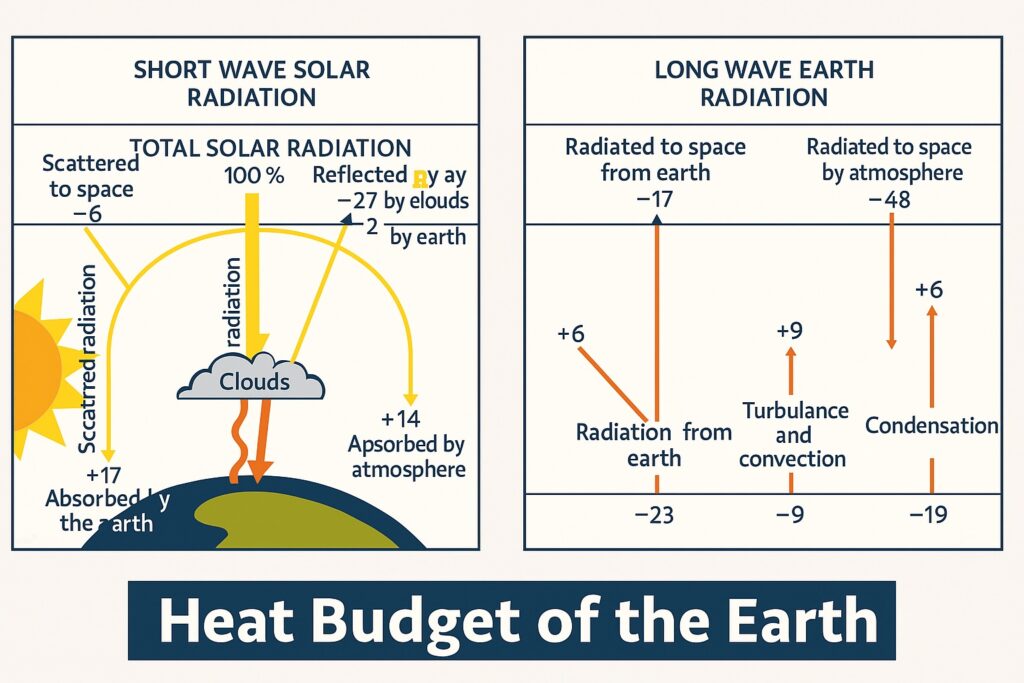
The climate of Earth is regulated by the heat budget of the Earth. It is the account of the amount of energy entering the planet from the sun and the amount of energy being released back into space. Heat budget of the Earth is a critical aspect of climate and weather patterns.
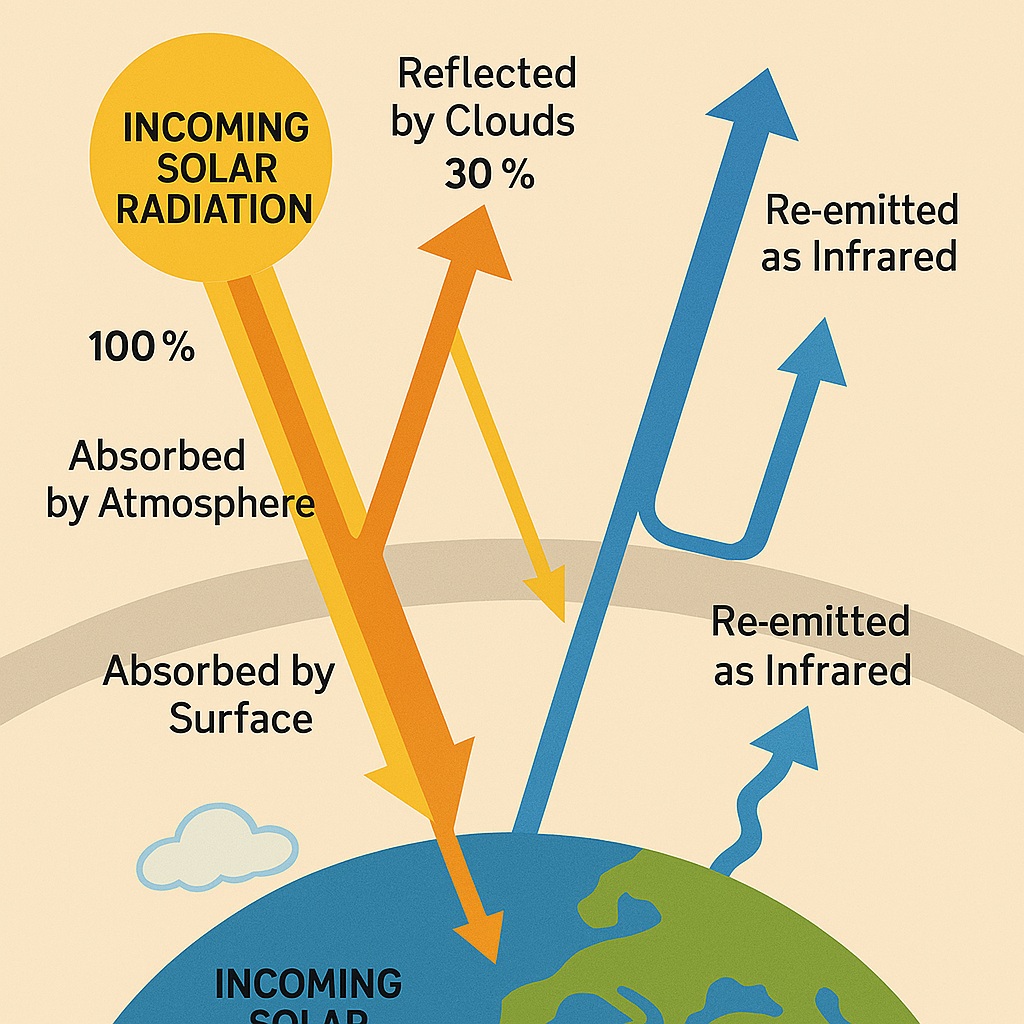
Table of Contents
What is Heat Budget?
The Sun gives Earth energy in the form of short-wave radiation—this is called insolation. Earth also gives off energy as heat (long-wave radiation), just like any warm object. This outgoing energy is called terrestrial radiation.
Even though energy is always coming in and going out, Earth’s average temperature stays steady. That’s because there is a balance between the energy coming in and the energy going out. This balance is called the Earth’s Heat Budget.
Incoming Short Wave Solar Radiation
The main source of energy for the Earth’s climate system is incoming solar radiation. The sun emits energy in the form of shortwave radiation, which is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. This absorbed energy is then re-emitted as longwave radiation, which is also known as infrared radiation.
"The Sun emits electromagnetic radiation across a wide range of wavelengths, like ultraviolet (UV), visible light, and near-infrared (NIR)."
The Earth’s atmosphere and surface absorb different amounts of incoming solar radiation, depending on their composition and structure. For example, the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs a significant amount of ultraviolet radiation, which is harmful to living organisms. The Earth’s surface, on the other hand, absorbs a significant amount of visible and infrared radiation, which drives the planet’s climate and weather patterns.
"Shortwave solar radiation travels through the vacuum of space at the speed of light, covering a distance of approximately 150 million kilometers from the Sun to the Earth."
Outgoing Longwave Radiation
The energy that is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface is re-emitted as longwave radiation, which is then emitted back into space. This outgoing longwave radiation is critical in regulating the Earth’s temperature and is influenced by several factors, like the atmospheric composition, cloud cover, and surface temperature.
The atmospheric composition, particularly the concentration of greenhouse gases, plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature by trapping some of the outgoing longwave radiation and re-radiating it back towards the surface. This results in an increase in the Earth’s average temperature, which is known as the greenhouse effect.
