The Cauvery River is one of the most important rivers in India, originating in the Western Ghats and flowing through the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala. It is considered a sacred river and is known for its cultural and historical significance. In this article, we will discuss the Cauvery River in detail, including its origin, course, importance, and challenges.
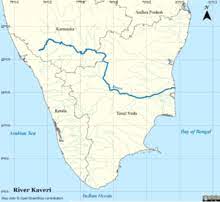
Table of Contents
Geography and Origin of Cauvery River
The Cauvery River originates in the Brahmagiri Hills in the Western Ghats of Karnataka. It then flows through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, before emptying into the Bay of Bengal in Tamil Nadu. The river has a length of 765 km and a drainage area of 81,155 square km.
Importance of the Cauvery River
The Cauvery River is of great importance to the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, as it provides water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial purposes. The river is also a source of hydroelectric power and supports a rich ecosystem of flora and fauna.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The River has a rich cultural and historical significance, with many important temples and pilgrimage sites located along its banks. The river is considered sacred by Hindus, and many festivals and rituals are held along its banks. Despite its importance, the River faces several challenges that threaten its ecosystem and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
Water Disputes of Cauvery River
One of the biggest challenges facing the River is the ongoing water disputes between the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The dispute dates back to the 19th century and centers around the sharing of water between the two states. The issue has been the subject of several court cases and negotiations, but a lasting solution has yet to be found.
Environmental Degradation
It is also facing environmental degradation due to pollution and overuse. Industrialization and urbanization have led to an increase in pollution levels, which has a negative impact on the river’s ecosystem. Additionally, the overuse of water for irrigation and other purposes has led to a decrease in the river’s flow, which has further worsened the situation.
Conclusion
It is an important river in India, with significant cultural, historical, and ecological importance. However, it faces several challenges, including water disputes and environmental degradation. Addressing these challenges will be critical to ensure the long-term sustainability of the river and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
Important Links