What is the difference between Determinism and Possibilism? Determinism and Possibilism are two concepts of human geography. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial in comprehending how geographers study human-environment interaction.
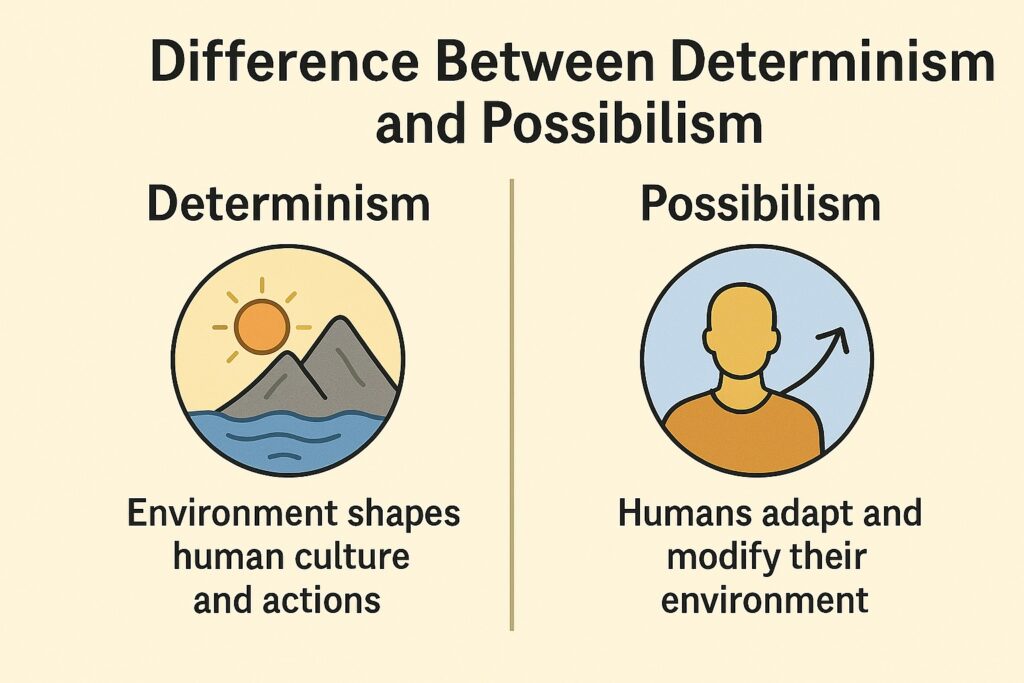
Table of Contents
Determinism
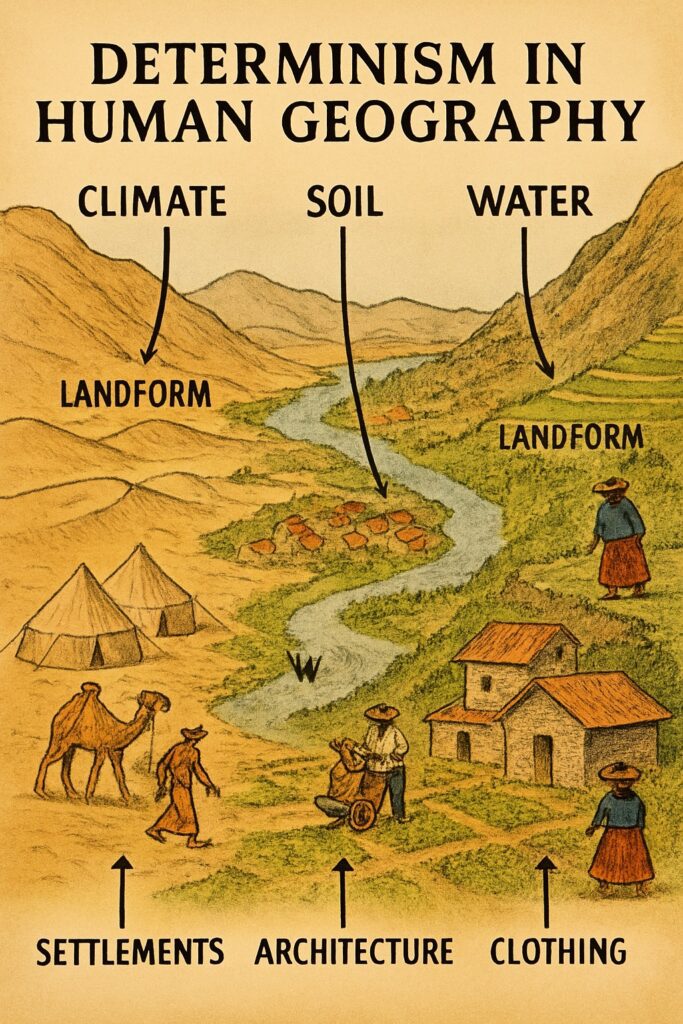
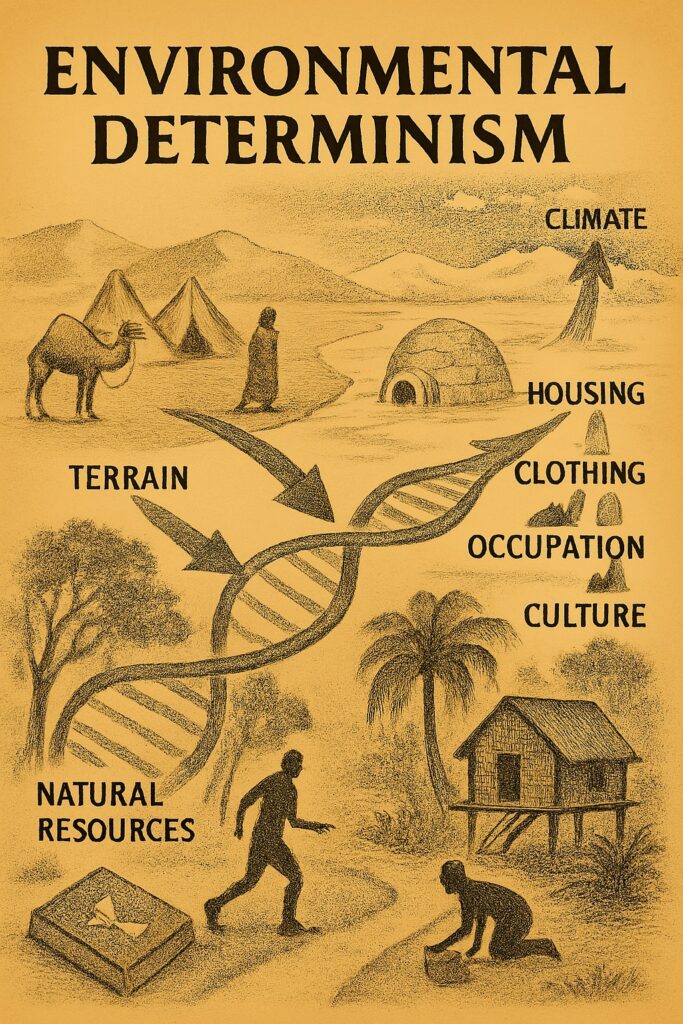
Determinism is the belief that environmental factors solely determine the nature of human societies. In other words, the environment has complete control over how societies develop, and humans have little to no say in the matter. Determinism suggests that the natural environment, such as climate, terrain, and available resources shape human societies, lifestyles, occupations, and cultures. This perspective was especially influential in early geographic thought, where scholars argued that physical conditions strictly dictated human possibilities.
"Man is the product of the earth."- Ellen Churchill Semple
"Environmental factors solely determine the nature of human society"
Geographers in favour of Determinism
Determinism is a controversial concept in human geography, some geographers have argued in favor of determinism, believing that environmental factors play a crucial role in shaping human societies. For example, human settlements in cold regions adopt the lifestyle to protect themselves from the cold waves (a fore of nature) in order to survive. Here are some geographers who have supported determinism:
Ellsworth Huntington
Ellsworth Huntington was an American geographer who believed that climate was the primary determinant of human history and civilization. He argued that the environment had a direct impact on human biology, which in turn shaped cultural and societal practices.