How the Atmosphere Gets Heated and Cooled
Even though the Sun is the main source of heat, we don’t feel it directly when we go higher in the atmosphere (like on mountains), because the air gets cooler. Why? Let’s look at 4 ways the atmosphere is heated:
Radiation
- Heat travels as waves, even through empty space
- The Sun sends shortwave energy to Earth (called insolation)
- Earth gives back heat to the atmosphere as long waves
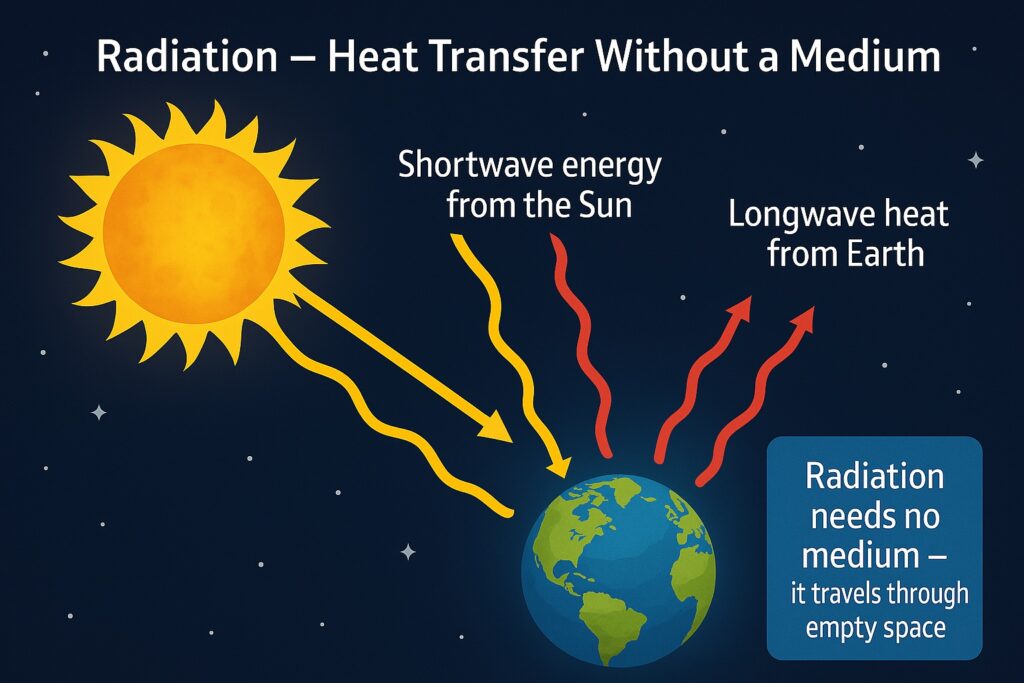
Facts about radiation:
- Everything (hot or cold) gives off radiant energy
- Hotter objects release more energy
- Hotter objects give off shorter waves
- Earth receives heat in short waves and sends it back in long waves
Conduction
- Heat moves from the hot Earth’s surface to the air touching it
- It happens only near the surface, where air touches the ground
- Example: Like how a spoon gets hot when left in a hot pot
Convection
- After air near the surface gets hot (by conduction), it rises upward
- This movement of hot air going up and cool air coming down is called convection
- This keeps mixing the air and spreads heat in the lower atmosphere
Advection
- This is the sideways movement of heat through wind
- Wind moves warm or cool air from one place to another
- Example: Sea breeze is cool wind moving from sea to land during daytime
Factors Affecting Heat Budget of the Earth
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover is another factor that affects the Earth’s heat budget by influencing the amount of incoming solar radiation that reaches the surface and the amount of outgoing longwave radiation that is emitted back into space. Clouds reflect a significant portion of incoming solar radiation back into space, reducing the amount of energy that is absorbed by the surface. Clouds also trap a portion of outgoing longwave radiation, resulting in an increase in the amount of energy that is re-radiated back towards the surface.

Surface Temperature
The Earth’s surface temperature is influenced by several factors, including incoming solar radiation, cloud cover, and atmospheric composition. The surface temperature affects the amount of energy that is absorbed and re-emitted as longwave radiation, and is also influenced by the presence of land and water masses. Land masses, for example, tend to heat up and cool down more quickly than water masses, resulting in a more variable surface temperature.
Ocean Currents
Ocean currents play a crucial role in Heat budget of the Earth by transporting heat and moisture around the planet. The ocean currents are driven by differences in temperature and salinity and play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate by transporting heat from the equator to the poles.
Impact on Climate
The Earth’s heat budget plays a critical role in determining the planet’s climate and weather patterns. The balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing longwave radiation, as well as the influence of cloud cover, surface temperature, and ocean currents, all contribute to the formation of global climate patterns.
For example, the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere results in an increase in the Earth’s average temperature, leading to global warming and the potential for climatic disasters, such as sea level rise, hurricanes, and droughts. Understanding the Earth’s heat budget and its impact on the planet’s climate is essential in predicting and preparing for these events and in mitigating their effects.
Read: Geography Notes