000
(d) Rs 3,75,000
Answer: D
Here, it is important to remember that the Profit and Loss are calculated on the basis of Cost Price.
SP= 300000 (i.e. 3L)
Loss Percentage= ((Cost Price- Selling Price)/Cost Price)*100
or, 20=((CP-3L)/CP)*100
or, 1=((CP-3L)/CP)*5
or, CP=5CP-15L
or, 4CP=15L
or, CP=375000
Q.11 Passage–1
Private investment in general is volatile. Foreign private investment is more volatile because the available investment avenues are significantly greater (i.e., the entire world). Therefore, the responsibility of providing employment cannot be left to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The current FDI inflows are (volatile over time and across sectors and regions, which is a necessary consequence of their search for the highest returns. The adverse consequences are unstable employment and an accentuation of income and regional inequalities. A probable positive consequence of foreign investment is the inflow of new technology and its subsequent diffusion. However, the technology diffusion is not at all certain because the existing state of physical and human capital in India may prove inadequate for the diffusion.
With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
- Relying on foreign investment in the long run is not an economically sound policy.
- Policies must be undertaken to reduce volatility in foreign private investment.
- Policies must be undertaken to strengthen domestic private investment.
- Public investment should be given priority over private investment.
- Substantial public investment in education and health should be undertaken.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 5
(c) 2, 4 and 5
(d) 3 only
Answer: B
UPSC has introduced passage with the options of ‘assumptions’ from the Prelims Paper of 2019.
In order to solve such questions, you must understand the mind-set of the author drafting the Passage.
Lets, apply this process here.
S1: From the first two opening statements, it is clear that the author is quite anxious about the volatile nature of the FDI. He clearly disapproves the reliance on it for economic prosperity of the region. Hence, S1 is the right assumption.
S2: The author agree that FDI inflows are volatile which is a necessary consequence of their search for the highest returns.
So, can the government change such volatility?
No, it can’t! Hence, bringing policies to regulate such funds will have very limited impact. S2 is not the correct assumption.
S3: The prime concern of the author is the volatility of the fund and the private investment less volatile compared to FDI. Hence, private investment needs to be promoted. S is correct assumption.
S4: No, not at all. Author has nowhere mentioned such requirements. S4 is not the right assumption.
S5: Just refer the last statement of the paragraph, it stress the requirement of uplifting the human capital to absorb the emerging technology. S5 is correct.
Q.12 Passage–2
Many opportunities to harness the highly skewed, seasonal and spatial distribution of monsoon flows, which occur in a four-month period from June to September annually, have been lost. Since these few months account for most of the rainfall and consequent freshwater availability, the need for holding rainwater in reservoirs, for subsequently releasing it for use over the year, is a necessity nobody can afford to overlook. Climate change will continue to affect weather conditions and create water shortages and excesses. While millions suffer from droughts and floods, waters in the country’s many rivers flow unutilized, and are discharged into the sea every year.
With reference to the above passage, which of the following could be the most rational and practical implications for India?
- Inter-linking of rivers should be undertaken.
- A network of dams and canals should be built across the country for proper distribution of water.
- Farmers should be provided easy loans for digging bore wells.
- Usage of water for agriculture should be regulated by law.
- Distribution of river water among regions should be regulated by the Union Government.
Select the correct answer using the code
given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 5
Answer: A
S5: Not a correct option, author nowhere talks about the political responsibility. In fact, you should start solving the question from this option. Just eliminate option 5, and two options are gone. You are left with options (a) and (c).
S3: Will more bore wells help in tapping the monsoon water? No it will have opposite impact. So S3 is not a good option.
Now, option (c) is gone. So, we are left with option (a) only.
S1: Refer the last statement of the paragraph, to ensure better availability of water, interlinking of river is a feasible option. S1 is correct.
S2: In order to tap the flowing rainwater, building dams and canals are good options. S2 is correct.
S4: Regulating the usage of water for agriculture will lead to optimum utilization of ground water and will be helpful in ensuring the water availability but the author has nowhere mentioned the necessity of such regulation. S4 is incorrect.
Q.13 Passage–3
People will invest in education whenever they are granted the economic freedom to fully enjoy its benefits. Again, this is for the obvious reason that the return on education increases as the level of economic freedom rises. When people, thanks to lower tax rates, are allowed to retain most of the higher income that they gain from each incremental level of education, it makes eminent sense to invest in education. On the other hand, when the government decides to tax the higher income of educated individuals at even higher rates, it makes very little sense to invest in educating oneself further. The same incentives apply to parents who decide on whether to invest in their children’s education.
With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
- Lower tax rates in a country invariably translate into greater investments in higher education.
- Investment in the education of children ensures their economic freedom.
- Economic freedom has a positive impact on building up human capital.
Which of the above assumptions is/are
valid?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
S1: Focus on the word invariably, it has generalized the statement. Yes, it is true to some extent but Lower Tax Rate will not always lead to greater investment in higher education.
S2: There is no such guarantee that education ensures their economic freedom. Such assumption has nowhere been mentioned in the passage. Hence, this statement is not an assumption.
S3: The statement is nowhere present in the entire passage but the author has expressed a close association between education and economic returns associated with it. Hence, S3 is a correct assumption.
Q.14 Passage-4
Our urban bodies cannot possibly ensure sustainable delivery of water in our cities unless financing mechanisms are put in place. Water delivery requires heavy investment in collecting it from a natural source, treating it to make it potable, and laying a distribution network of pipes for delivery to the users. It also requires investments in sewerage infrastructure and sewage treatment plants so that the sewers can carry the wastewater to these plants to ensure
that no untreated sewage is discharged back into natural water bodies. If our cities were rich enough to meet the entire cost, water could be delivered free. They are not.
14. What is the most logical and crucial message conveyed by the passage?
(a) Urban local bodies must recover costs through user charges.
(b) Urban local bodies are not efficient enough to meet the water requirements of our cities.
(c) Water shortage in our cities is a perennial problem that cannot be solved.
(d) In view of the water crisis in our cities, there is an urgent need to limit the population of cities by adopting an upper limit of population size.
Answer: (a)
So, the theme may be written as “Financing the urban bodies for sustainable supply of water”.
The crucial message must be centred around it. The most suitable being option (a).
15. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. Rich cities only can ensure sustainable delivery of water.
2. Sustainable delivery of water in cities means much more than supplying water to households.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
S1: Incorrect, an extreme statement.