Jared Diamond
Jared Diamond is a contemporary geographer who has argued in favour of environmental determinism. He believes that geographical and environmental factors have had a significant impact on human history and culture, shaping the development of different societies over time.
Friedrich Ratzel
Friedrich Ratzel was a German geographer who believed that the physical environment played a fundamental role in shaping human societies. He argued that environmental factors such as climate, topography, and natural resources were the key determinants of human history and culture.
Types of Determinism
Determinism is a philosophical belief that all events and actions are determined by preceding events or causes. There are several types of determinism, each with its own approach to the concept of causality.
Causal Determinism
Causal determinism asserts that all events are caused by preceding events and that the universe is a chain of cause-and-effect relationships. This means that every event is predetermined by the events that preceded it. In true causal determinism, nothing happens by chance. Even what seems like a “random” action is actually caused by earlier conditions. According to this view, your choices (e.g., what you eat, where you go) are determined by previous experiences, your biology, and the environment—not by free will.
"Just like a line of falling dominoes, each event triggers the next. Example: A glass falls → it hits the ground → it breaks."- Causal Determinism

Logical Determinism
Logical determinism holds that all events are predetermined by the laws of logic. This means that everything that happens in the universe is determined by the logical relationships between things. Logical determinism is the philosophical idea that the future is already fixed.

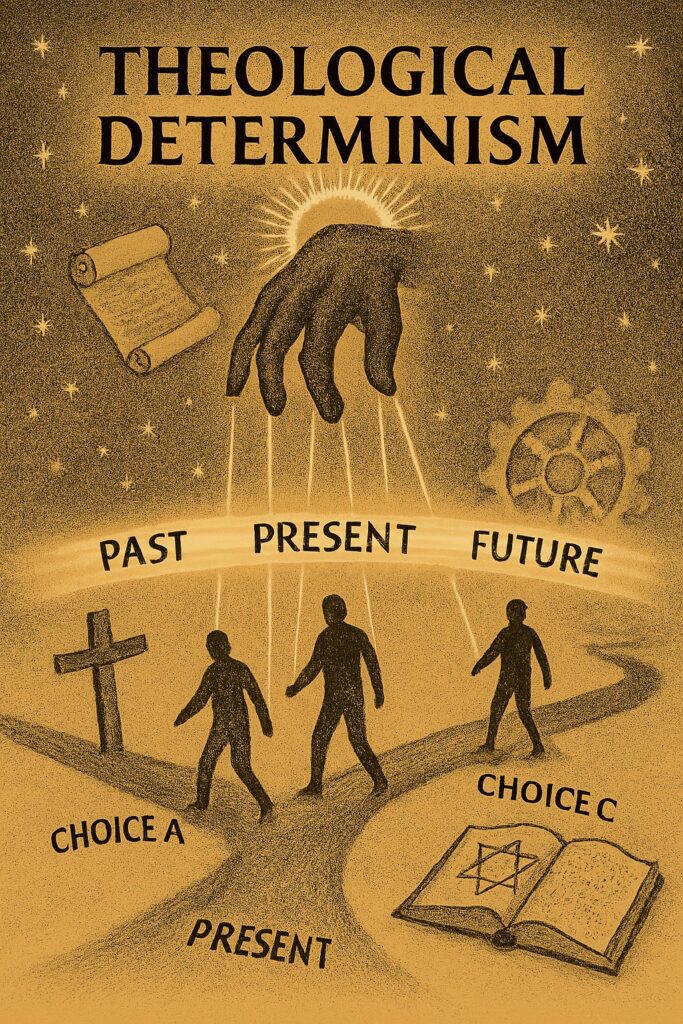
Theological Determinism
Theological determinism is the belief that God or a divine being has predetermined all events and actions in the universe. This view asserts that all events are part of a divine plan or purpose. Theological determinism is the view that God determines all events, making the future predetermined and unchangeable.
