Fundamental units are the basic units of measurement defined by a system of physical quantities. These units are independent and cannot be derived from any other units. All other units (called derived units) are formed by combining these fundamental units.
Table of Contents
Fundamental Units
In SI System (International System of Units), the 7 Fundamental Units are:

What is a Meter?
A meter (m) is the SI (International System of Units) unit of length. A meter is defined as the distance that light travels in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 seconds. This precise definition ensures that the meter remains the same everywhere in the universe.

What is Kilogram (kg)?
A kilogram (kg) is the SI unit of mass — it is used to measure how much matter an object contains. A kilogram is defined based on a constant of nature called the Planck constant. 1 kilogram is the mass that, when used in the definition of the Planck constant, makes ℎ exactly equal to 6.62607015 × 10⁻³⁴ joule·second.

What is a Second?
A second (s) is the SI unit of time. A second is defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 vibrations (oscillations) of the radiation corresponding to the transition between two energy levels of the cesium-133 atom.

What is an Ampere (A)?
The ampere (A) is the SI unit of electric current. An ampere is defined as the current that flows when one coulomb of electric charge passes through a conductor in one second.

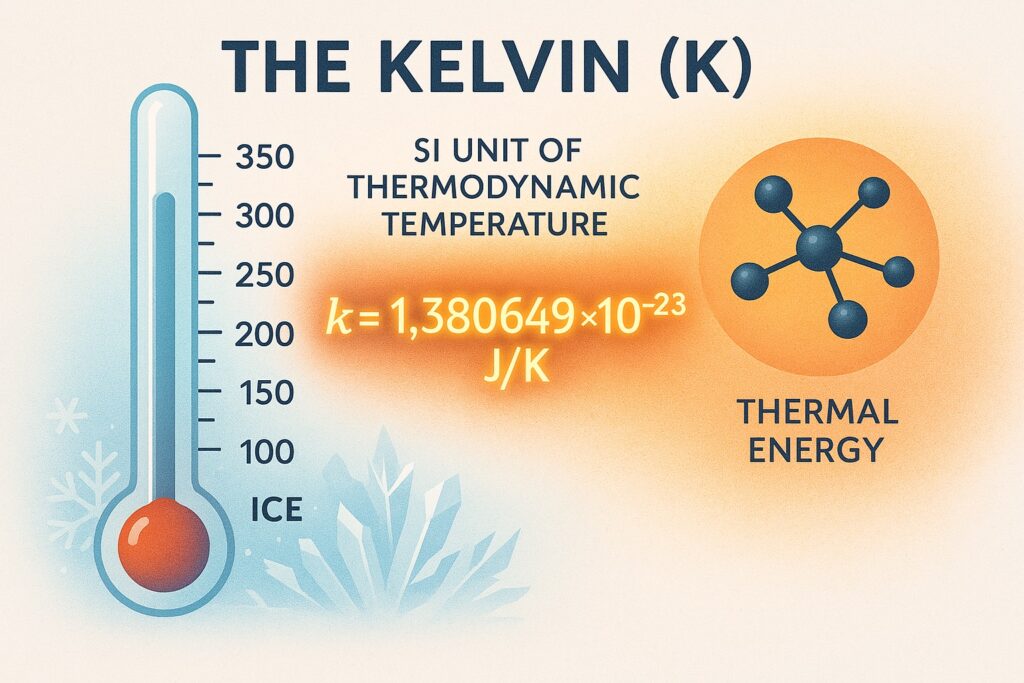
What is Kelvin (K)?
The kelvin (K) is the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature. A kelvin is defined by setting the Boltzmann constant exactly to 1.380649 × 10⁻²³ joules per kelvin (J/K).
What is a Mole (mol)?
The mole (mol) is the SI unit for the amount of substance.

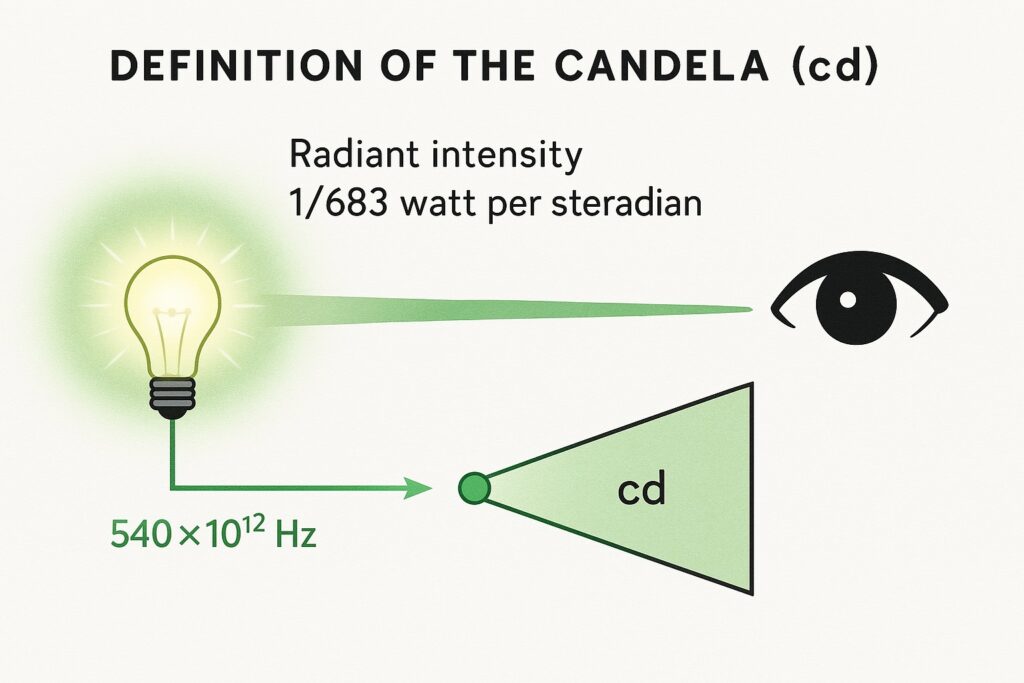
What is Candela (cd)?
The candela (cd) is the SI unit of luminous intensity — that is, how bright a light source appears to the human eye. A candela is defined as the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic light of frequency 540 × 10¹² hertz (which is green light) and has a radiant intensity of 1/683 watt per steradian in that direction.
Key Features of Fundamental Units
- Base of Measurement: All physical quantities can be expressed using combinations of these 7 units.
- International Standard: Used universally to maintain consistency in science, engineering, and everyday life.
- Independence: They are not derived from each other.
- Precise Definition: Each unit is defined based on universal constants (e.g., the metre is defined by the speed of light in a vacuum).