S2: Correct, it also requires investments in sewerage infrastructure and sewage treatment plants
Passage–5
In India, agriculture still engages about half of its workforce, and about 85 per cent of its farms are small and marginal. Compared to China and Vietnam, which have experienced fast structural and rural transformation, India’s story is of slow transformation. As a result, poverty reduction in India was at a much slower pace during 1988-2014, compared to China and Vietnam. India’s poverty reduction was slow during 1988-2005, but during 2005-2012, it accelerated dramatically—almost three times faster than during the earlier period. What did India do during this period? Research reveals that the relative price scenario changed significantly (by more than 50%) in favour of agriculture in the wake of rising global prices. This boosted private investments in agriculture by more than 50%. As a result, agri-GDP growth touched 41% during 2007-2012 as against 2.4% during 2002-2007. The net surplus of agri trade touched $25 billion in 2013-2014; real farm wages rose by 7% per annum. All this led to unprecedented fall in poverty.
16. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. Structural and rural transformation is impossible when farms are mainly small and marginal.
2. A good price incentive can trigger investments in agriculture.
3. India needs to build value chains for high-value agri-products like livestock
and horticulture.
4. Higher global prices of agricultural commodities are essential for India’s poverty reduction.
Which of the above assumptions are valid?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Answer: B
S1: Incorrect, Structural and rural transformation not directly linked with the landholdings.
S2: Correct, it has happened in the year 2007-12
S3: Incorrect, No mention of the livestock in the passage.
S4: Correct, it is required for fall in poverty
17. Which one of the following statements best reflects the critical message of the
passage?
(a) India should create large-scale off-farm rural employment to reduce poverty in
the near future.
(b) India should create a large number of farmer producer companies.
(c) Private investment in agriculture should be given priority over public investment.
(d) Inclusive agricultural growth is key to reduce poverty in the near future.
Answer: D
Theme of the passage is Effects of increasing Price of agro-commodity on the private investment in agriculture.
The critical message will be centred around it. Most suitable option is D.
Q. 18. Two Statements SI and S2 are given below with regard to four numbers P, Q, R and S followed by a Question:
S1 : R is greater than P as well as Q.
S2 : S is not the largest one.
Question: Among four numbers P, Q, R and S, which one is the largest?
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above Statements and the Question?
(a) SI alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(b) S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(c) S1 and S2 together are sufficient to answer the Question, but neither SI alone nor S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(d) SI and S2 together are not sufficient to answer the Question.
Answer: C
S1: R> (P,Q)
S2: (Largest Number)>S
We need to club both these statements, then only we can say that R is the greatest number.
Q.19. Two Statements SI and S2 are given below followed by a Question:
S1 : n is a prime number.
S2 : n leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 4.
Question: If n is a unique natural number between 10 and 20, then what is n?
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above Statements and the Question?
(a) SI alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(b) S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(c) S1 and S2 together are sufficient to answer the Question, but neither SI alone nor S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(d) SI and S2 together are not sufficient to answer the Question.
Answer: D
According to question, numbers may be 10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20
Again,
S1: n is a prime number, i.e. 11,13,17,19
S2: n=4x+1, where x is a whole number, i.e. 13,17
Hence, both S1 and S2 combined is not sufficient to answer the question.
20. Two Statements SI and S2 are given below with regard to two numbers followed by a Question:
S1 : Their product is 21.
S2 : Their sum is 10.
Question:
What are the two numbers?
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above Statements and the Question?
(a) SI alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(b) S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(c) S1 and S2 together are sufficient to answer the Question, but neither SI alone nor S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(d) SI and S2 together are not sufficient to answer the Question.
Answer: a
Let the two numbers be
S1: m*n=21, (if m is 3, then n is 7) and there is no other possible factorization of 21.
S2: m+n=10, (if m is 1, n will be 9), (If m is 2, n will be 8), so on
So, S1 alone is sufficient to answer the question. S2 alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
Hence answer is a.
21. In the sum
Ä + l Ä + 5 Ä + Ä Ä + Ä l = l Ä Ä
for which digit does the symbol Ä stand?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer: B
Here, you need not check all the numbers one by one. Just check unit place addition by putting the numbers.
If, 2 is placed
The addition of unit place on the left hand side of the equation will be 2+2+2+2+1=9
Hence, the unit place of the number on the right hand side of the equation will be 9. But, we have 122 on the right.
Hence, 2 cannot be the answer.
Similarly, If, 3 is placed
The addition of unit place on the left hand side of the equation will be 3+3+3+3+1=13 (unit place is 3)
Hence, the unit place of the number on the right hand side of the equation will be 3. We have 133 on the right. Unit place is matching. This may be the possible option.
Hence, 3 can be the answer.
Similarly, when checked for 4 and 5, the unit places do not match. Hence, correct answer is b.
22. If you have two straight sticks of length 7.5 feet and 3.25 feet, what is the minimum length can you measure?
(a) 0.05 foot
(b) 0.25 foot
(c) 1 foot
(d) 3.25 feet
Answer: B
Here, minimum has been asked. So, we have to take the HCF of the two numbers.
7.5= 75/10=15/2
3.25= 325/100=13/4
FCF of (15/2 and 13/4) = (HCF of 15,13)/ (LCM of 2,4)
=1/4
=0.25
23. A simple mathematical operation in each number of the sequence 14, 18, 20, 24, 30, 32, … results in a sequence with respect to prime numbers. Which one of the following is the next number in the sequence?
(a) 34
(b) 36
(c) 38
(d) 40
Answer: C
Note that the difference between the consecutive numbers are not big, hence this might be the case of addition/subtraction.
Let’s check it
14, 18, 20, 24, 30, 32, …
4 2 4 6 2 (First iteration by subtraction)
-2 2 2 -4 (Second iteration by subtraction)
We are not getting any conclusive result.
So, let’s check the solution with prime numbers.
14= 13+1 (13 is a prime number)
18=17+1 (17 is a prime number)
20= 19+1 (19 is a prime number)
24= 23+1 (23 is a prime number)
30= 29+1 (29 is a prime number)
32=31+1 (31 is a prime number)
38= 37+1 (37 is a prime number next to 31)
Hence, 38 is the right answer.
24. One page is torn from a booklet whose pages are numbered in the usual manner starting from the first page as 1. The sum of the numbers on the remaining pages is 195. The torn page contains which of the following numbers?