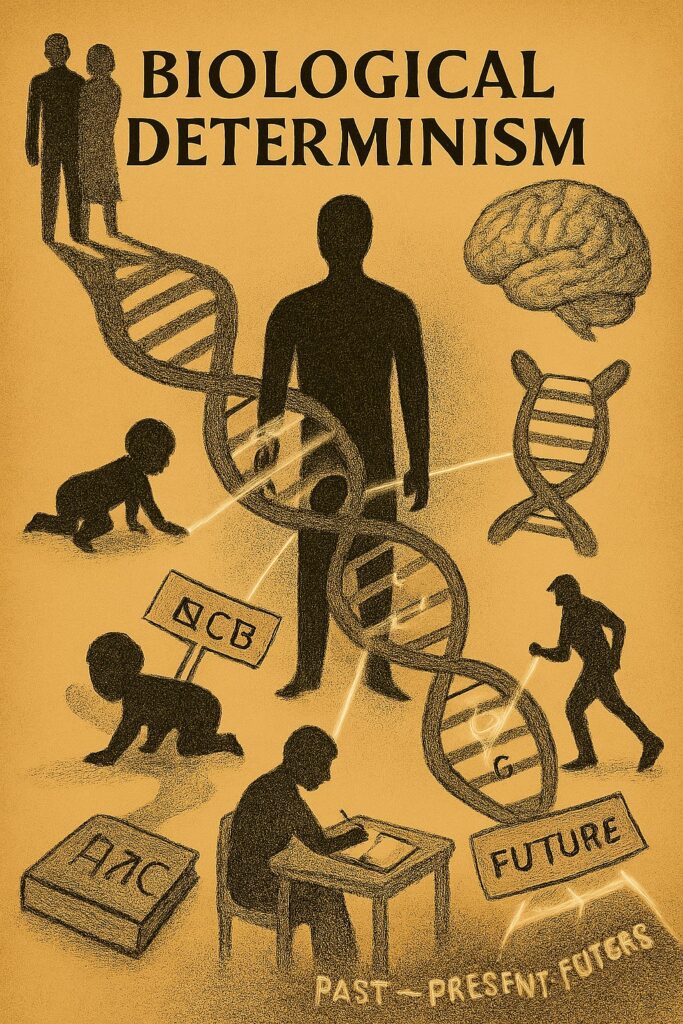
Biological Determinism
Biological determinism suggests that human behaviour and actions are determined by biological factors, such as genetics or brain chemistry. This view implies that human actions and choices are predetermined by their biology and that free will is an illusion.
Environmental Determinism
Environmental determinism asserts that human behaviour and culture are determined by environmental factors such as climate, geography, and natural resources. This view argues that the physical environment of a place determines the cultural and social practices of the people who live there.
Possibilism
Possibilism is the belief that human societies have the ability to adapt and modify their environment to meet their needs. Possibilism asserts that while the environment can be limiting, humans have the power to overcome these limitations through technology and innovation. Possibilism says that humans are active agents, not passive victims of their environment. The environment sets limits, but culture and technology shape choices.
Examples:
- Desert, Instead of just moving away, people build cities using air conditioning, solar energy, and irrigation.
- Mountains, People create terraced farms and roads, showing they can live and farm in steep areas.

"Human society has the ability to adapt and modify their environment to meet their needs"
Geographers in Favor of Possibilism
Possibilism is a philosophical belief that humans have the ability to overcome environmental limitations through technology and innovation. Many geographers argue that human societies have agency and can actively shape their environment, rather than being completely determined by it. Here are some geographers who have supported the Possibilism:
Paul Vidal de la Blache
Paul Vidal de la Blache was a French geographer who argued that human societies were not completely determined by their environment. He believed that humans had the ability to shape their surroundings and adapt to their needs through agriculture, technology, and social organization.
Carl Sauer
Carl Sauer was an American geographer who believed that human societies were not determined by environmental factors alone. He argued that humans actively transformed their environment through agriculture and settlement, shaping the landscape to meet their needs.
Yi-Fu Tuan
Yi-Fu Tuan is a contemporary geographer who has advocated for a more humanistic and subjective approach to geography. He believes that humans have agency and can shape their environment, but also recognizes that cultural and social factors play a significant role in human-environment interaction.