(a) 5, 6
(b) 7, 8
(c) 9, 10
(d) 11, 12
Answer: B
Let the book contains n number of pages. Let the page no. x and x+1 have been removed.
Sum of all the number will be (n(n+1))/2
Or, (n(n+1))/2=195+(x) +(x+1)
Here, it is important to note that both n and x are natural numbers.
Now, to balance the equation, n must be selected in such a way that the term (n(n+1))/2 yields more than 195
To get that, lets us take n as 10,
Then, n(n+1)/2= 55 (tool less than 195)
Let’s check with n as 20
Then, n(n+1)/2=210 (fine, this may work, let’s check it)
210= 195+(x) + (x+1)
Or, 2x=14
Or, x=7 and x+1= 8
Hence, pages are 7 and 8.
25. Consider the following arrangement that has some missing letters:
abab_b_bcb_dcdcded_d
The missing letters which complete the arrangement are
(a) a, b, c, d
(b) a, b, d, e
(c) a, c, c, e
(d) b, c, d, e
Answer: C
Look at the series and just focus on the biggest chunk of data.
Here, the biggest chunk of data is dcdcded.
What next?
Just find out what gets repeated in this biggest chunk of data. The repetition is marked in bold: is of dcdcded (5 letters getting repeated).
Now, form the group of 5 from the beginning.
abab_/b_bcb/_dcdc/ded_d
obviously, we will fill a,c,c,e
Hence, the answer is c.
26. Let A3BC and DE2F be four-digit numbers where each letter represents a different digit greater than 3. If the sum of the numbers is 15902, then what is the difference between the values of A and D?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer: C
A3BC
DE2F
……….
15902
Sum of E and F must be 12 as the unit digit is 2.
C+F=12
Now, One 2 comes at the unit place we have to add 1 to the next sum of digit. Hence,
B+2+1=10 (as zero is at the second place)
B=7
Again,
E+3+1=9, so, E=5
A+D=15
So, A, D= (6,9), (7,8)
But, A, D cannot be (7,8) as, B is 7
Hence, A, D is (6,9), difference is 3.
27. Two Statements S1 and S2 are given below followed by a Question:
S1: There are not more than two figures on any page of a 51-page book.
S2: There is at least one figure on every page.
Question:
Are there more than 100 figures in that book?
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above Statements and the Question?
(a) Both SI and S2 are sufficient to answer the Question, but neither SI alone nor S2 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(b) S1 alone is sufficient to answer the Question.
(c) SI and S2 together are not sufficient to answer the Question.
(d) S2 alone is sufficient to answer the
Question.
Answer: C
S1: Images on each pages will be either 1 or 2.
S2: Every Page has images more than or equal to 1
Case1: if each page has 2 images
Total images in book will be 102.
Case: 2
If each page has 1 page
Total images will be 51.
Hence, we are not sure if the total figures are less than or more than 100.
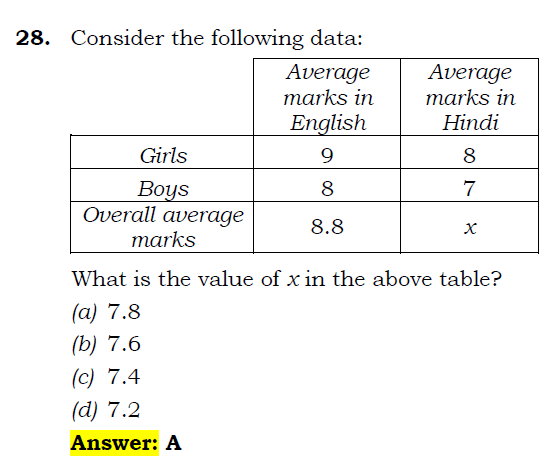
Let the number of girls in the class is g and the number of boys is b.
English
So, 9g+8b=(b+g)*8.8
Or, 9g+8b=8.8b+8.8g
Or, 0.2g=0.8b
Or, g=4b
Hindi
8g+7b=(b+g)*x
Or, 8*4b+7b=(b+4b)*x
Or, 39b=5b*x
Or, x=39/5=7.8
Short cut Method
We know that the average of marks will shift towards the marks of boys/girls depending upon who dominates by the numbers.
Here, if we look at the marks of English, the total average marks is inclined towards the score of girls (girls: 9, Average: 8.8).
Similarly, the average marks of Hindi will be tilted towards the average marks of boys.
The average marks should be 7.9 or 7.8. Option 7.8 is present.
29. A family of two generations consisting of six members P, Q, R, S, T and U has three males and three females. There are two married couples and two unmarried siblings. U is P’s daughter and Q is R’s mother-in-law. T is an unmarried male and S is a male. Which one of the following is correct?
(a) R is U’s husband.
(b) R is S’s wife.
(c) S is unmarried.
(d) None of the above
Answer: B

30. If in a particular year 12th January is a Sunday, then which one of the following is correct?
(a) 15th July is a Sunday if the year is a leap year.
(b) 15th July is a Sunday if the year is not a leap year.
(c) 12th July is a Sunday if the year is a leap year.
(d) 12th July is not a Sunday if the year is a leap year.
Answer: C
Jan: 19 days (odd days: 5)
Feb: 29 (odd days: 1, considering leap year)
March:31 (Odd days: 3)
April: 30 (Odd days: 2)
May: 31 (Odd days: 3)
June: 30 (Odd days: 2)
July: 12 (Odd days: 5)
Total: 21
21/7 gives 0 odd days.
12th Jan was Sunday, hence 12th July will be Sunday.
Q. 31 Passage–1
In India, over the last decade or so, labour has been departing agriculture, but is only going to construction and unregistered manufacturing which are not markedly better jobs. Services, where labour tends to be most productive, are not generating the additional jobs the country needs. India will need 24 million or so jobs over the next decade. The new sector, e-commerce, can at best close only half the jobs gap. Only those sectors that drive domestic demand such as health and education can comfortably fill the other half.
Which one of the following is best implied in the passage?
(a) Strong measures need to be taken to reduce the rural to urban migration of labour.
(b) The working condition in construction and unregistered manufacturing needs to be improved.
(c) Service sector has been reducing the problem of unemployment.
(d) Increased social sector spending is imperative for large-scale job creation.
Answer: d
Option a: Author has nowhere expressed the concern of rural-urban migration of labour.
Option b: No, it is true that the working condition is not good there but the prime focus of author is employment.
Option c: No, Service sector is actually not producing additional jobs as expected.
Option d: Increased social sector spending has not been stressed upon directly in the passage but, it is implied that social sector spending is imperative for large-scale job creation.
Q.32 Passage–2
In India, the current focus on the right to privacy is based on some new realities of the digital age. A right is a substantive right only if it works in all situations, and for everyone. A right to free expression for an individual about her exploitation, for instance, is meaningless without actual availability of security that guarantees that private force cannot be used to thwart this right. The role of the State, therefore, is not just to abstain from preventing rightful free expression, but also to actively ensure that private parties are not able to block it.
On the basis of the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. State should have some institutions to ensure its appropriate role in a digital society.
2. State should ensure that private parties do not violate the citizens’ right to privacy.
3. Digital economy is not compatible with the idea of not violating the citizens’ privacy.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2 only
Answer: a
S3: Eliminate this option first. Passage do not talk about such incompatibility.
Hence, options b and c are eliminated.
S1 and S2 are explicitly mentioned in the passage.
Q.33 Passage–3
One of the biggest ironies around water is that it comes from rivers and other wetlands. Yet it is seen as divorced from them. While water is used as a resource, public policy does not always grasp that it is a part of the natural ecosystem. Efforts at engineering water systems are thus efforts at augmenting water supply rather than strengthening the capacities of ecological systems.
Which one of the following is the most logical and rational inference that can be made from the above passage?
(a) Rivers and other wetlands should be protected under Ramsar Convention.
(b) Engineering water systems should be modernized and further augmented.
(c) Wetlands need to be reinforced as more than just open sources of water.
(d) Water supply should not be free of cost so as to prevent its misuse or overuse.
Answer: C
The question asks the inference. Author is concerned about the use of modern technology to just to harness the water source rather strengthening the source of water. Hence, option c is correct.
Q.34 Passage–4
Asset allocation is the most important investment decision we will ever make and sadly, most of us do not give that decision, the importance it deserves. We are adamant about seeking predictability with our future. We tend to think of investing in risky assets as extremely volatile and value eroding. We also dislike fluctuating returns and the loss of control of investment. We think our money is best left idle, unproductive but safe. There is no asset that is risk-free. We could lose our jobs, our homes can lose value, our banks can go bankrupt, our bonds can default, the government can collapse and companies we chose fondly may cease to exist. But we cannot live life assuming that all these extreme events are waiting to happen, and all at the same time. All these extreme forms of risks we know will not manifest at the same time.
Which one of the following statements best implies the suggestion given by the author of the passage?
(a) Distribute your wealth across different kinds of assets so that your risks would be minimized.
(b) Risk-taking behaviour should be a necessary component of your personality if you want to generate wealth.
(c) While making investments, find a trustworthy asset management organization which would manage your wealth for you.
(d) You should know that investing your money is a risky business.
Answer: b
The author finds that the most of us are over conservative so far as the wealth management is concerned and stresses upon the requirement of risk taking abilities for better wealth management. Hence, correct option is b.
Q.35 Passage – 5
Although most of the Genetically Modified (GM) crops cultivated now are genetically engineered for a single trait, in future, crops genetically engineered for more than one trait will be the norm. Thus, biotechnology’s role in agriculture and the regulation of the same cannot be understood solely in the context of the current generation of GM crops. Instead, there is a need to take a comprehensive look, taking into account various aspects, including socio-economic impacts, so that the potential of the technology can be harnessed while minimizing negative impacts. Given the importance of biotechnology in developing varieties that can help in climate change mitigation and adaptation, not using biotechnology as a part of the climate change action plan cannot be an option. Domestic regulation of biotechnology cannot be viewed in isolation of trade policy and obligations under various international treaties and conventions.
With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. Biotechnology regulation is an evolving process.
2. Participation of people is needed in policy decisions regarding biotechnology regulation.
3. Biotechnology regulation should take into account socio-economic aspects in decision-making.
4. Wider involvement of political executive in biotechnology regulation improves its effectiveness in dealing with the country’s trade policies and international obligations.
Which of the above assumptions are valid?
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: b
S4: Just start with this option. Nowhere such requirement of involvement of political executives have been made. Just cross it and three options are eliminated. You are left with option b only.
36. Which one of the following statements best implies the crux of the passage?
(a) Precautionary principle is not given importance in current debate on developing GM crops.
(b) Biotechnology is not currently used in climate change mitigation and adaptation mechanisms.
(c) Biotechnology’s role is not confined to the current priorities of developing GM crops.
(d) The negative impacts of biotechnology are not properly understood.
Answer: c
The author talks about the possible use of biotechnology as a measure to adopt and mitigate the climate change. It also talks about broadening the scope of biotechnology to develop GM crops having more than one developed qualities. Hence, correct option is c.
37. How many zeroes are there at the end of the following product?
1 × 5 × 10 × 15 × 20 × 25 × 30 × 35 × 40 × 45 × 50 × 55 × 60
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 15
Answer: A
1 × 5 × 10 × 15 × 20 × 25 × 30 × 35 × 40 × 45 × 50 × 55 × 60
Just extract factor 2 and 5 from the Product.
1 × 5 × 10 × 15 × 20 × 25 × 30 × 35 × 40 × 45 × 50 × 55 × 60
5 10 5 2X10 5X5 10 5 2X2X10 5 5X10 5 2X2X5
Count the pairs of (2 and 5) and 10
5+5= 10
38. Let XYZ be a three-digit number, where (X + Y + Z) is not a multiple of 3. Then (XYZ + YZX + ZXY) is not divisible by
(a) 3
(b) 9
(c) 37
(d) (X + Y + Z)
Answer: B
(X + Y + Z) is not divisible by 3.
(XYX+ YZX+ ZXY) will be divisible by three as (X+Y+Z) will be added thrice. But once, we take 3 as common, we will get (X+Y+Z) as the sum of digits. Hence, the sum will not be divisible by 9.
39. Let p, q, r and s be natural numbers such that
p – 2016 = q + 2017 = r – 2018 = s + 2019
Which one of the following is the largest natural number?
(a) p
(b) q
(c) r
(d) s
Answer: C
The no. will be largest where the subtracted number is greatest.
40. How many five-digit prime numbers can be obtained by using all the digits 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 without repetition of digits?