Difference Between Determinism and Possibilism
Determinism emphasizes the environmental factors as the primary influence on human societies while Possibilism stresses the role of human agency. Determinism views the environment as a limiting factor while Possibilism views the environment as a challenge to be overcome.
| Determinism | Possibilism | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All events and actions are determined by preceding events or causes. | Humans have the ability to overcome environmental limitations through technology and innovation. |
| Role of Environment | The environment is the primary determinant of human history and culture. | The environment is a limiting factor, but humans have agency and can shape their environment to meet their needs. |
| Human Agency | Human agency is limited by environmental factors. | Humans have agency and can actively shape their environment. |
| Approach | Environmental determinism | Environmental Possibilism |
| Examples | Ellsworth Huntington, Jared Diamond, Friedrich Ratzel | Paul Vidal de la Blache, Carl Sauer, Yi-Fu Tuan |
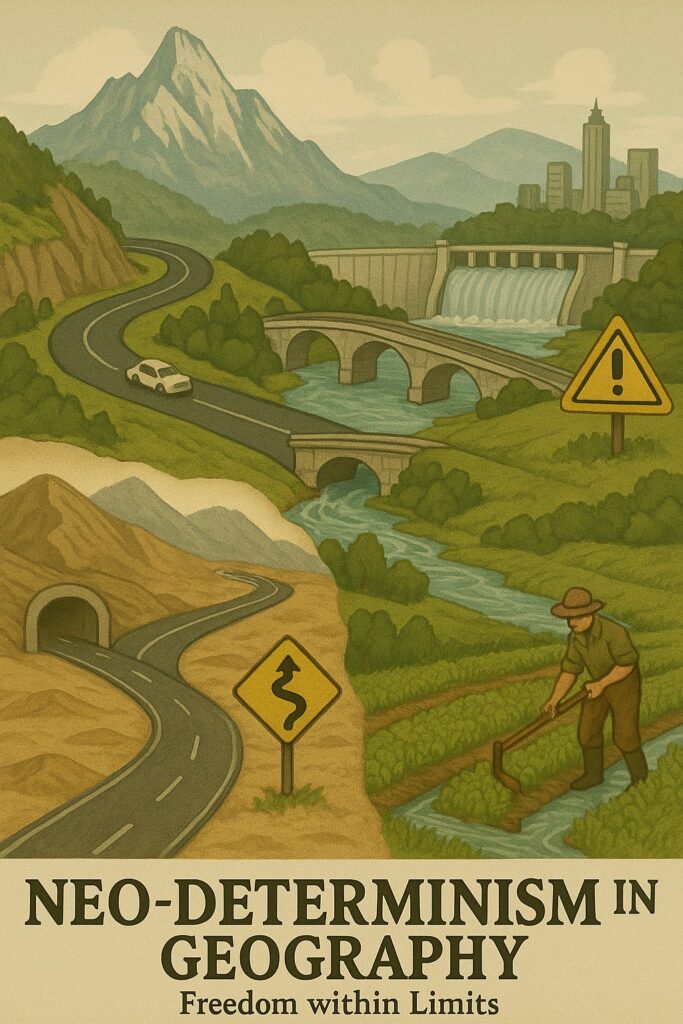
What is Neo-Determinism?
Neo-determinism, also known as probabilistic determinism, is a modernized form of environmental determinism that acknowledges the role of human agency in shaping society but still emphasizes the importance of environmental factors in determining human behavior.
"Neo-determinism is also called stop-and-go determinism"
while human actions are not predetermined, environmental conditions strongly influence and limit the range of possible human actions. This approach recognizes that there is a complex interplay between environmental factors and human agency, but still places a significant emphasis on the role of the physical environment in shaping human societies.
Neo-determinism has been criticized for oversimplifying the complex relationship between humans and their environment, and for underestimating the ability of humans to adapt and innovate in response to environmental challenges.

Conclusion
In summary, the difference between Determinism and Possibilism lies in their understanding of the relationship between human societies and the environment. While Determinism suggests that humans have no control over their environment, Possibilism argues that humans have the ability to adapt and shape their environment to suit their needs.