(a) Zero
(b) One
(c) Nine
(d) Ten
Answer: A
Since the sum of digits is divisible by 3, any number formed will get divided by three.
41. A person X can complete 20% of work in 8 days and another person Y can complete 25% of the same work in 6 days. If they work together, in how many days will 40% of the work be completed?
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer: A
X
20% work in 8 days
So, 100 % work in 40 days.
Per day he completes, 1/40 work.
Y
25 % work in 6 days
So, 100 % work in 24 days.
Per day 1/24 work
Together X and Y
Total work per day= 1/40+1/24
= 8/120= 1/15
So, together they can complete the work in 15 days.
To complete 40 % of the work, they will take 15X40/100 days.
i.e. 6 days.
42. A car travels from a place X to place Y at an average speed of v km/hr, from Y to X at an average speed of 2v km/hr, again from X to Y at an average speed of 3v km/hr and again from Y to X at an average speed of 4v km/hr. Then the average speed of the car for the entire journey
(a) is less than v km/hr
(b) lies between v and 2v km/hr
(c) lies between 2v and 3y km/hr
(d) lies between 3v and 4y km/hr
Answer: (b)
Total distance covered= 4x (let x be the distance between places)
Total Time Taken= T1+T2+T3+T4
= (x/v)+ (x/2v)+ (x/3v)+ (x/4v)
= (x/12v)(12+6+4+3)
= (x/12v)(25)
= (x/v)(2.08)
Now, average speed will be Total distance/ Total Time
= 4x/(2.08x/v)
= v(1.92)
43. Consider the following statements:
1. The minimum number of points of intersection of a square and a circle is 2.
2. The maximum number of points of intersection of a square and a circle is 8.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
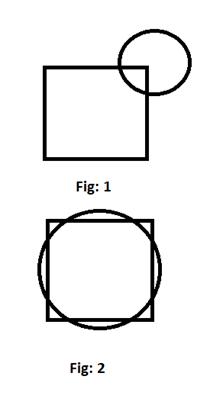
44. A man takes half time in rowing a certain distance downstream than upstream. What is the ratio of the speed in still water to the speed of current?
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 3
(d) 3 : 1
Answer: D
Let u= speed in still water, v= speed of current
Here, u+v= 2
u-v= 1
So, (u+v)/ (u-v)= 2/1
Or, u+v= 2u-2v
Or, u= 3v
Or, u/v= 3/1
45. How many pairs of natural numbers are there such that the difference of whose squares is 63?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 2
Answer: A
x^2- y^2= 63
Condition1:
or, (x+y)(x-y)= 9X7
if, x=8, y=1, Product is 63, valid, there are no other pairs of natural numbers satisfying the condition.
Condition 2:
(x+y)(x-y)= 21X3
If, x=12, y=9, there are no other pairs of natural numbers satisfying the condition.
Condition 3:
(x+y)(x-y)= 63X1
If, x=32, y=31, there are no other pairs of natural numbers satisfying the condition.
Hence, there are three pairs of the natural numbers.
(8,1), (12,9), (32,31)
46. Which one of the following will have minimum change in its value if 5 is added to both numerator and the denominator of the fractions 2/3, 3/4, 4/5 and 5/6?
(a) 2/3
(b) 3/4
(c) 4/5
(d) 5/6
Answer: D
Higher the numbers in the numerator and de-numerator, lower will be the effect.
47. A digit n > 3 is divisible by 3 but not divisible by 6. Which one of the following is divisible by 4?
(a) 2n
(b) 3n
(c) 2n + 4
(d) 3n + 1
Answer: D
Take a digit satisfying both the conditions,
Here, it is 9
3n+1= 28, divisible by 4.
Other conditions are not met.
48. If 1 litre of water weighs 1 kg, then how many cubic millimetres of water will weigh 0.1 gm?
(a) 1
(b) 10
(c) 100
(d) 1000
Answer: C
1000 L is 1 cubic metre.
1000 L is 10^9 cubic millimetre.
Hence, 1 Litre is 10^6 cubic millimetre. This is equal to 1 Kg.
Or, 1 g will be 10^3 cubic millimetre.
Or, 0.1 g will be 10^2 cubic millimetres.
49. A vessel full of water weighs 40 kg. If it is one-third filled, its weight becomes 20 kg. What is the weight of the empty vessel?
(a) 10 kg
(b) 15 kg
(c) 20 kg
(d) 25 kg
Answer: A
Let Vessel weighs V Kg. and full tank water weighs W Kg.
V+W= 40
Or, V+W(1/3)= 20
So, 40-W+W/3= 20
Or, (2/3)W= 20
Or, W= 30 Kg.
So, V= 10 Kg.
50. A frog tries to come out of a dried well 4.5 m deep with slippery walls. Every time the frog jumps 30 cm, slides down 15 cm. What is the number of jumps required for the frog to come out of the well?
(a) 28
(b) 29
(c) 30
(d) 31
Answer: B
15 cm each jump counts.
Total depth is 450 sm.
So it should take 30 jumps.
But, there is a trap here, when from completes 29th jump, it will be out of the well.
Q.51 Passage- 1
Bank credit to the industrial sector has started shrinking. Its decline has been a serious concern as credit growth is essential to revive investment. The problem’s origins lie in the incomplete reforms of the last 25 years. An institutional change that should have followed the 1991 reforms should have been setting up of a resolution corporation for banks. In a market economy with booms and busts, banks should be allowed to be set up and to fail. Today, we cannot shut down banks because there is no proper system to shut them down. Weak loss-making banks continue to need more capital.
Which one of the following is the most logical and rational inference that can be made from the above passage?
(a) Indian banking system is not able to help the country in its economic growth.
(b) Economic reforms that started in 1991 have not helped in improving the economy to expected levels.
(c) India lacks the institutional mechanism to deal with the failure of banks.
(d) Encouraging the foreign investments in our industrial sector is a good alternative to this sector’s dependence on banks for credit.
Answer: c
The main message of the passage is the needs and measures required for helping the banks to sync itself as per changing economic situation of the country. Option c reflects the same message.
Passage–2
India has tremendous potential for solar energy. We all realize that we have to stop burning fossil fuels to meet our energy needs. But certain renewable resources are still going through their cost curves and learning curves to get the required amount of output. The Indian Government has strongly committed to its targets of reducing emissions by 33 per cent by 2030, and towards this it has initiated a strong push towards a gas-based economy and has also invested heavily in renewable energy. However, business houses are wary of investing too heavily in renewable energy at a time when the technology is not yet ready.
Q. 52. Which one of the following is the most logical and rational inference that can be made from the above passage?
(a) India’s commitment to reduce emissions by 33% is unlikely to be achieved.
(b) India should import gas rather than invest in renewable resources.
(c) Getting renewable resources to market too soon may be costly.
(d) India should put in more efforts in the exploration of natural gas.
Answer: C
Let us proceed with the process of elimination.
Option a: No, author has nowhere claim such apprehension.
Option b: No, import of natural gas has not been stressed upon.
Option c: Yes, author talks about the bottlenecks in utilization of renewable sources due to lack of knowledge and high cost involved so, getting renewable resources to market too soon may be costly.
Option d: No, such necessity has not been stressed upon.
53. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. Governments often provide inefficient and costly subsidies for technologies that may not be ready in the near future.
2. India’s commitment of reducing emissions by 33% by 2030 shall be on the basis of gas-based economy.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: d
S1: Passage do not discuss about the government subsidy and neither it is implicit in any of the lines.
S2: No, gas bases economy may help but it’s the renewable energy that has to contribute the most.
Passage–3
Genome editing is different from genome modification. Genome editing typically involves finding the part of a plant genome that could be changed to render it less vulnerable to disease, or resistant to certain herbicides, or to increase yields. Researchers use ‘molecular scissors’ to dissect the genome and repair it, which is a process that occurs naturally when plants are under attack from diseases and can throw up new mutations that enable the plant to survive future attacks. This evolutionary process can effectively be speeded up now that it is possible to examine plant genomes in detail in laboratories, and create mechanisms through which the relevant genes can be altered very precisely.
54. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. Genome editing does not require the transfer of genes from one plant to another.
2. Through genome editing, the chosen genes can be altered precisely in a manner akin to the natural process that helps plants to adapt to the environmental factors.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
S1: According to the passage, genome editing involves to dissect the genome and repair. There is no need to transfer the genes from one plant to the other.
S2: Explicitly mentioned in the passage.
Passage–4
Many people understand the connection between solid waste management and health in terms of the consequences of unattended heaps of dry garbage which become home for flies and other vermin. However, there is another aspect that is not well-understood, that is, what happens when unscientific solid waste management combines with poor drainage and dumping of untreated sewage into drains which are meant to carry storm water during rains. The result is choked drains which are full of stagnant water breeding mosquitoes, resulting in the spread of water-borne diseases.
55. In the context of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the critical message of the passage?
(a) In India, the drainage networks are not separate for sewerage and storm water.
(b) Urban local bodies do not have enough resources and legislative authority to deal with the problems of waste management.
(c) Solid waste management should be integrated with the maintenance of drainage and sewerage networks.
(d) Bad management of solid waste and sewerage systems by our municipalities is the reason for drinking water shortages in our cities.
Answer: c
Here, the critical message has been asked and the critical message can never be the facts/figures/data explicitly mentioned in the passage.
Option 1: It is true that the drainage networks are not separate from the sewerage channel but it is not the message the passage is trying to give.
Option b: Fund crunch has not been discussed.
Option c: This is the most logical message that can be extracted from the passage.
Option d: No, the accountability has not been fixed.
Passage–5
In Part III of the Constitution, which assures people certain fundamental rights, Article 25 proclaims that “all persons are equally entitled to freedom of conscience and the right freely to profess, practise and propagate religion”. What people fail to notice is that this proclamation is prefixed with the words “subject to public order, morality, health and to the other provisions of this Part”, which set conditions precedent for the legal protection of religious practices of any community. The closing words of this prefatory rider in Article 25 virtually constitute a subordination clause placing other fundamental rights mentioned in Part III over and above the right to religious freedom. Among those other fundamental rights is the right to equality before law and equal protection of laws—assured at the outset and elaborated in later articles to mean, inter alia, that the State shall not deny equal protection of laws to any person or group to persons on the basis of religion alone.
56. What is the most logical inference from the above passage?
(a) State shall not interfere with the religious affairs of the citizens.
(b) Religious freedom under the Constitution is open to State intervention.
(c) Religious freedom of the citizens is not covered under fundamental rights.
(d) Religious practices of any community are immune to State laws.
Answer: b
The central message of the passage is that the right to practice and profess religion is not above other fundamental rights and the state can impose reasonable restriction on its implementation. This is reflected in option b.
57. How many different 5-letter words (with or without meaning) can be constructed using all the letters of the word ‘DELHI’ so that each word has to start with D and end with I?
(a) 24
(b) 18
(c) 12
(d) 6
Answer: D
The First and the Last Alphabets are fixed, remaining three places are void.
The void places can be filled in 3X2X1 ways.
Hence 6 ways.
58. A bottle contains 20 litres of liquid A. 4 litres of liquid A is taken out of it and replaced by same quantity of liquid B. Again 4 litres of the mixture is taken out and replaced by same quantity of liquid B. What is the ratio of quantity of liquid A to that of liquid B in the final mixture?
(a) 4 : 1
(b) 5 : 1
(c) 16 : 9
(d) 17 : 8
Answer: C
Zero Condition
A= 20 L, B=0
First Iteration,
A=16 L, B= 4 L
Second Iteration,
4 Litre of the mixtures is removed.
Now, 1 L of mixtures has (16/20) A and (4/20) B
I.e. 4/5 Litres A and 1/5 Litres B
So, 4 Litres will have, 16/5 Litres of A and 4/5 Litres of B.
What is added
0 Litres of A and 4 Litres of B.
| A | B |
| 16-(16/5)+0= 16X(4/5)= 64/5 | 4-(4/5)+4= 36/5 |
A: B= 64:36
= 16:9
59. The average score of a batsman after his 50th innings was 46.4. After 60th innings, his average score increases by 2.6. What was his average score in the last ten innings?
(a) 122
(b) 91
(c) 62
(d) 49
Answer: C
Total Score in after 50th inning= 50X46.4
Total Score in after 60th inning= 60X(46.4+2.6)= 60X49
Average Score in the last 10 innings= (60X49-50X46.4)/10
= (2940- 2320)/ 10
= 62
60. As a result of 25% hike in the price of rice per kg, a person is able to purchase 6 kg less rice for Rs. 1,200. What was the original price of rice per kg?
(a) Rs. 30
(b) Rs. 40
(c) Rs. 50
(d) Rs. 60
Answer: B
Let the original price of the rice is p Rs./Kg
Revised Price will be 1.25 p
So,
(1200/p)- (1200/1.25p) = 6
Or, p= Rs. 40 per kg.

Take HCF of the two numbers.
7/2 and 35/4
HCL will be 7/4
Hence, option d is correct.
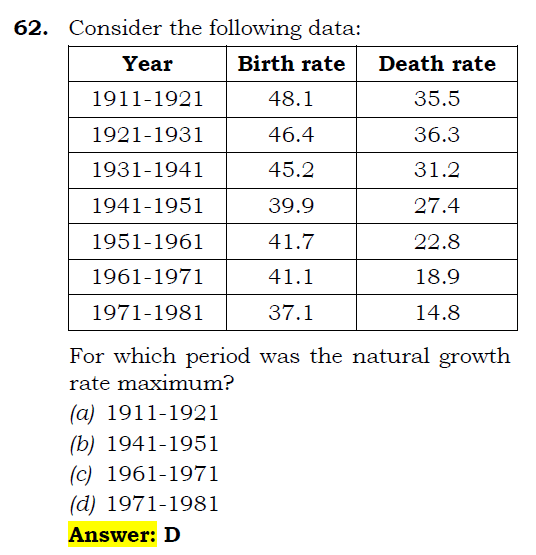
The maximum difference between Birth Rate and the Death Rate is in the decade 1971-81.
63. The recurring decimal representation 1.272727… is equivalent to
(a) 13/11
(b) 14/11
(c) 127/99
(d) 137/99
Answer: (b)
Let x= 1.272727…..
So, 100x = 127.272727…
Or, 99x= 126
Or, x= 126/99
= 42/33
=14/11
64. What is the least four-digit number when divided by 3, 4, 5 and 6 leaves a remainder 2 in each case?
(a) 1012
(b) 1022
(c) 1122
(d) 1222
Answer: (b)
Let the number be x
So, x= 3n+2= 4m+2= 5p+2= 6q+2
Where, m,n,p,q are integers.
The desired number will be the LCM of 3,4,5,6 added 2
= 60
Least 4 digit number is 1000 but least 4 digit number in the multiple of 60 is 1020
Hence, the required number will be 1022.

Clearly, Married Male and Married Female will be Equal in number.
Now, Let the total male population be x and total female population is y.
So, 0.4x= 0.3y
Or, 4x=3y
X=(3/4)y
Again, Total population is x+y
Married Population= 0.8x= 0.6y
Hence Required %= (0.6y)/ (x+y)
= ((0.6y)/((3/4)y+y))X100
=34.28
66. What is the remainder when 51 × 27 × 35 × 62 × 75 is divided by 100?
(a) 50
(b) 25
(c) 5
(d) 1
Answer: (a)
51 × 27 × 35 × 62 × 75
= 51X27X5X7X2X31X5X5X3
The unit place of the product will be 0 as both 5 and 2 are present in the factor.
This unit place will be the unit place of the reminder.

LCM of 2,4,6 will be 12.
Multiply the ratio by 12.
6:9:10
Now,
2500/(6+9+10)= 100
So the biggest share will be (10/25)X2500
And the smallest share will be (6/25)X2500
Difference will be (4/25)X2500
= 400

Put n=1,2,3,…..
The sum of the digits will always be 2.
69. In a class, there are three groups A, B and C. If one student from group A and two students from group B are shifted to group C, then what happens to the average weight of the students of the class?
(a) It increases.
(b) It decreases.
(c) It remains the same.
(d) No conclusion can be drawn due to insufficient data.
Answer: C
Total weight and Total number of students will remain the same as groups are part of the class.
70. How many different sums can be formed with the denominations Rs. 50, Rs. 100, Rs. 200, Rs. 500 and Rs. 2,000 taking at least three
denominations at a time?
(a) 16
(b) 15
(c) 14
(d) 10
Answer: A
Total ways= 5C3+ 5C4+ 5C5
= 10+ 5+ 1= 16 ways.
Passage–1
Spanish ships in the late 16th century first brought the potato tuber from South America to Europe whereby in the early 19th century, it had become a reliable backup to cereal crops, particularly in the cold, rain-soaked soils of Ireland. The Irish were soon almost wholly dependent on the potato as their staple food. And they were planting primarily one prodigious variety, the ‘Lumper’ potato, whose genetic frailty would be cruelly exposed by the fungus ‘Phytophthora infestans’. In 1845, spores of the deadly fungus began spreading across the country, destroying nearly all the Lumpers in its path. The resulting famine killed or displaced millions.
71. Which one of the following statements best reflects the critical message of the passage?
(a) For introducing any foreign plant into a country, the soil and climate conditions of that country should be suitable.
(b) As a staple food of a country, tuber crops like potato cannot replace cereal crops.
(c) Some of the fungal infections of plants cannot be prevented or stopped from spreading across large areas.
(d) Relying on a homogeneous food source is not desirable.
Answer: d
Here, the key is understanding the essence or the key message of the passage. What we can infer from the passage is that the famine was caused by a fungal disease infecting a particular variety of potato. As the ‘Lumper’ potato was the reliable back up, people faced famine. Hence, the reliance on the single source as food was the main problem and the answer is d.
Passage–2
India is at once among the fastest growing global economies and home to the largest number of malnourished children in the world. There are regions where malnutrition is not the exception but the norm. And across the country, malnutrition is the cause of death for roughly half the 1.3 million children who die before their fifth birthday each year. Even those children who survive suffer permanently from the damage that has already been done to their bodies and minds from not getting enough of the right foods and nutrients. Around 44 million children under 5 are stunted. That makes it harder for them to learn in school and subsequently earn a living as adults. Their lifetime earnings potential is almost a quarter less than that of their healthy peers.
72. With reference to the above passage, which of the following is/are the most rational and practical implication / implications?
1. India’s Public Distribution System should be monitored by the Union Government.
2. Girls should be encouraged to delay marriage and first pregnancy.
3. Mothers should be encouraged to breastfeed their children immediately after birth.
4. The supply of safe drinking water and proper sanitation facilities to all should be ensured.
5. Authorities should ensure the vaccination as prescribed.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1 only
(d) 3 and 5 only
Answer: b
Let’s solve the question by elimination.
S1: The passage nowhere talks whether the PDS should be monitored by the State government or the central government. So, S1 is incorrect. Options b and d are gone.
S2, S3, S4, S5 all are the practical implications to solve the problem of malnutrition.
Passage–3
The pulse variety ‘Pusa Arhar 16’ has the potential to be grown in the paddy-growing regions of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh and eventually in all of India. Its yield (about 2000 kg/hectare) will be significantly greater than those of the existing varieties and because its size will be uniform, it will be amenable to mechanical harvesting, an attractive feature for farmers in northern India who currently use this technology for paddy. Most important, Arhar straw, unlike paddy straw, is green and can be ploughed back into the soil. In paddy straw, the problem is the high silica content, which does not allow for easy decomposition. In the case of Arhar, the farmer, even after combine harvesting, just needs to run a rotovator to cut the leftover straw into pieces, which can be ploughed back and will decompose very fast. All this is difficult with leftover paddy stalks that cannot be easily salvaged or ploughed back. Farmers, therefore, choose the easiest option of simply burning it.
73. Which of the following are the most rational inferences that can be made from the passage?
1. Farmers’ income will be higher with pulse cultivation than with paddy cultivation.
2. Pulse cultivation causes less pollution as compared to paddy cultivation.
3. Pulse straw can be used to improve soil quality.
4. In the context of northern Indian agriculture, paddy straw has no usefulness.
5. Mechanized agriculture is the main cause for stubble burning.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 2, 3 and 5
(b) 1, 4 and 5
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Answer: D
S1: The second line of the passage says that yield of Pusa Arhar is significantly greater than those of the existing varieties, this will augment the income of farmers. Hence, S1 is correct.
S5: The role of mechanized agriculture in stubble burning is not mentioned. Incorrect statement.
S3: Not mentioned although true as per common belief.
S2: Pulse cultivation does not cause less pollution as compared to paddy cultivation. Not mentioned anywhere in the passage.
Hence, answer is d.
Passage–4
In India, authorities always look to store the maximum amount of water in reservoirs during the monsoon season, which is then used for irrigation and generation of electricity during the summer months. It is an internationally accepted practice that the water level of a reservoir should be kept below a certain level before the onset of monsoon season. This is so that when monsoon rains come, there is space to store the excess rainwater and also so that water can be released in a regulated manner. But the authorities store the maximum amount of water in reservoirs even before the close of the monsoon, only to ensure greater electricity generation and irrigation.
74. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. High risks involved in holding maximum water in reservoirs are due to our over-dependence on hydropower projects.
2. Storage capacity of dams should not be fully used before or during monsoon season.
3. Role of dams in flood control is underestimated in India.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: b
S1: The passage accepts that holding the water in reservoir is an accepted norm. It is done to ensure the generation of electricity and water for irrigation. It does not talk about the risks. S1 is incorrect.
S2: it has been explicitly mentioned in the passage. S2 is correct.
S3: No, there is mention of role of dams in flood control.
Passage–5
Economic liberalization in India was shaped largely by the economic problems of the government than by the economic priorities of the people or by the long-term development objectives. Thus, there were limitations in conception and design which have been subsequently validated by experience. Jobless growth, persistent poverty and rising inequality have mounted as problems since economic liberalization began. And all these years later, four quiet crises confront the economy; agriculture, infrastructure, industrialization and education as constraints on the country’s future prospects. These problems must be resolved if economic growth has to be sustained and transformed into meaningful development.
75. Which of the following is/are the most rational and logical inference / inferences that can be made from the passage?
1. It is essential to rethink and redefine the economic role of the State in the quest for development.
2. India has not made effective implementation of its policies in social sectors nor made sufficient investments in them.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: a
What is the theme of the passage?
The role of government in the economic liberalization in India. The inference must be centred around it.
S1: Correct statement in the light of passage. It is implied that the government has to take the necessary steps to eradicate the shortcomings of the economic liberalization.
S2: Not a correct statement. The passage does not opine such shortcoming.
76. With reference to the above passage, the following assumptions have been made:
1. India’s economy needs to be greatly integrated with global economy so as to create large number of jobs and to sustain its growth momentum.
2. Economic liberalization would cause large economic growth which would reduce poverty and create sufficient employment in the long run.
Which of the above assumptions is/are valid?
(a) 1 only (b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: d
S1: Need of further global integration has not been discussed in the passage. Incorrect.
S2: It is not guaranteed. Incorrect statement.
77. A shop owner offers the following discount options on an article to a customer:
1. Successive discounts of 10% and 20%, and then pay a service tax of 10%
2. Successive discounts of 20% and 10%, and then pay a service tax of 10%
3. Pay a service tax of 10% first, then successive discounts of 20% and 10%
Which one of the following is correct?
(a) 1 only is the best option for the customer.
(b) 2 only is the best option for the customer.
(c) 3 only is the best option for the customer.
(d) All the options are equally good for the customer.
Answer: D
Let the original price is Rs. 100
S1: Final price will be 100X0.9X0.8X1.10= 0.18X1.10X100= 1.8X11
S2: Final Price will be 100X0.8X0.9X1.10= 1.8X11
S3: Final Price will be 100X1.10X0.8X0.9= 1.8X11
All the three gives equal final price.
78. The letters from A to Z are numbered from 1 to 26 respectively. If GHI = 1578 and DEF = 912, then what is ABC equal to?
(a) 492 (b) 468
(c) 262 (d) 246
Answer: (d)
Here, just write the numerical position of alphabets.
DEF= 456 but, 456 is not given, rather it is 912 (i.e. 456X2)
Again, GHI= 789, but 789 is not there in the option, rather 789X2= 1578 is given.
Hence, ABC will be (123)X2= 246
79. What is the missing term @ in the following?
ACPQ : BESU :: MNGI : @
(a) NPJL (b) NOJM
(c) NPIL (d) NPJM
Answer: D
Note that as we progress, the alphabets are increased by +1, +2, +3 etc.
So, MNGI will be NPJM
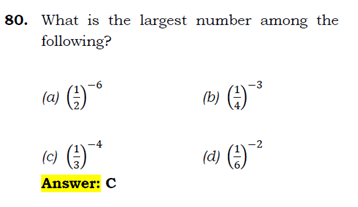
Option a: 2^6= 64
Option b: 4^3= 64
Option c: 3^4= 81
Option d: 6^2= 36
Greatest number is 81.